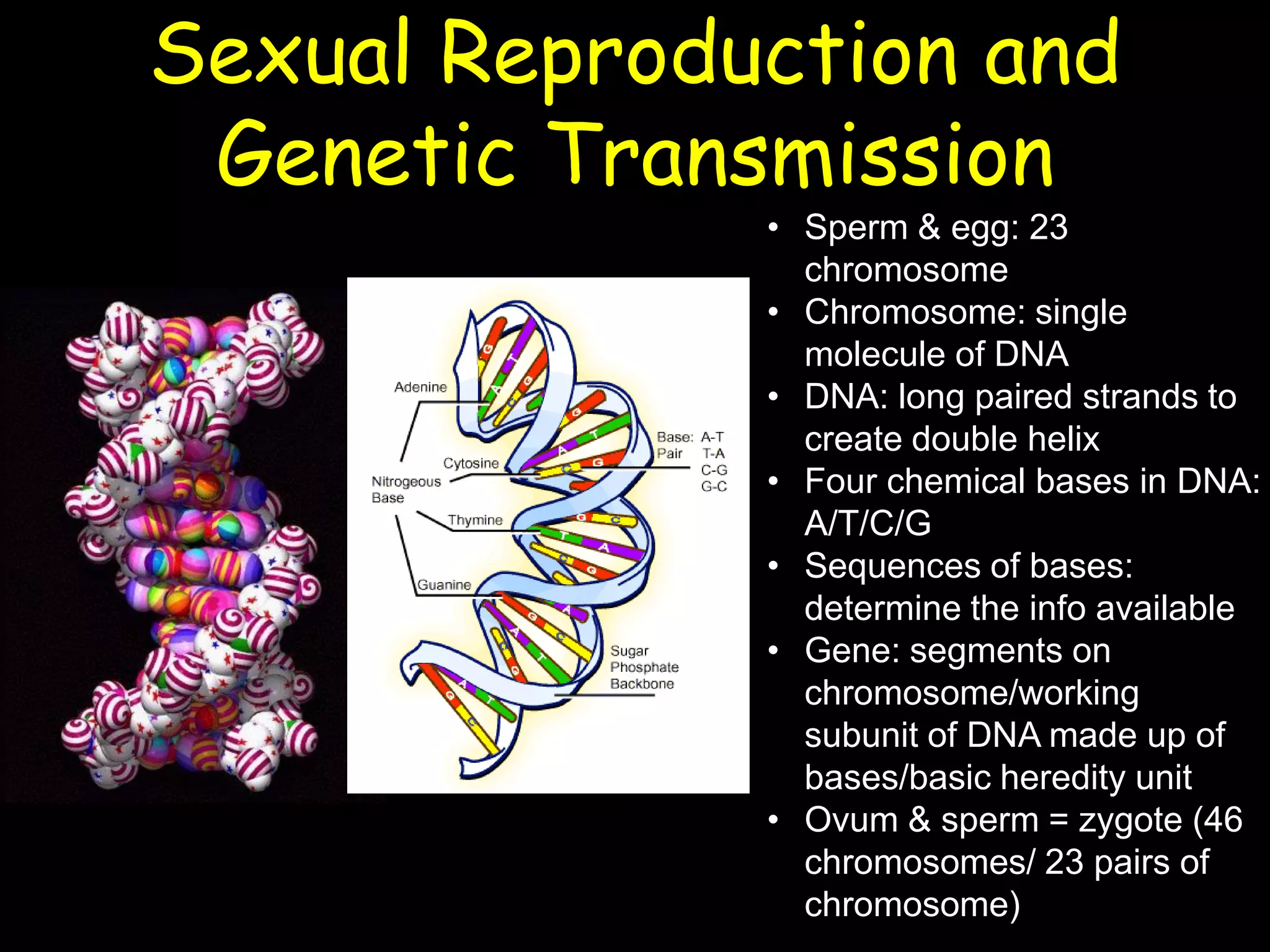
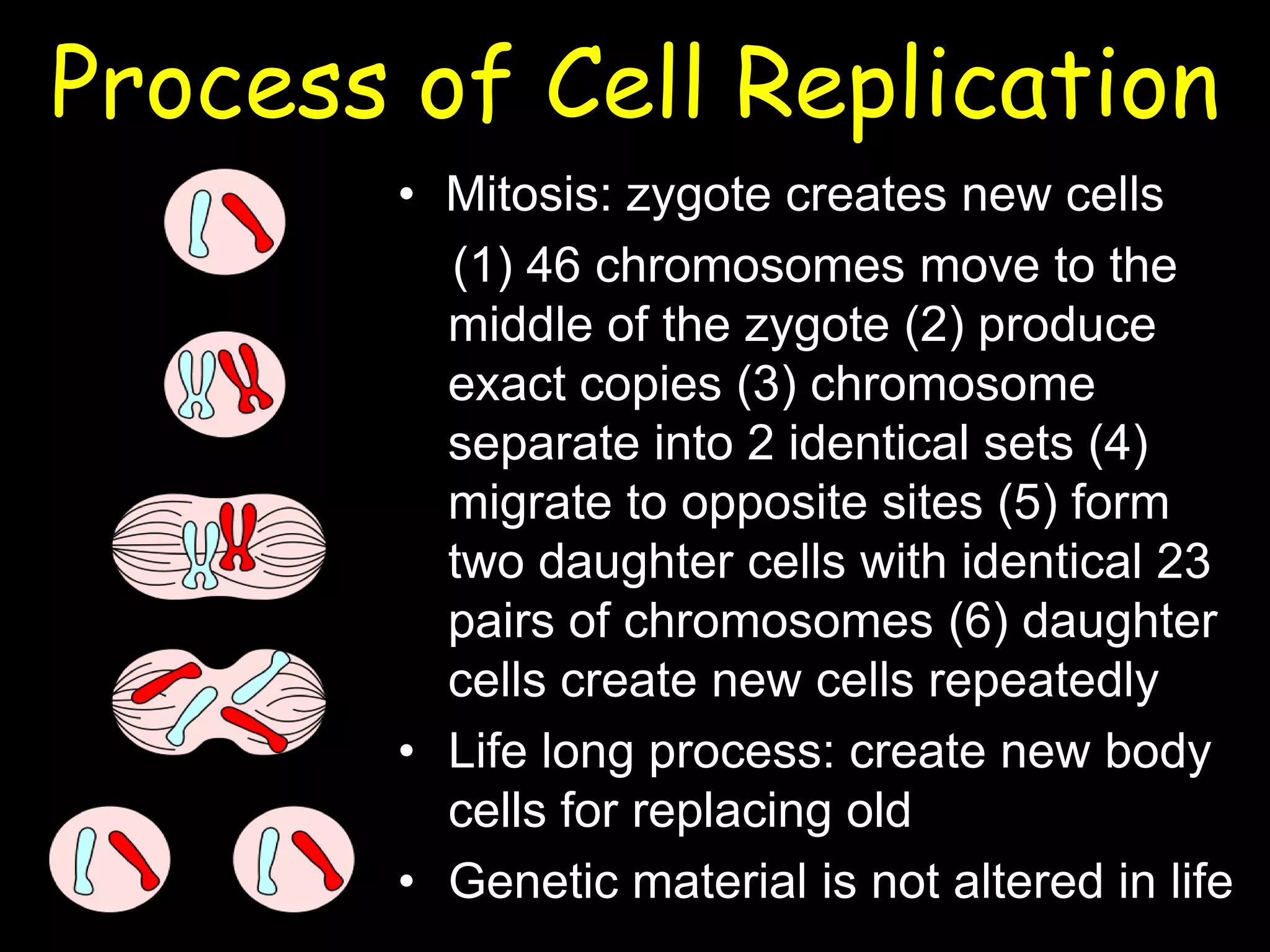
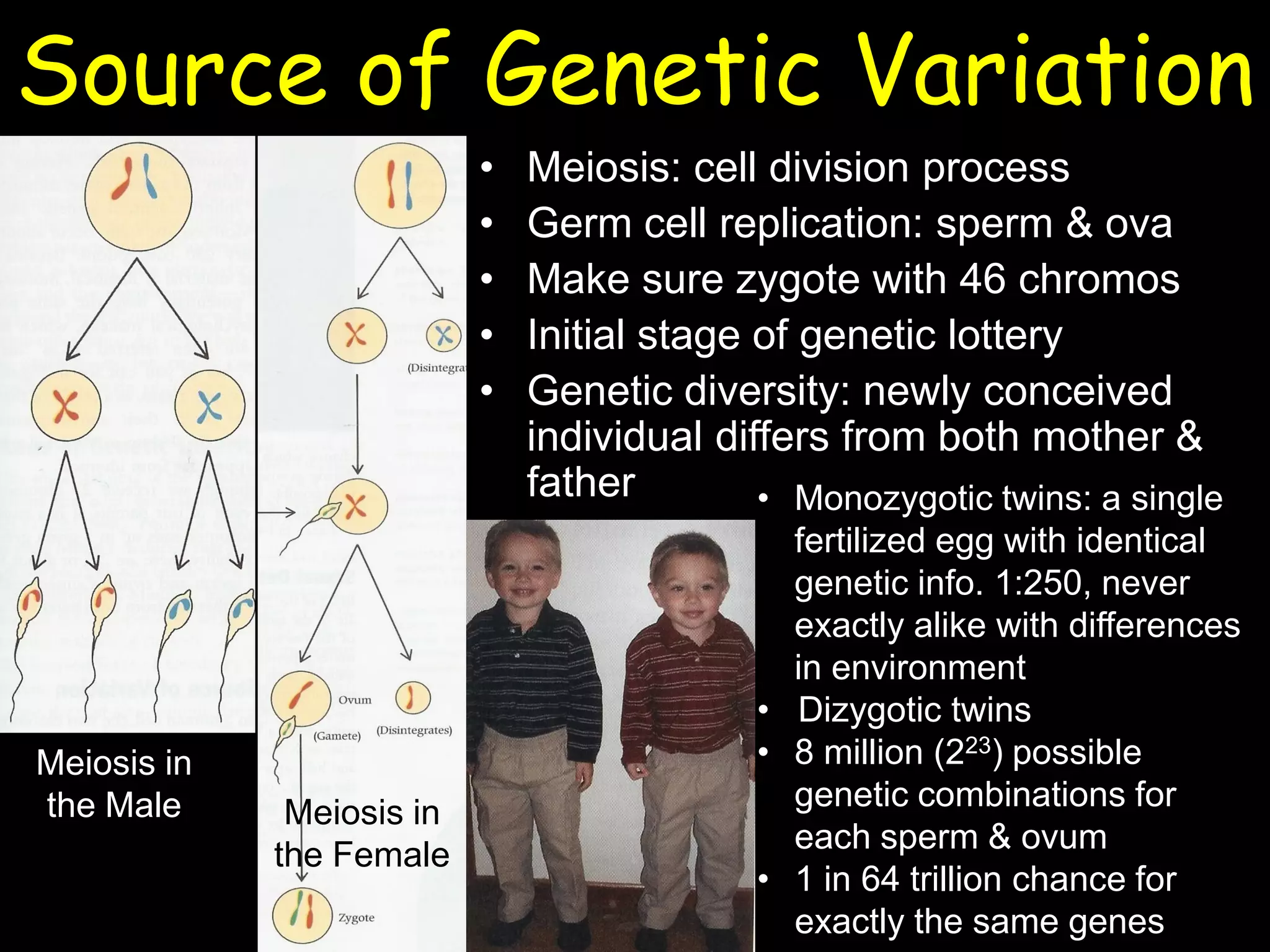
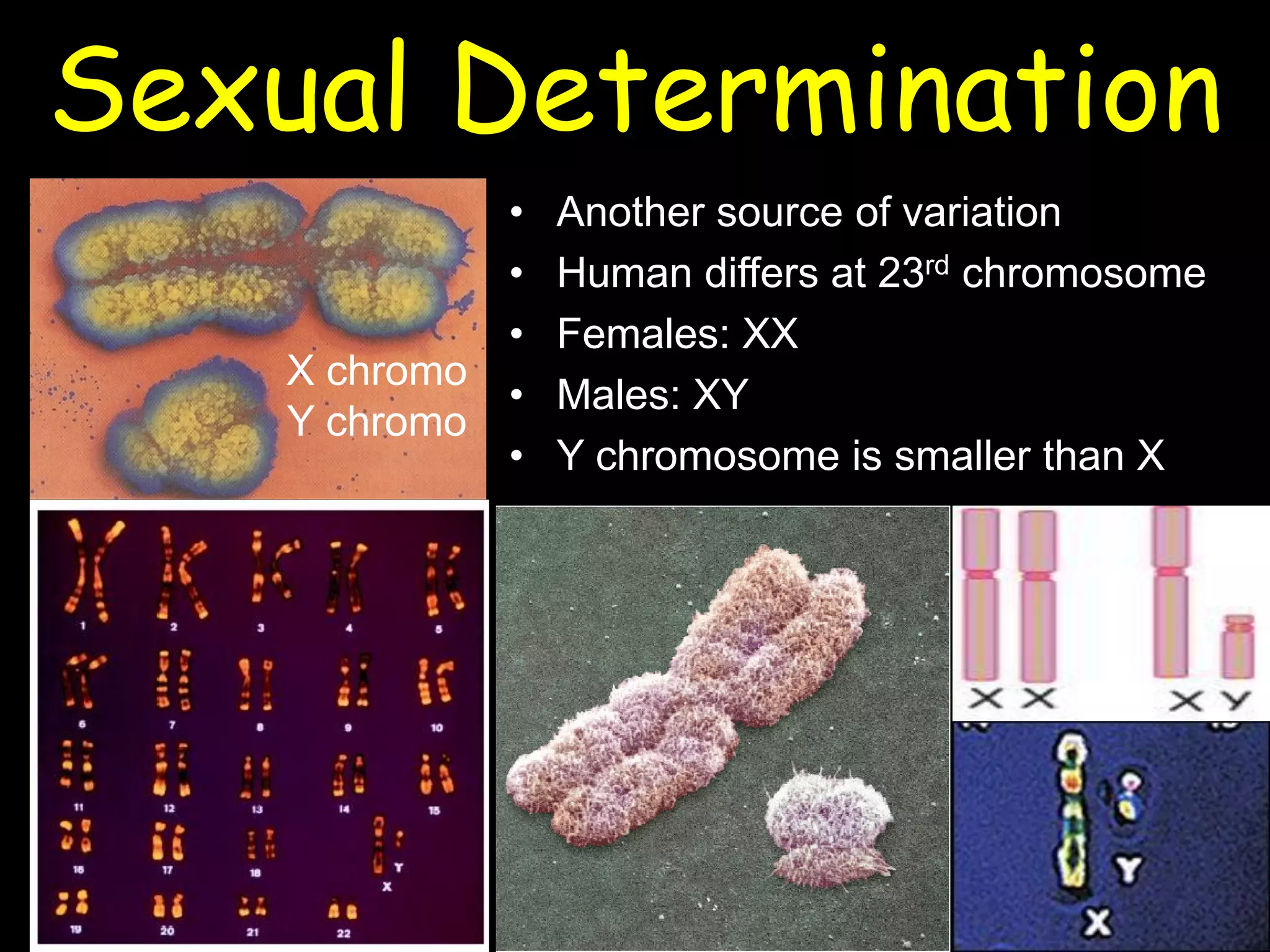
