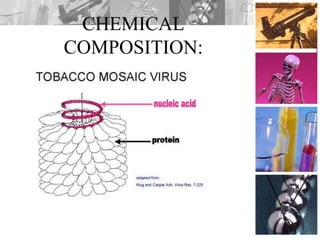
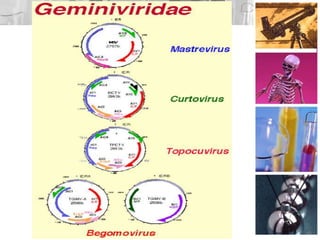
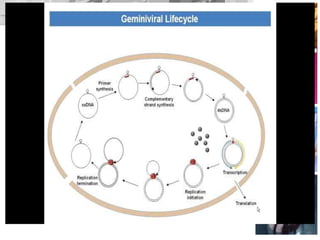
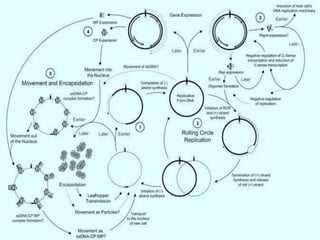
Plant viruses, particularly geminiviridae, are pathogenic to higher plants and can reduce crop yield and quality. They are classified as class II viruses with a structure that involves circular single-stranded DNA, which requires transmission of both segments for infection. Geminiviruses replicate inside host nuclei using host cell factors and can induce plant cells to reenter the cell cycle for successful replication.