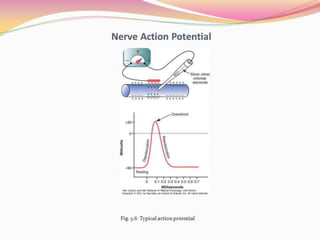
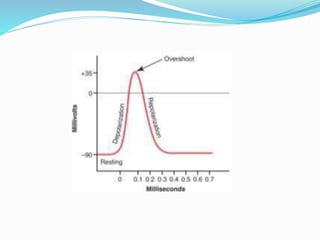
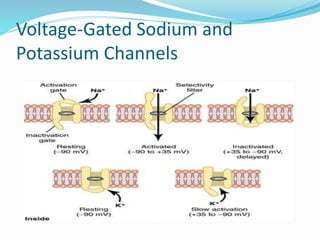
Nerves and muscles are excitable tissues that respond to electrical, chemical, or mechanical stimuli. The action potential in nerves occurs in four stages: resting stage with a polarized negative membrane potential; depolarization where sodium channels open allowing sodium ions to enter rapidly; overshoot where some fibers see the potential become briefly positive; and repolarization where potassium channels open returning the membrane to the negative resting potential. Voltage-gated sodium channels have activation and inactivation gates that open and close the channel during an action potential. The all-or-none principle states that when a nerve is stimulated, it will either respond at maximum strength or not at all.