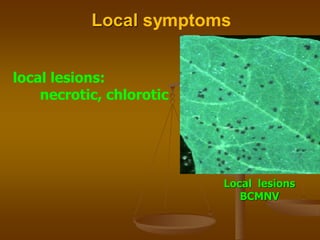
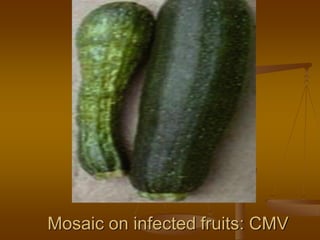
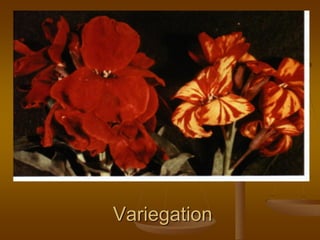
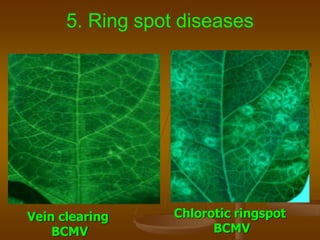
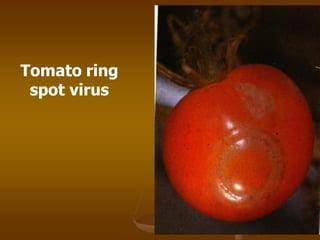
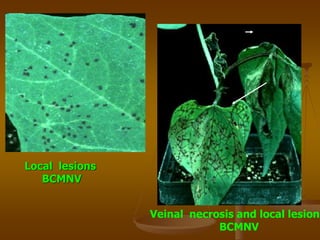
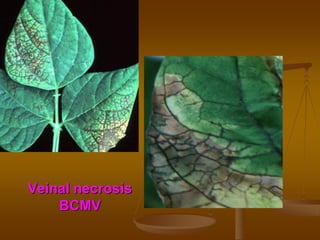
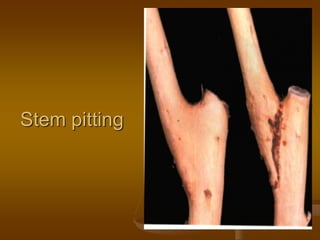
1) Plant virus symptoms can be local or systemic and include mosaic patterns, chlorosis, yellowing, leaf rolling, and stunting. They are important for virus identification but cannot solely characterize a virus which can be affected by many environmental and biological factors.
2) Microscopic symptoms include anatomical changes like necrosis, hypoplasia, hyperplasia, and formation of inclusion bodies which are intracellular structures that may contain virus particles. Nuclear inclusions are a characteristic of geminiviruses.
3) Proper identification of virus symptoms is important but must be combined with other identification methods as symptoms can vary depending on virus strain, host variety, and environmental conditions.