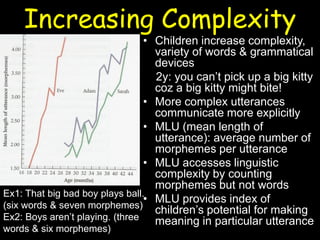
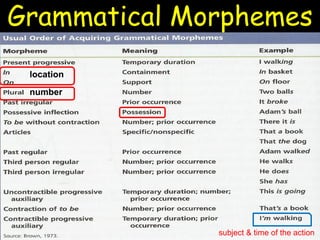
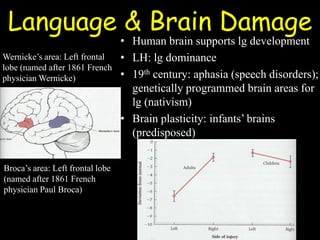
This document summarizes key aspects of language acquisition in children. It discusses how children progress from prelinguistic communication like babbling to understanding words and basic sentences. Children first learn nouns and verbs referring to objects and actions around them. They develop the ability to share attention and experiences with others. The document also examines how children learn meanings of words, grammar rules, and pragmatic uses of language in social contexts. Both nativist and interactionist perspectives on language learning are presented. Essential ingredients for language development include biological prerequisites in the brain and environment, cognitive abilities, fast mapping skills, social interaction, and exposure to language.