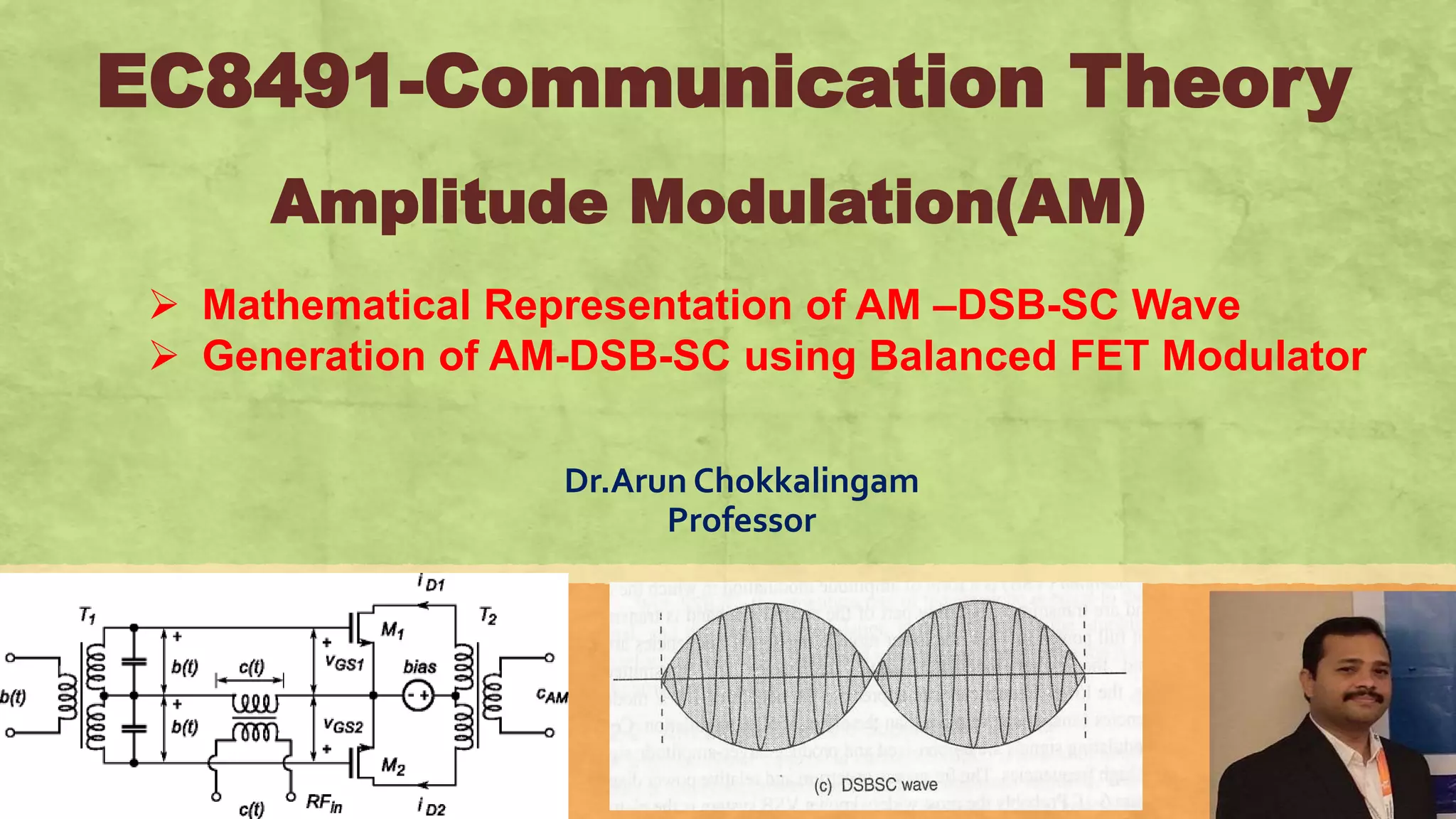
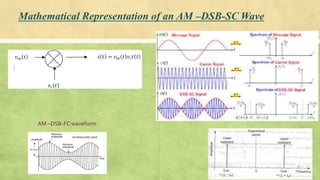
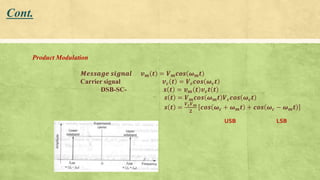
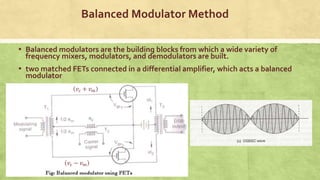
This document discusses amplitude modulation using a balanced FET modulator. It begins by providing the mathematical representation of an AM-DSB-SC waveform. It then describes how a balanced FET modulator can be used to generate an AM-DSB-SC signal. Specifically, it explains that a balanced FET modulator uses two matched FETs in a differential amplifier configuration. The carrier signal is applied in phase to the gates, while the message signal is applied out of phase. This results in an output signal that is amplitude modulated by the message signal. The document concludes by noting that while a balanced FET modulator can heavily suppress the carrier, it cannot achieve 100% carrier suppression due to imperfect matching of the F