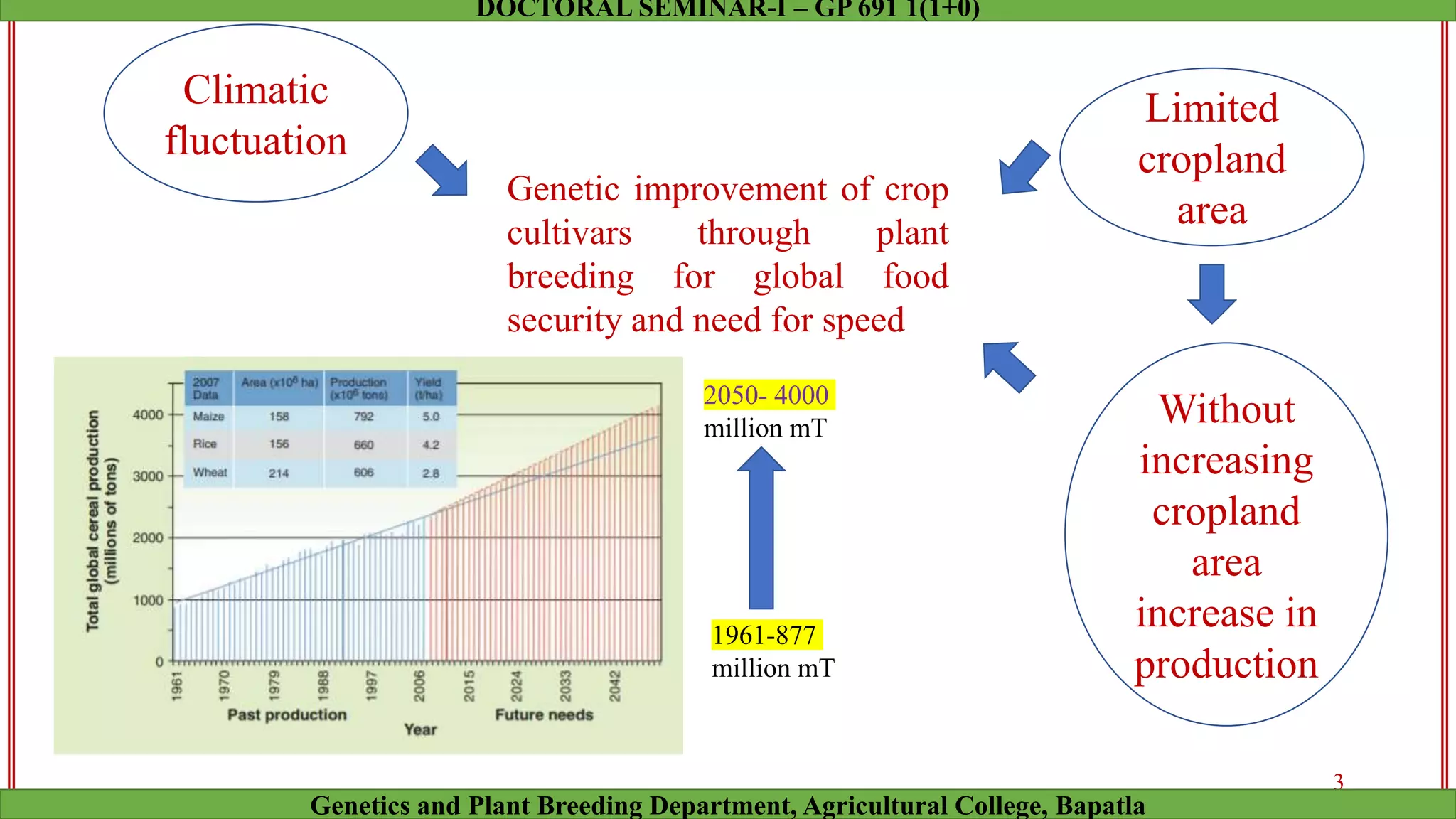
