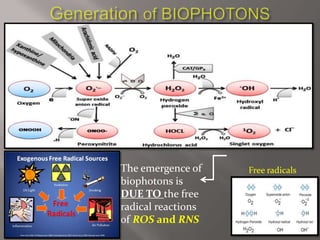
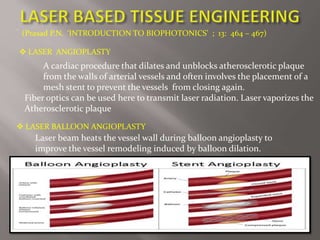
Biophotons are photons of light produced by biological systems in the UV and low visible light range. Each cell emits around 100,000 photons per second due to free radical reactions of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Free radicals can cause cell malfunction and damage, which is correlated with increased biophoton emission. Applications of biophotonics in pharmaceutical sciences include using compounds to reduce biophoton emission from stressed cells to determine new drug candidates, imaging mitochondrial potential during apoptosis, and using photodynamic therapy and targeted nanoparticles for cell imaging, repair, or death. Biophotonics is a highly sensitive technique that depends on free radical generation characteristic of diseases and can be used for drug discovery, laser procedures, and tissue