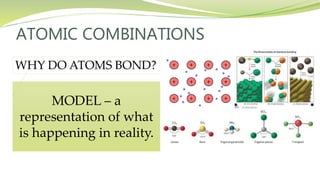
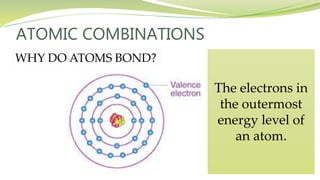
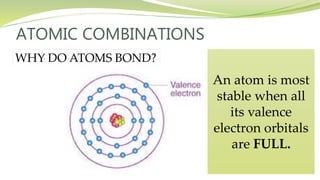
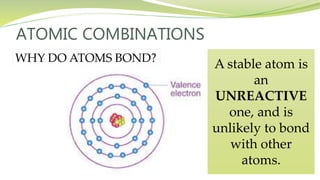
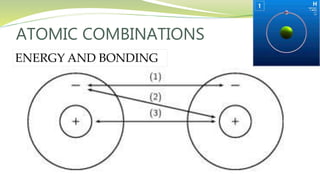
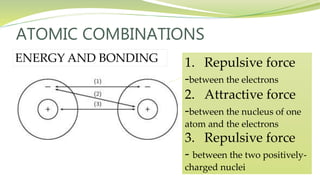
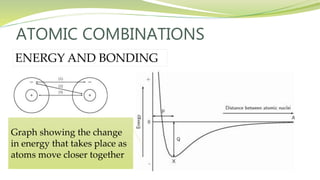
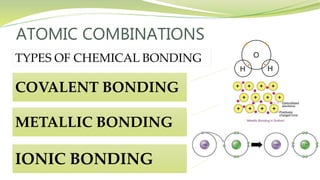
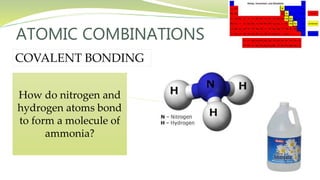
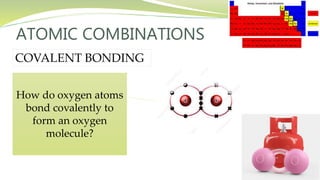
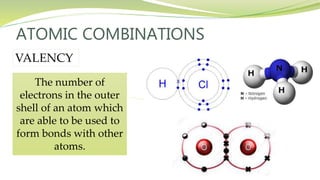
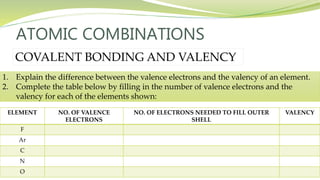
The document covers the topic of atomic combinations and chemical bonding, explaining why atoms bond and the forces involved, such as attractive and repulsive forces between electrons and nuclei. It describes types of chemical bonds including covalent, metallic, and ionic bonding, with a focus on covalent bonding between non-metals and the role of valence electrons. Additionally, it includes examples and diagrams illustrating covalent bonding in molecules like hydrogen chloride and water.