Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times



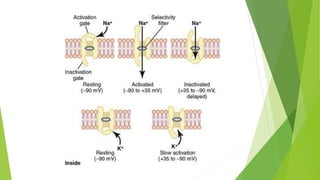
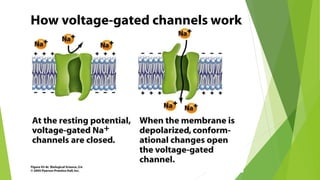
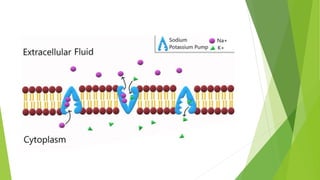



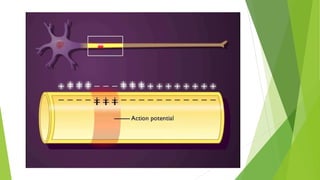
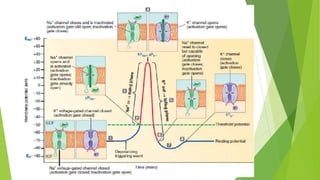



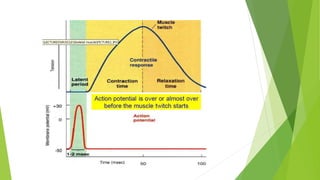
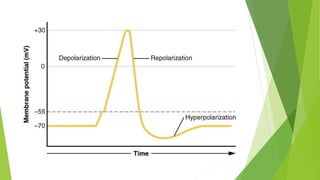


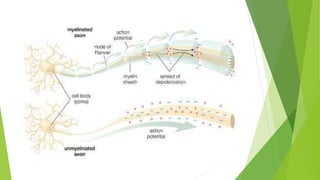


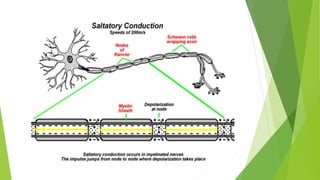
An action potential occurs when a stimulus causes the membrane of a neuron to depolarize, reversing the electrical charge from negative to positive. Normally, sodium levels are higher outside the cell and potassium levels are higher inside. When depolarization occurs, sodium rushes into the cell, making the outside more negative. This action potential then automatically propagates along the axon from node to node in myelinated fibers or point to point in unmyelinated fibers.





















