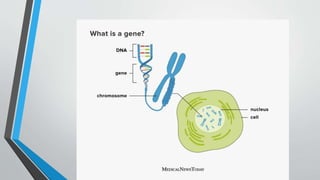
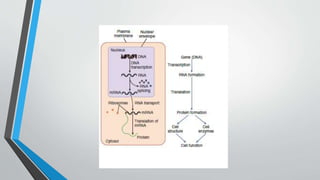
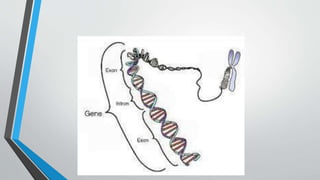
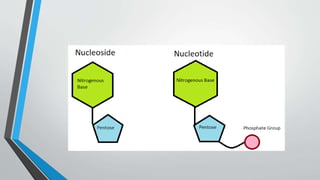
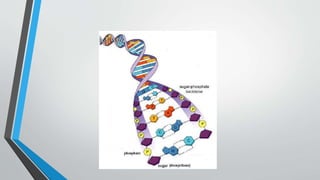
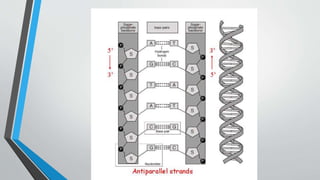
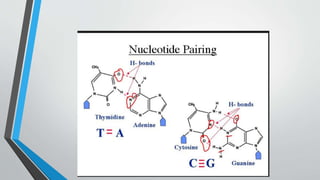
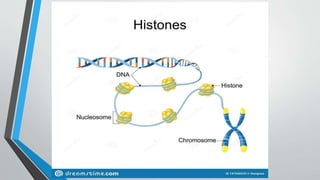
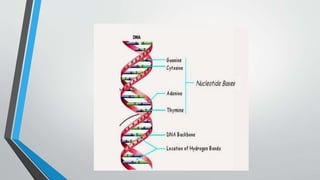
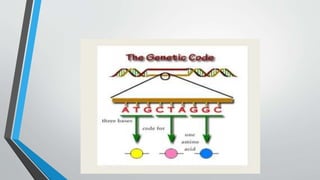
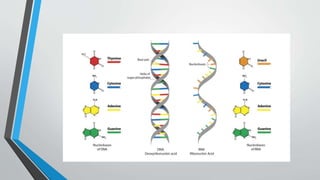
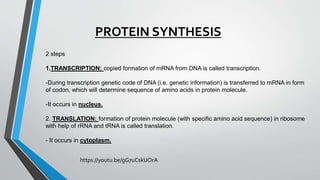
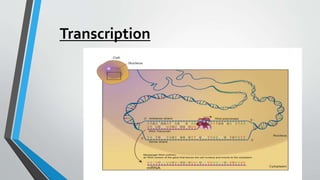
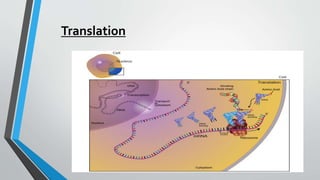
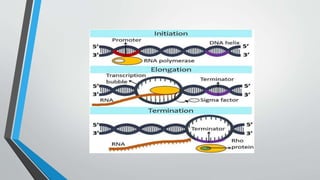
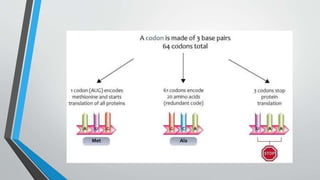
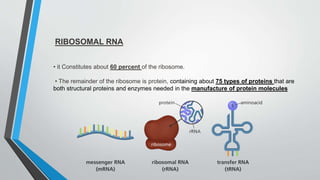
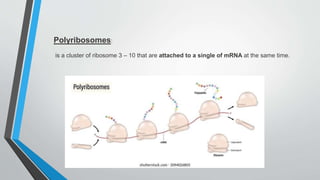
The document discusses genetic control of protein synthesis, cell function, and cell reproduction. It explains that genes located in cell nuclei control protein synthesis through transcription and translation. Transcription copies DNA's genetic code into mRNA in the nucleus. Translation then uses mRNA to assemble specific protein sequences in ribosomes located in the cytoplasm. The genetic code is made up of triplets of nucleotides called codons, which correspond to transfer RNA anticodons and the amino acids used to build proteins. Different types of RNA, including mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, facilitate moving genetic information from DNA and synthesizing proteins. The document also briefly discusses cell mitosis, where a cell divides into two identical daughter cells, and apoptosis, the process of programmed cell