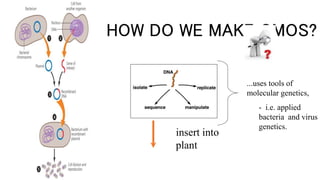
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are created by altering an organism's DNA to change its characteristics, a process more precise and faster than traditional selective breeding. Common uses of GMOs include agriculture, medicine (such as producing insulin), and biofuel production, but they are subject to strict regulations. While proponents argue that GMOs can increase food supply and nutritional value, critics raise concerns over potential environmental risks and health issues.