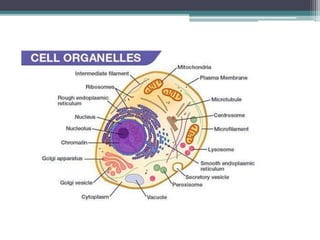
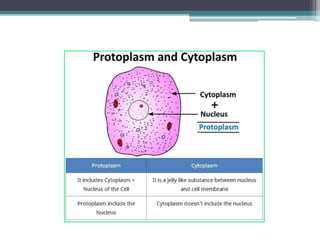
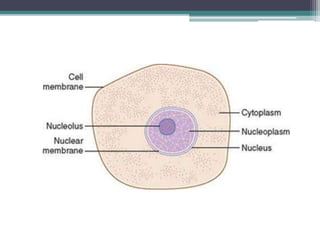
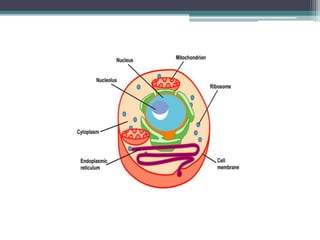
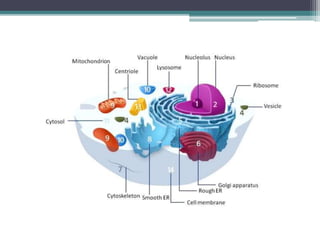
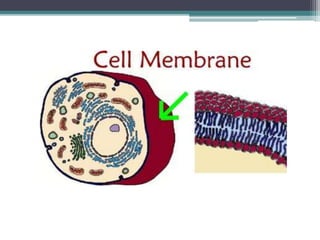
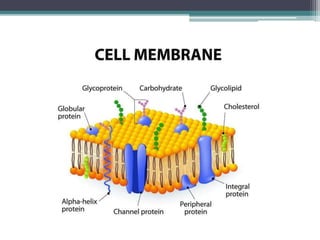
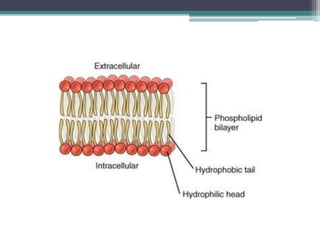
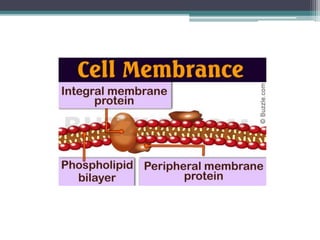
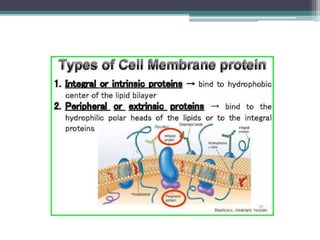
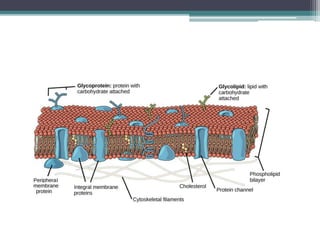
The cell membrane envelops the cell and is composed of a lipid bilayer with embedded and attached proteins and carbohydrates. It regulates what enters and exits the cell. The nucleus houses the genetic material and is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear membrane. Organelles such as the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum are enclosed by their own membranes and perform specialized functions to keep the cell functioning.