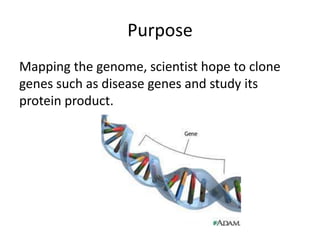
This document discusses genetic and physical mapping of genomes. Genetic mapping determines the relative positions of genes on chromosomes using linkage analysis, while physical mapping determines absolute positions using available techniques. The goals of genome projects are to complete a detailed human genome map and physical map, acquire the genome as clones, determine full sequences, and find all genes. Genetic mapping uses markers and restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites. Benefits include locating disease genes, more nutritious foods, and research applications, while costs have decreased from $350,000 to an hoped for $1,000.