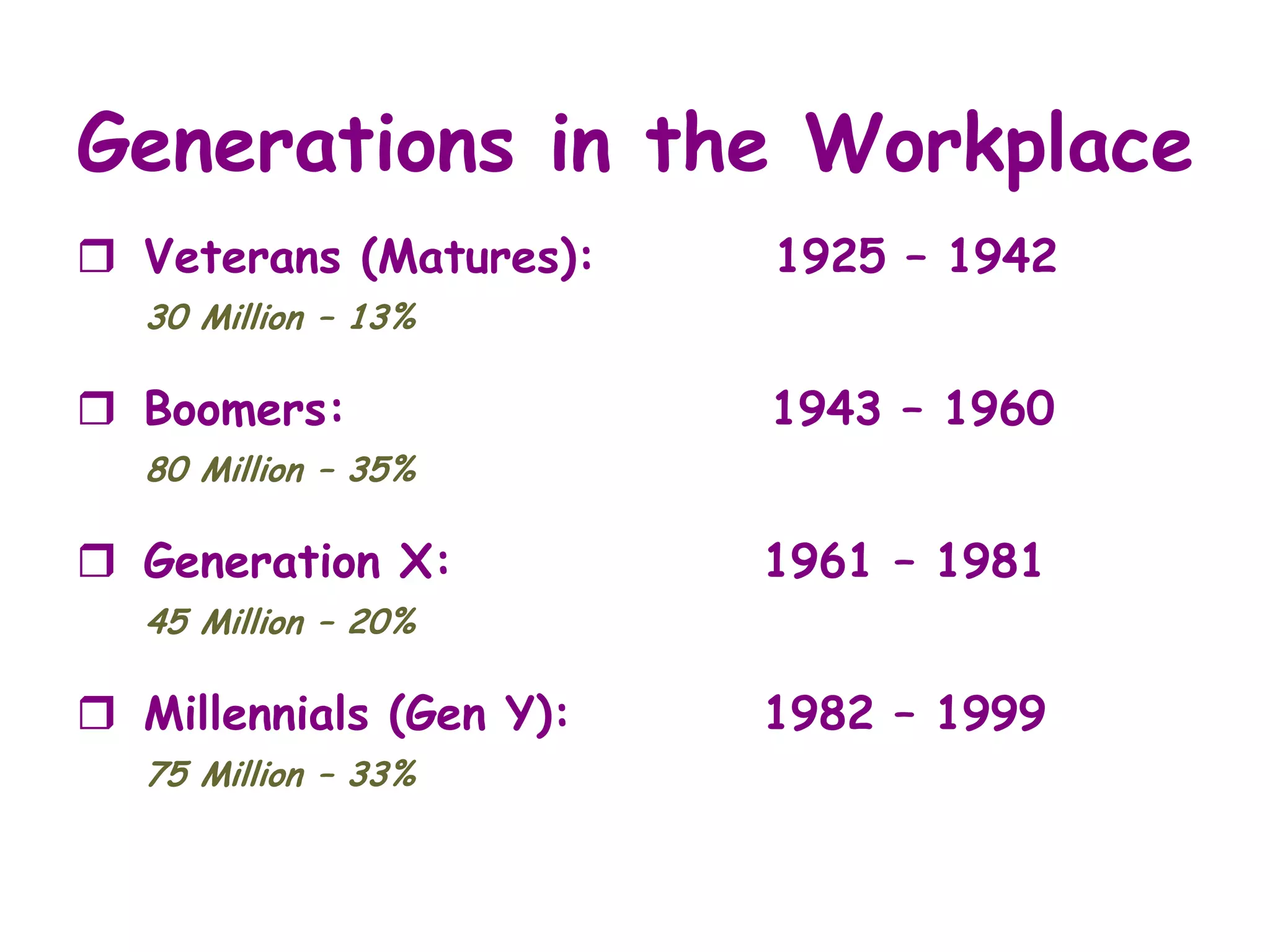
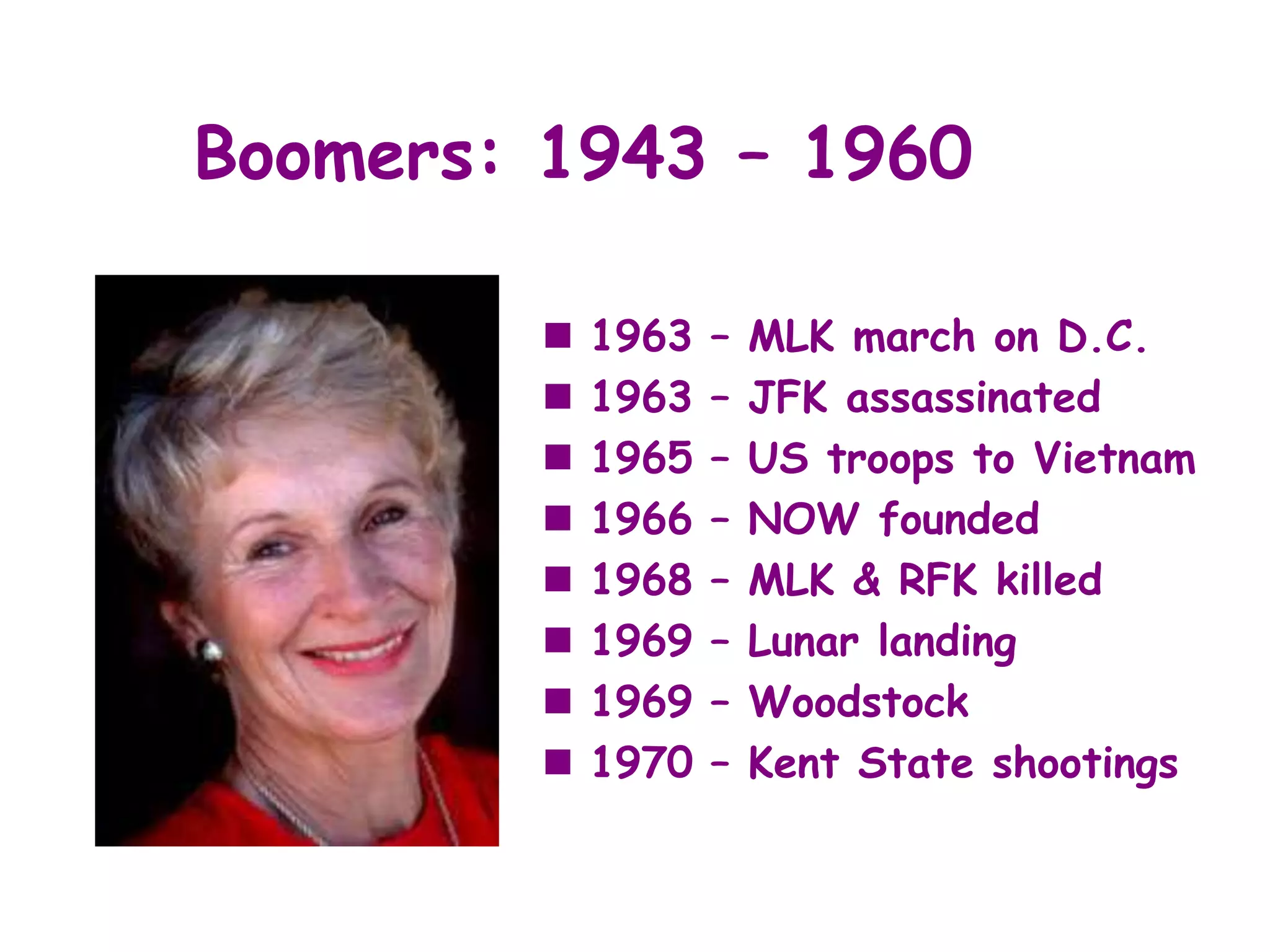
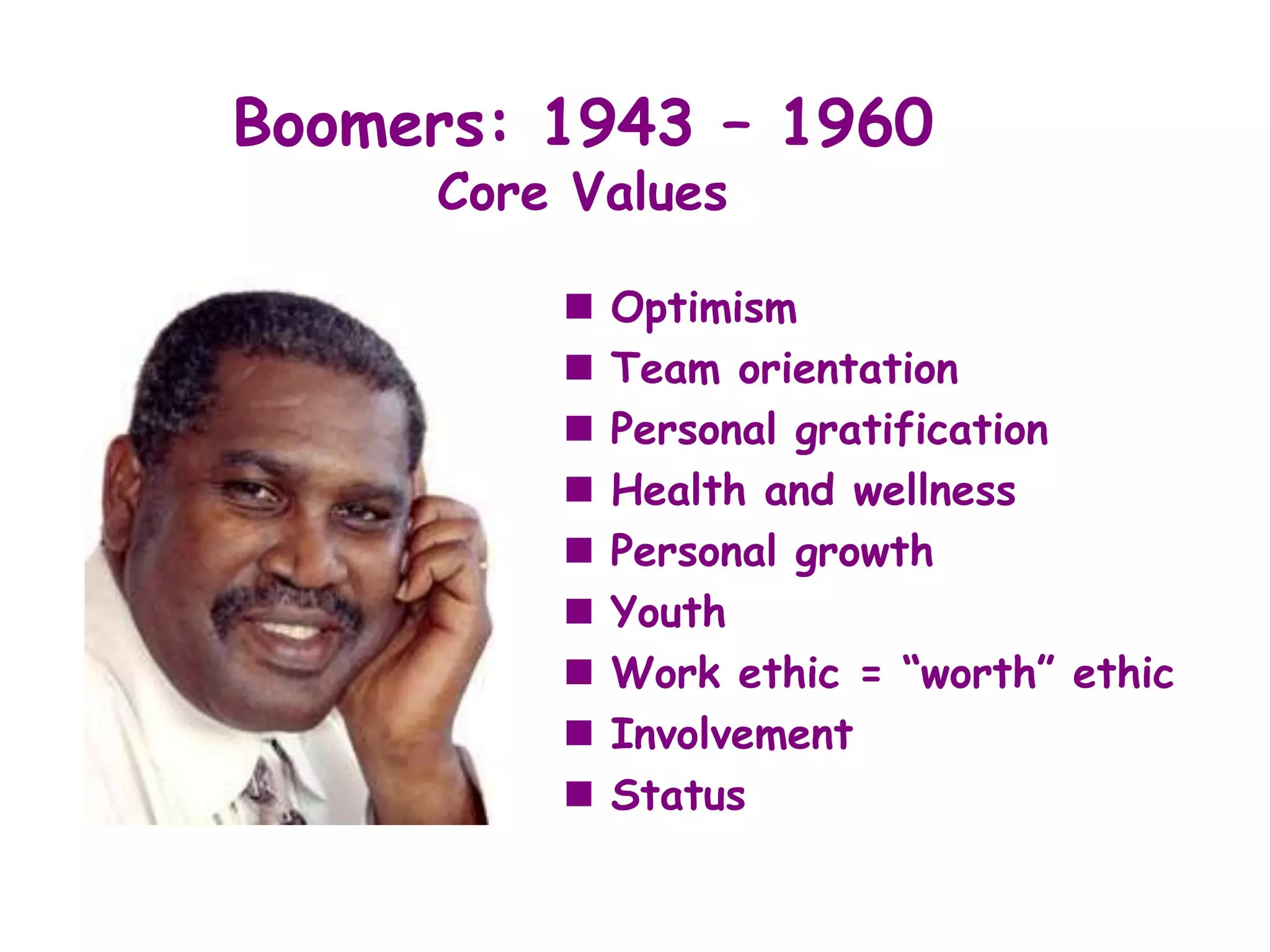
