Embed presentation
Downloaded 202 times



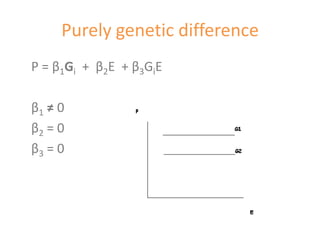




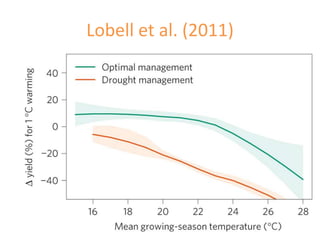








This document discusses genotype by environment interactions (GxE) and how climate change can impact them. It presents equations to model production (P) as a function of genotype (G), environment (E), and their interaction (G*E). Different values for the coefficients β1, β2, and β3 represent purely genetic differences, additive interactions, and non-additive interactions between G and E. Methods like AMMI and RDA are described that use statistical models to analyze GxE, predict impacts of climate change, and define variety adaptation zones.
















