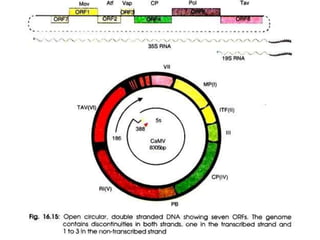
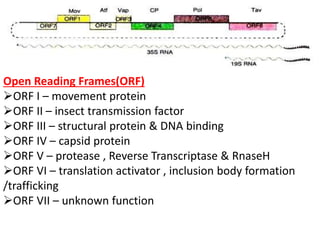
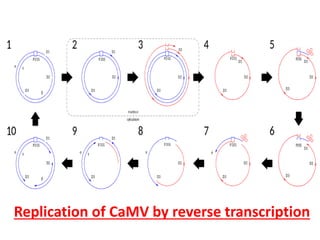
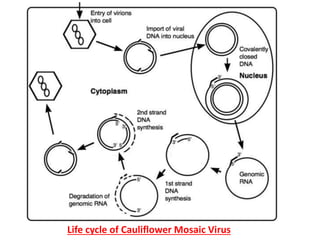
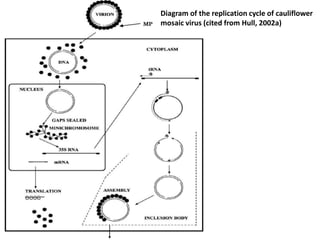
The document provides a detailed overview of the Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV), including its taxonomy, structure, genome organization, and replication process. CaMV primarily infects Brassicaceae and Solanaceae plants, leading to symptoms such as mosaic patterns and necrotic lesions. The virus replicates through reverse transcription, involving various open reading frames that encode proteins essential for its life cycle and pathogenicity.