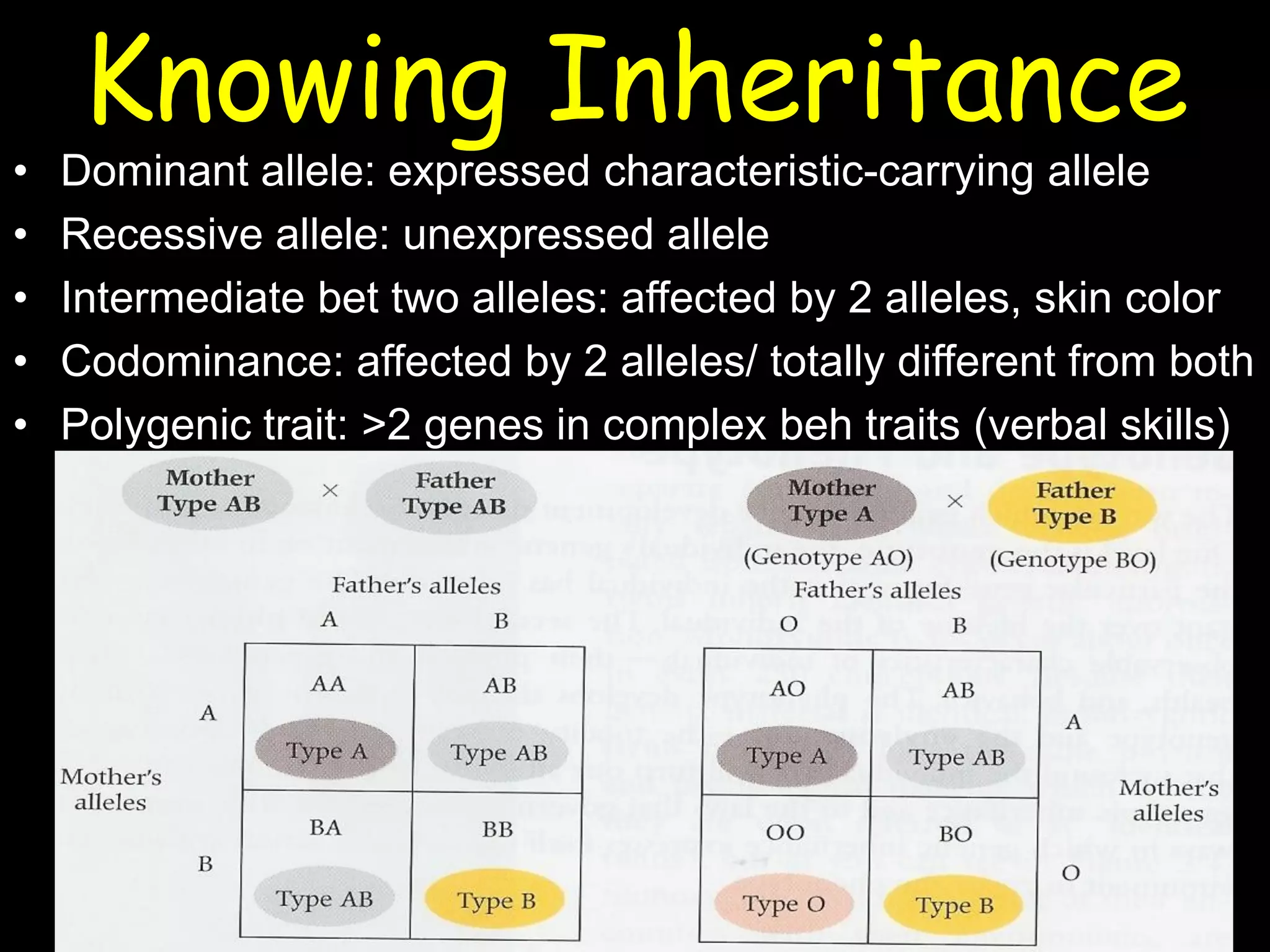
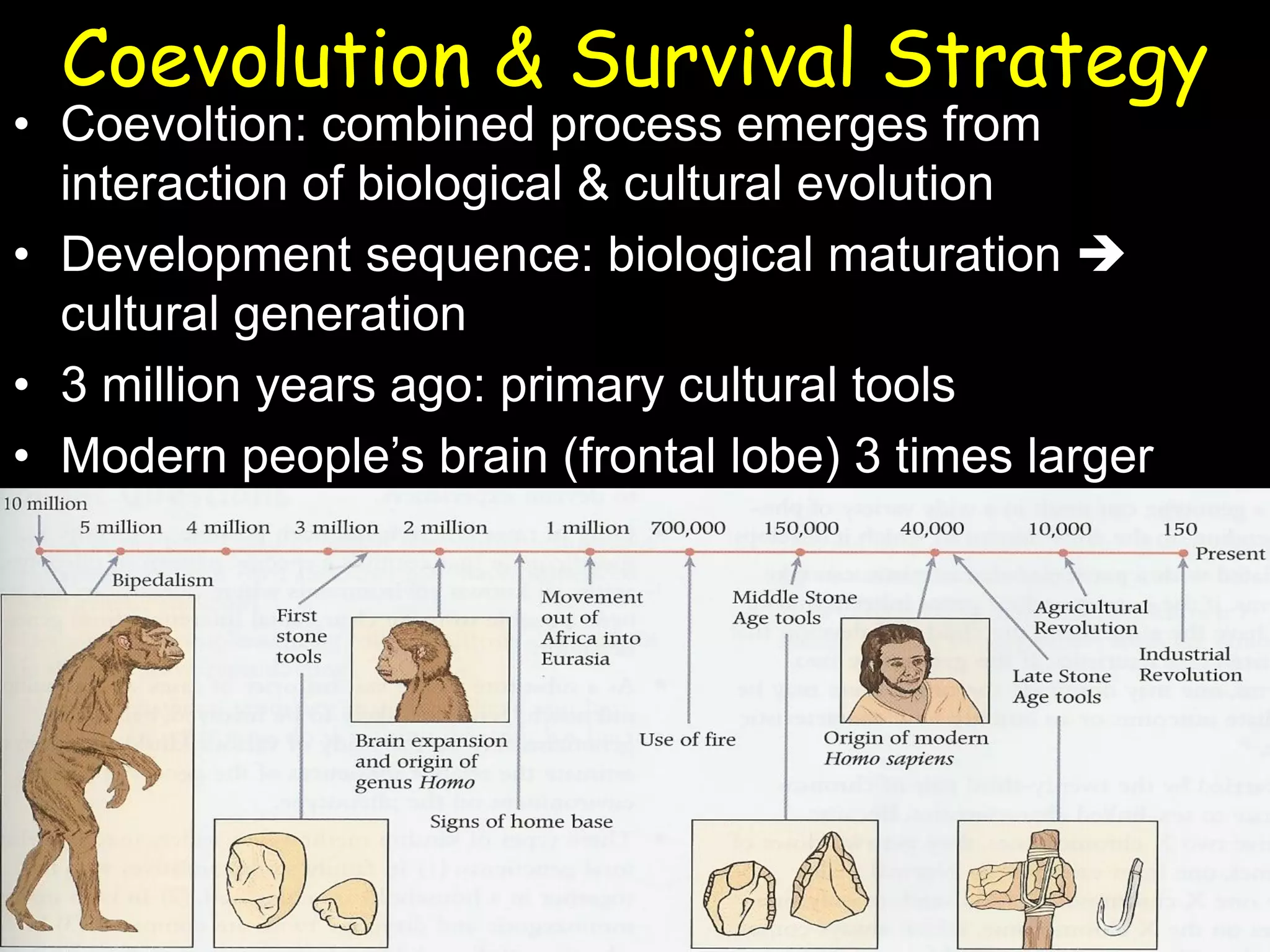
This document summarizes a lecture on human genetics and heredity. It discusses key topics like sexual reproduction, genetic transmission through DNA, cell replication, genetic variation through meiosis and recombination, sex determination, the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes, Mendel's laws of inheritance, sex-linked traits, the interaction between genes and the environment, heritability, genetic influences on behavior through family and twin studies, genetic mutations and abnormalities like Down syndrome, phenylketonuria, and sickle cell anemia. Cultural evolution and gene-culture coevolution are also briefly covered.