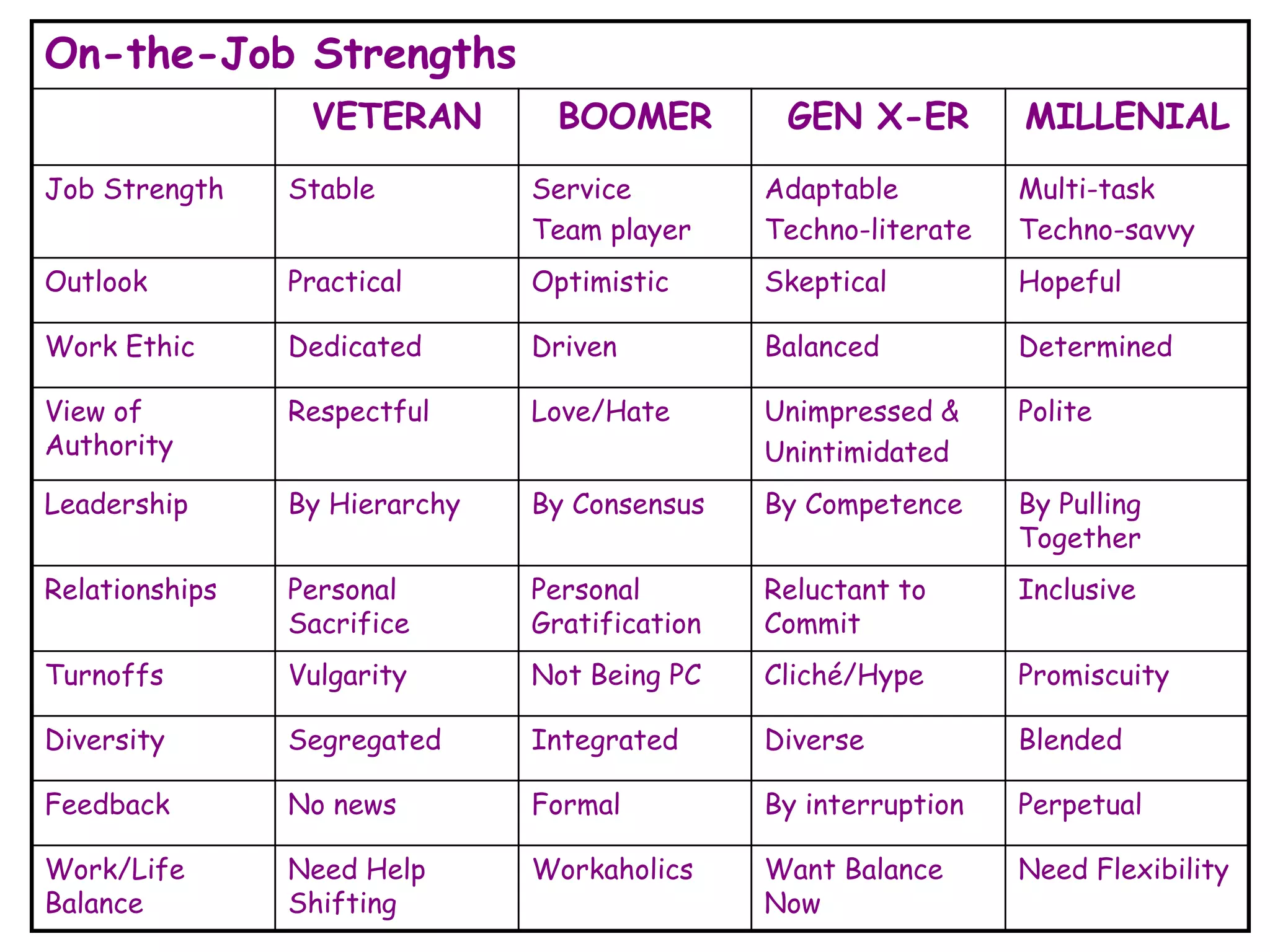
The document discusses the characteristics and values of four different generations in the workplace: Veterans, Baby Boomers, Generation X, and Millennials. It outlines the impact of formative experiences on each generation's work ethic, communication style, and management preferences. Additionally, it provides strategies for effectively managing and motivating employees from each generational cohort.