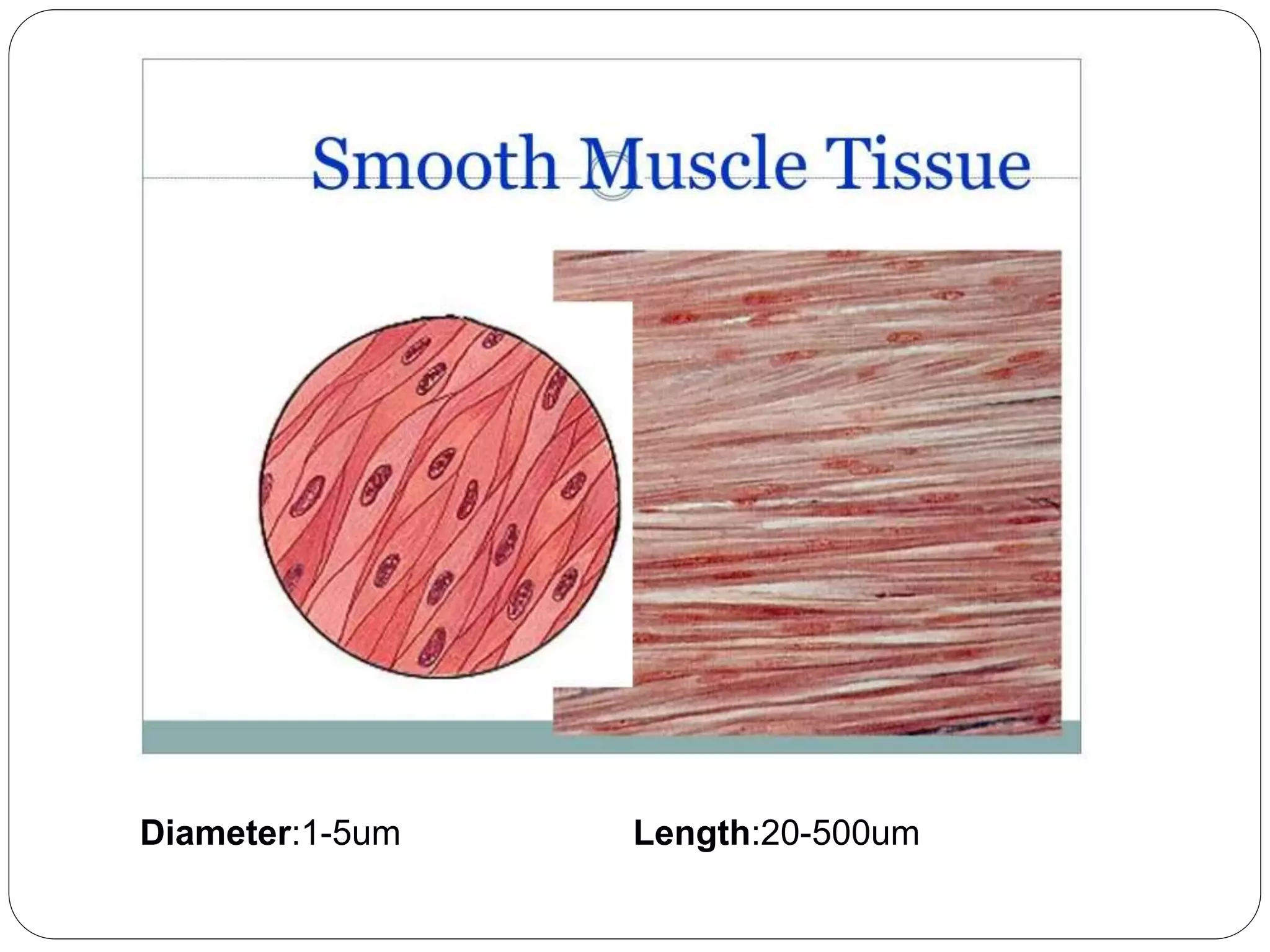
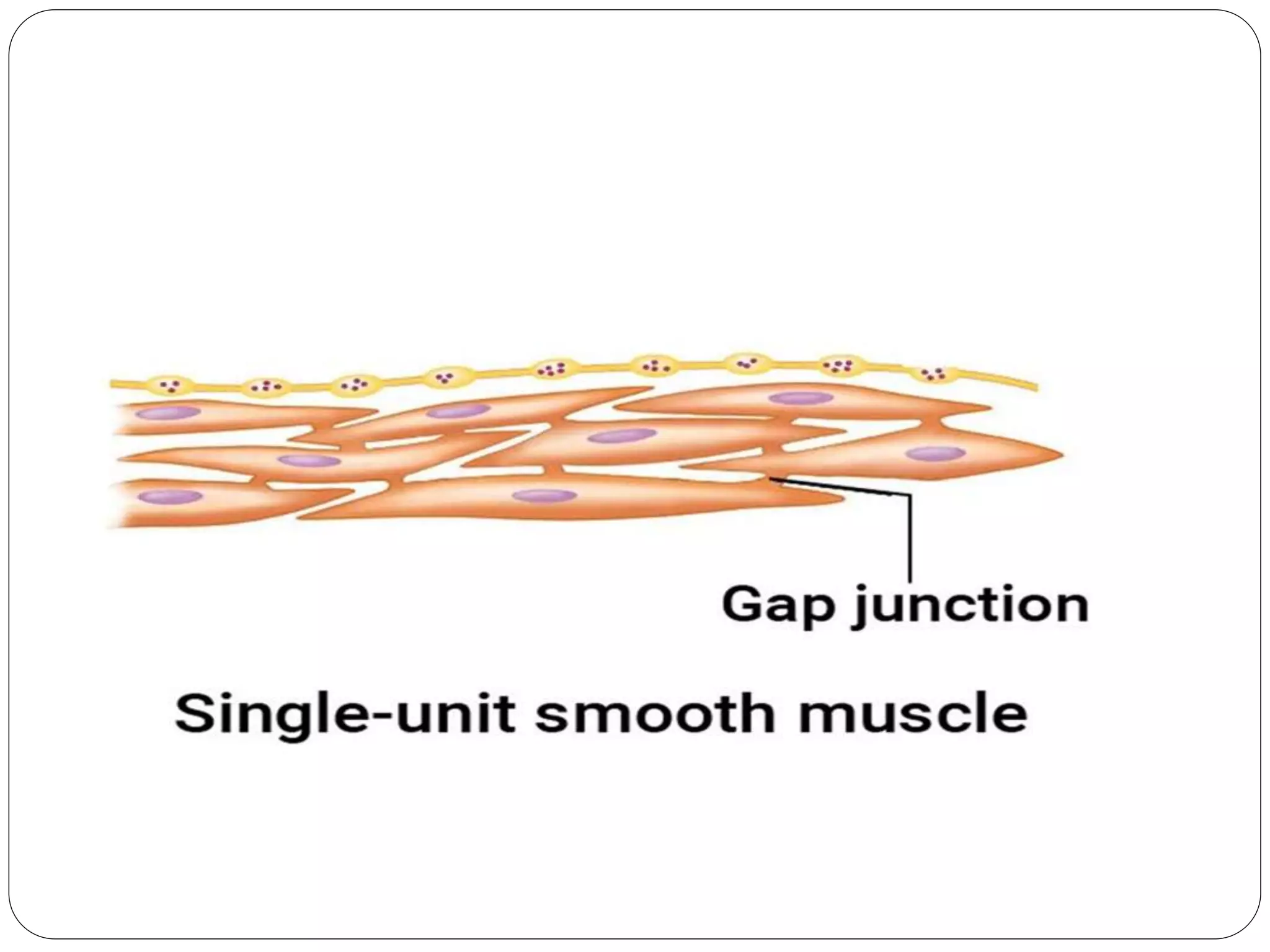
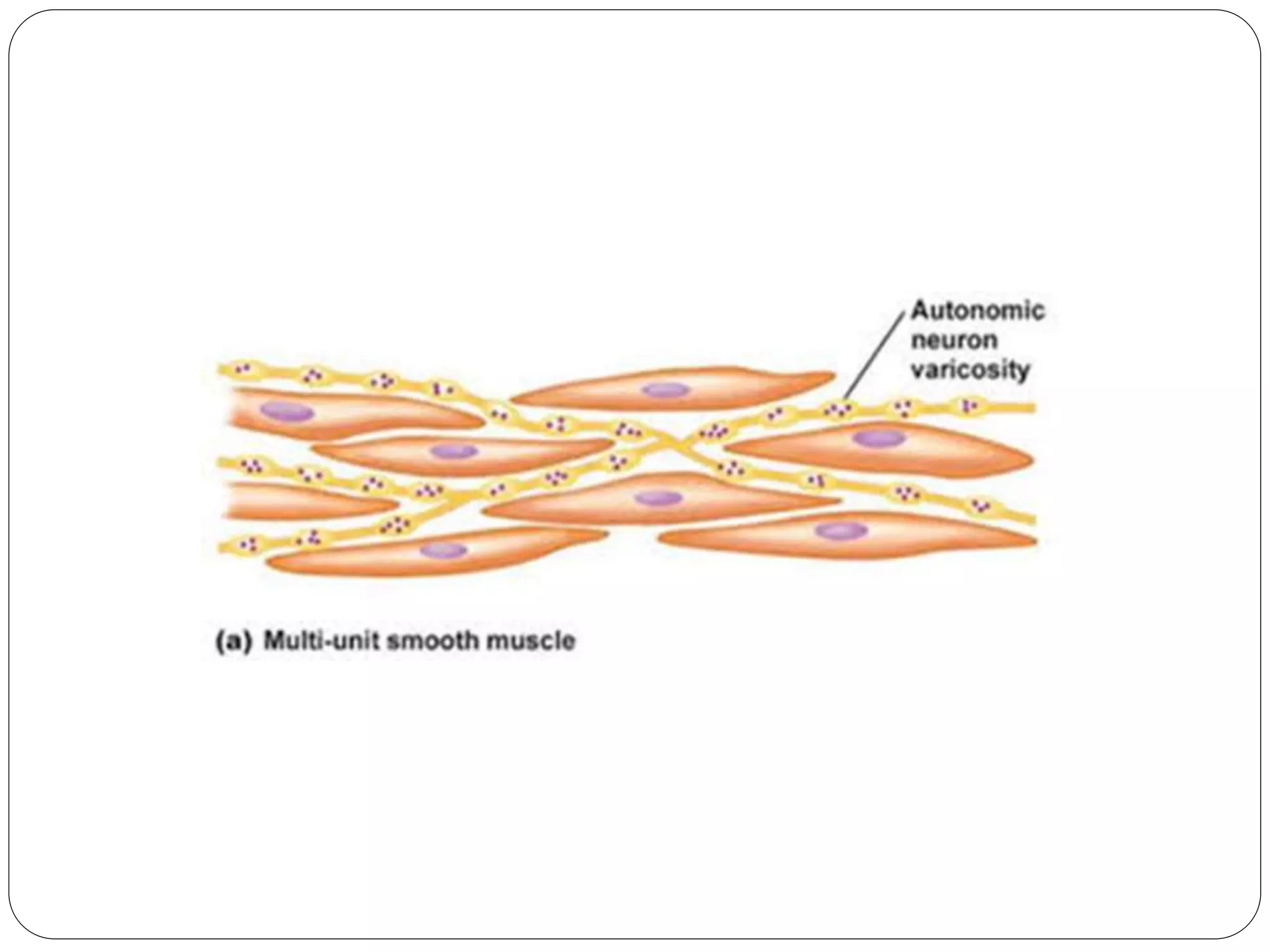
