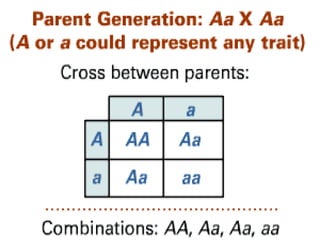
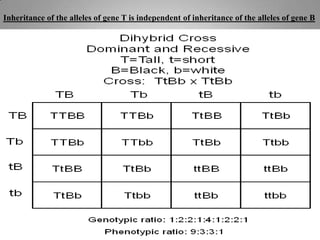
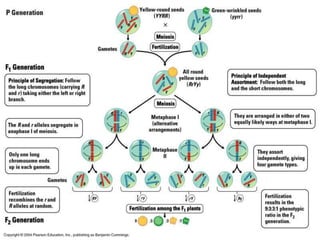
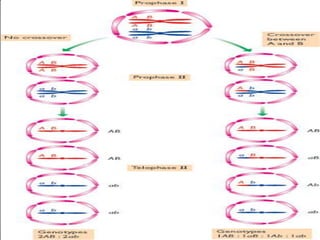
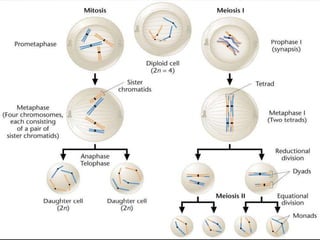
Genetic mapping involves constructing maps that show the positions of genes and other sequences on a genome. It uses genetic techniques like cross-breeding experiments or examining family histories. Markers like genes, RFLPs, SSLPs, and SNPs are used in mapping. Genetic mapping is based on genetic linkage and inheritance. By determining the recombination frequency between markers, which is proportional to their distance apart, a genetic map can be constructed showing the relative positions of genes on chromosomes.