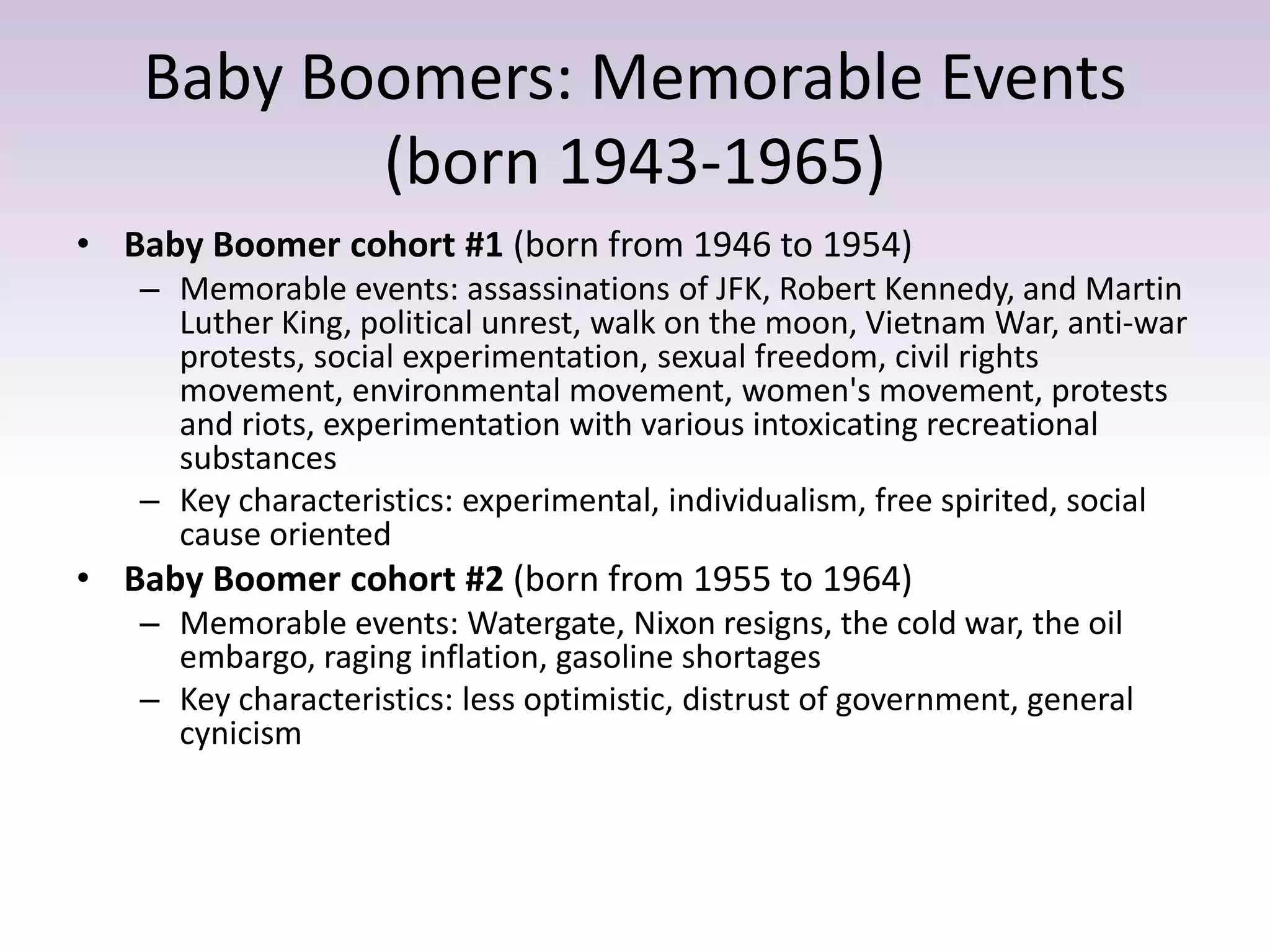
The document discusses generational differences in the workplace, focusing on how attitudes and behaviors vary among four generations: Silent Generation, Baby Boomers, Generation X, and Millennials. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these differences to facilitate better communication and collaboration across generations, while also highlighting common values and challenges faced by each group. Case studies are used to explore strategies for improving intergenerational interactions in a professional setting.