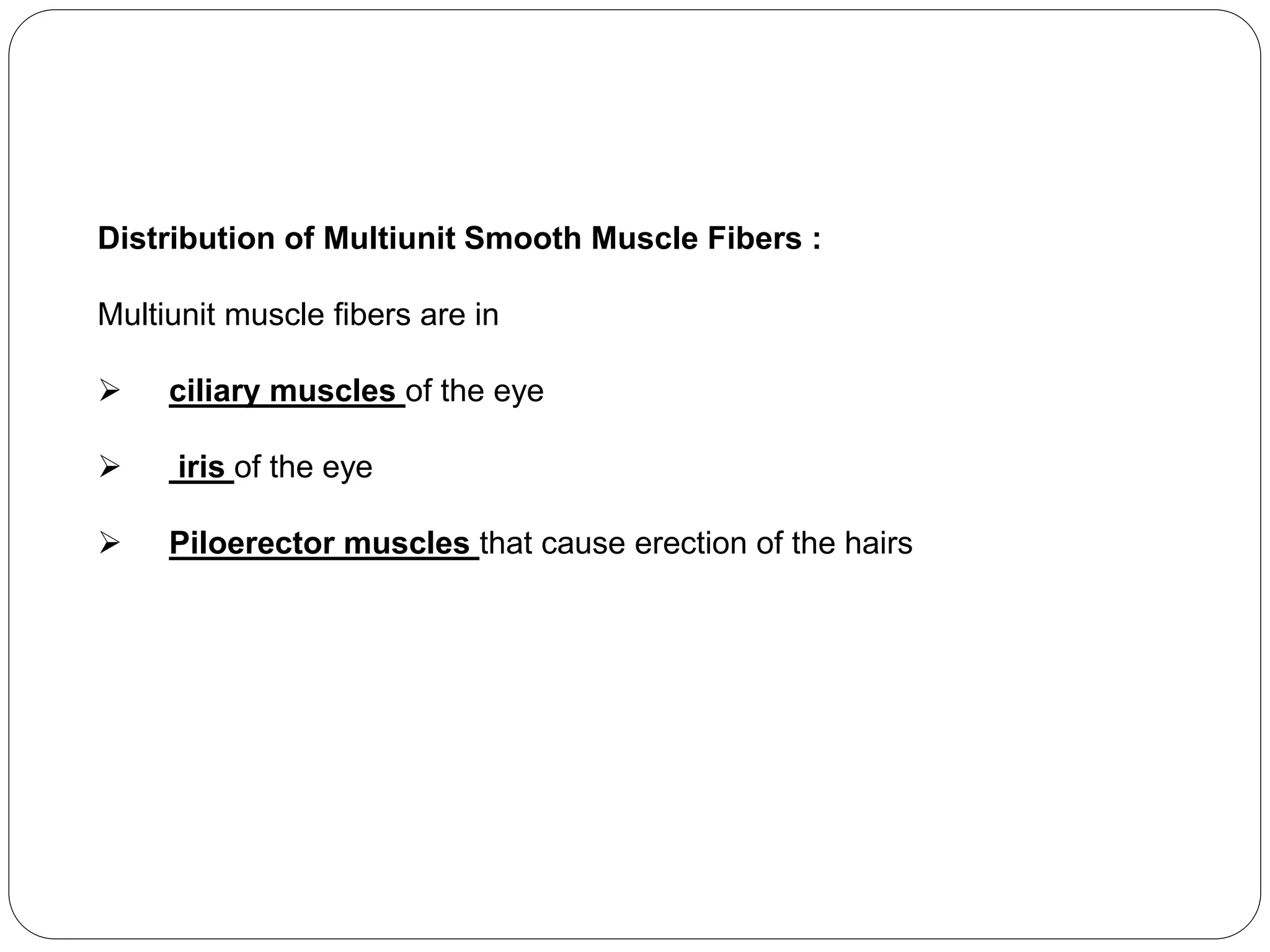
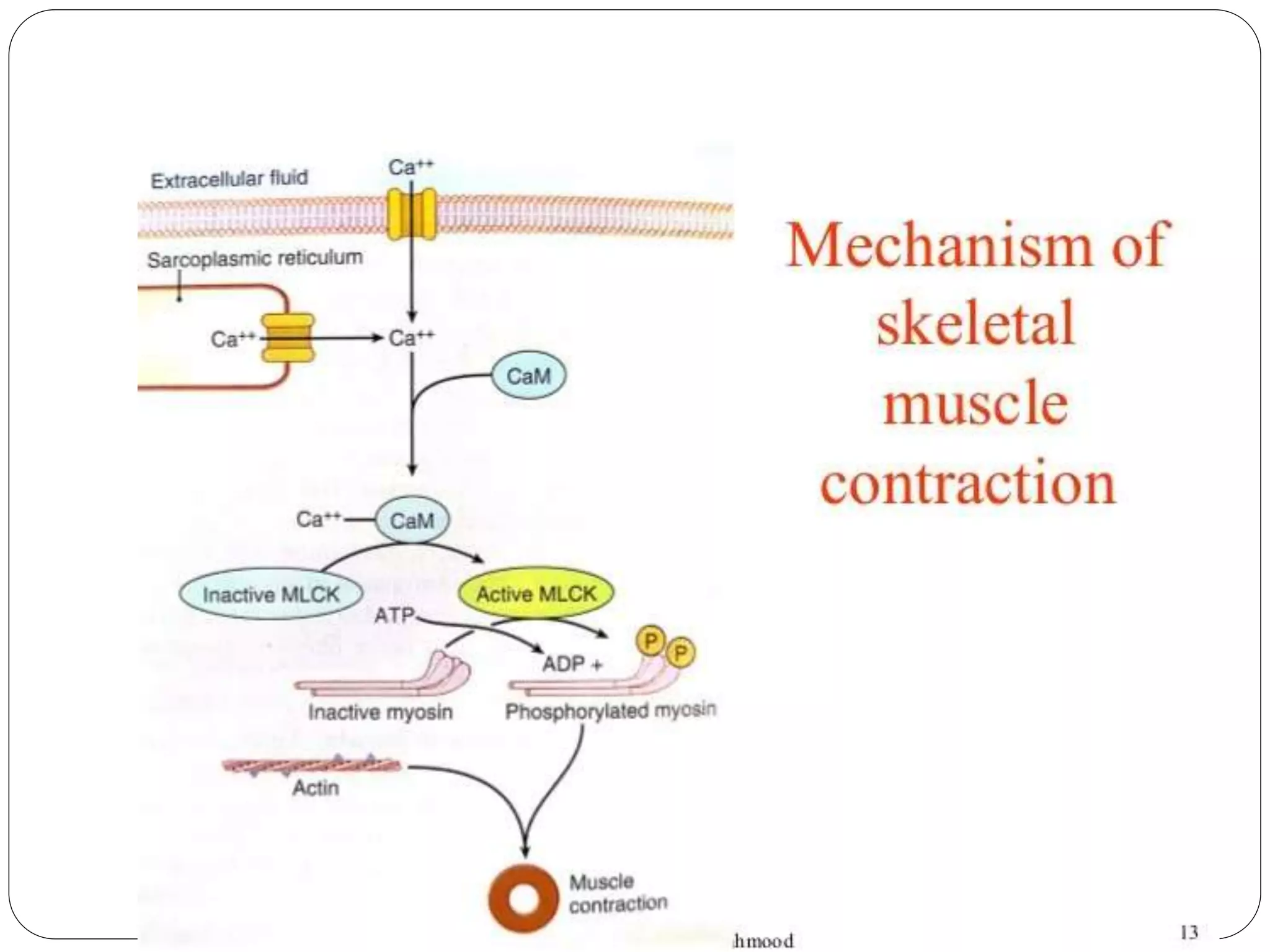
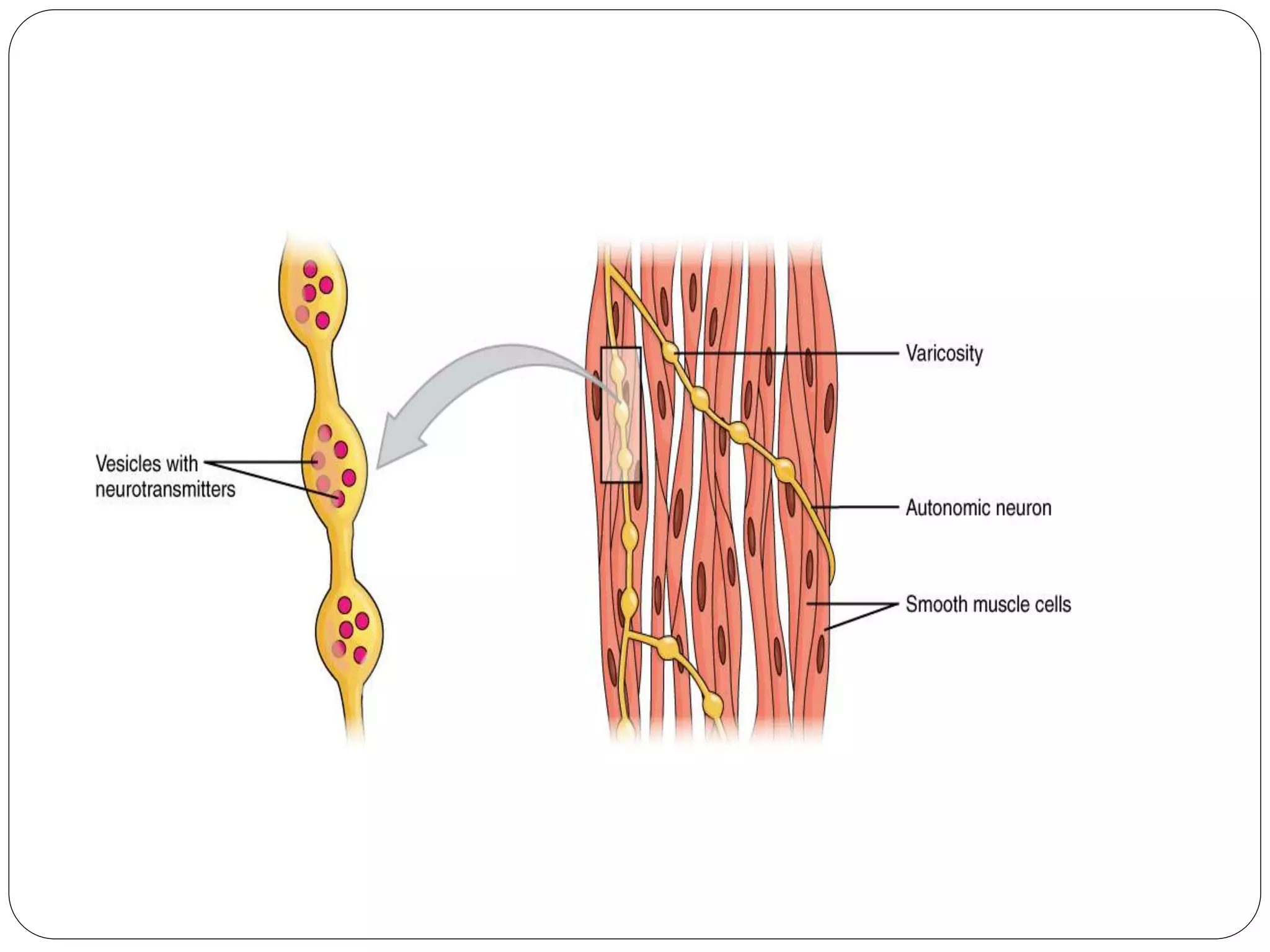
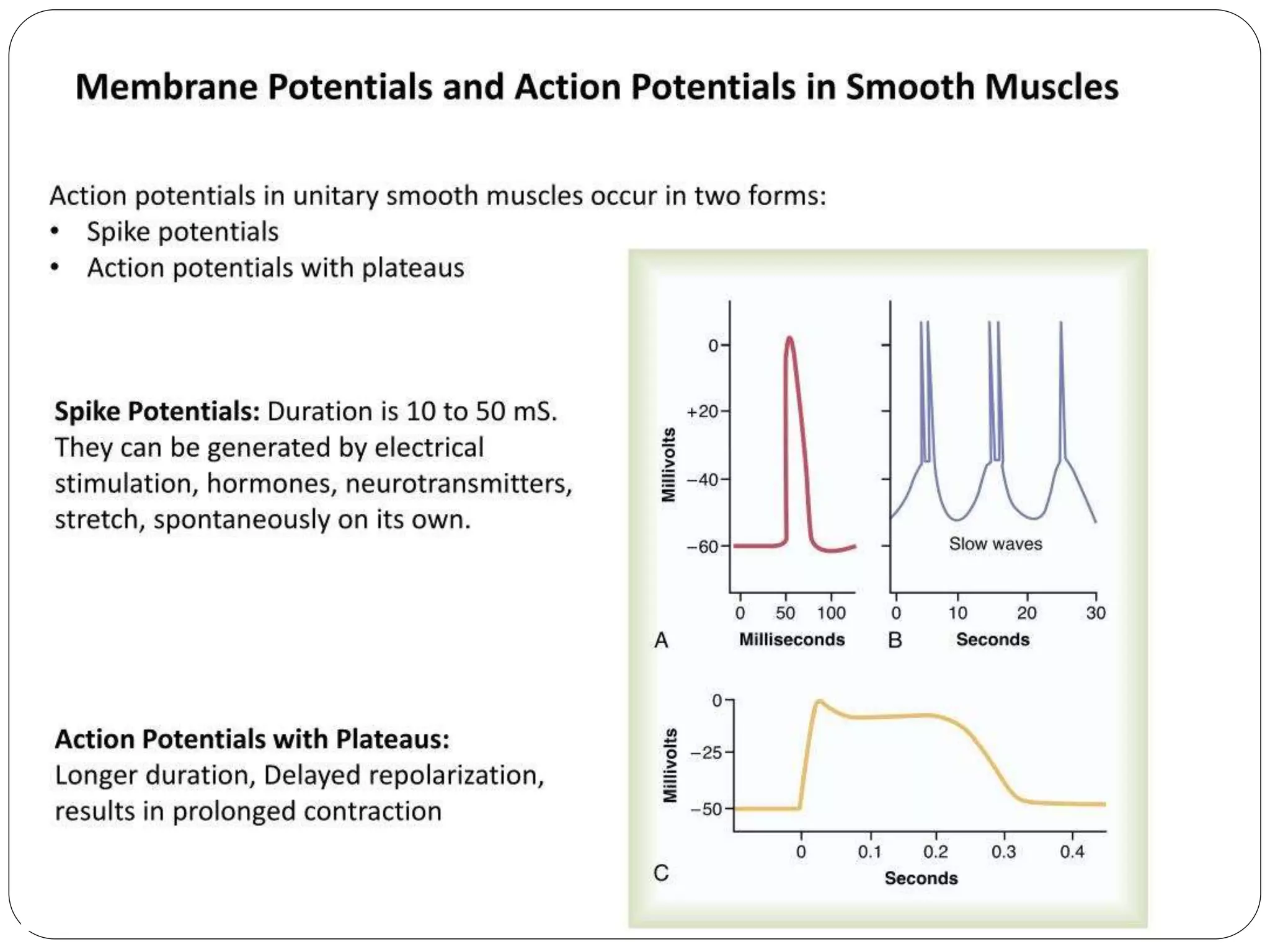
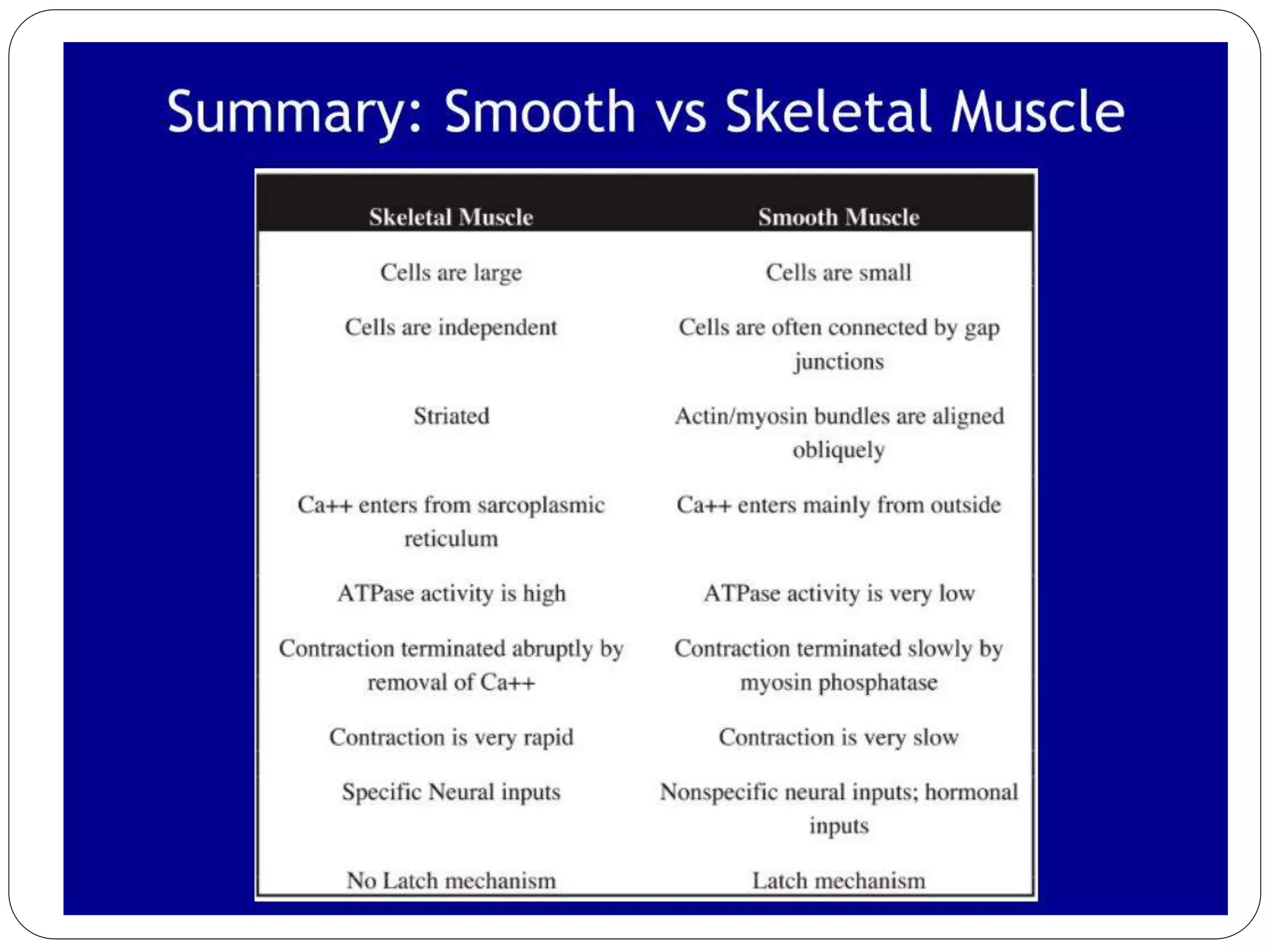
Smooth muscle comes in two types - single-unit and multi-unit fibers. Single-unit fibers contract as a syncytium in response to hormonal stimuli and form gap junctions. Multi-unit fibers contract independently in response to nerve signals. Smooth muscle lacks striations and uses calcium and calmodulin instead of troponin for contraction. It exhibits prolonged tonic contractions via a latch mechanism even after stimuli cease. Contraction is initiated by calcium influx through membrane channels or sarcoplasmic reticulum release.