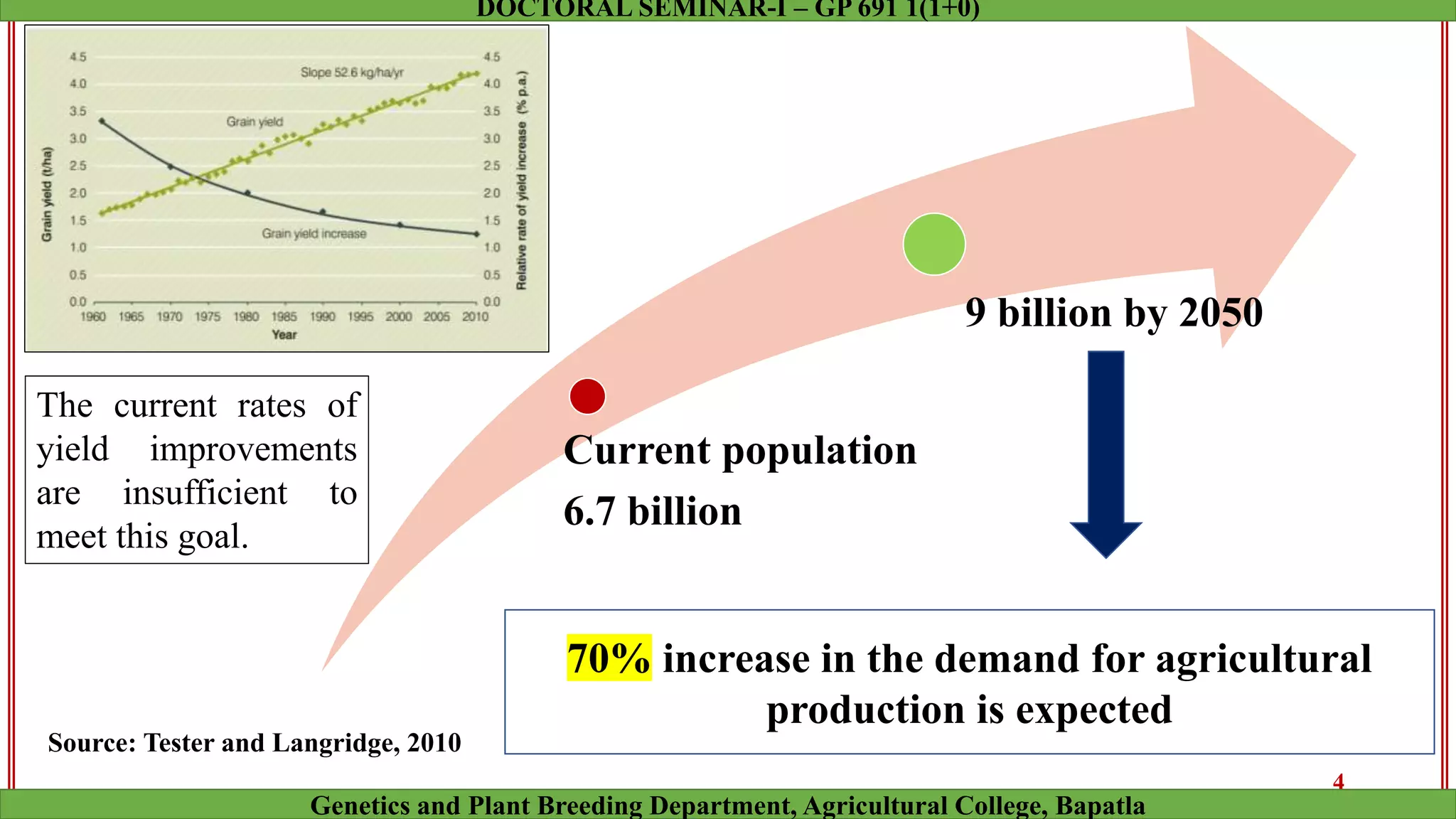
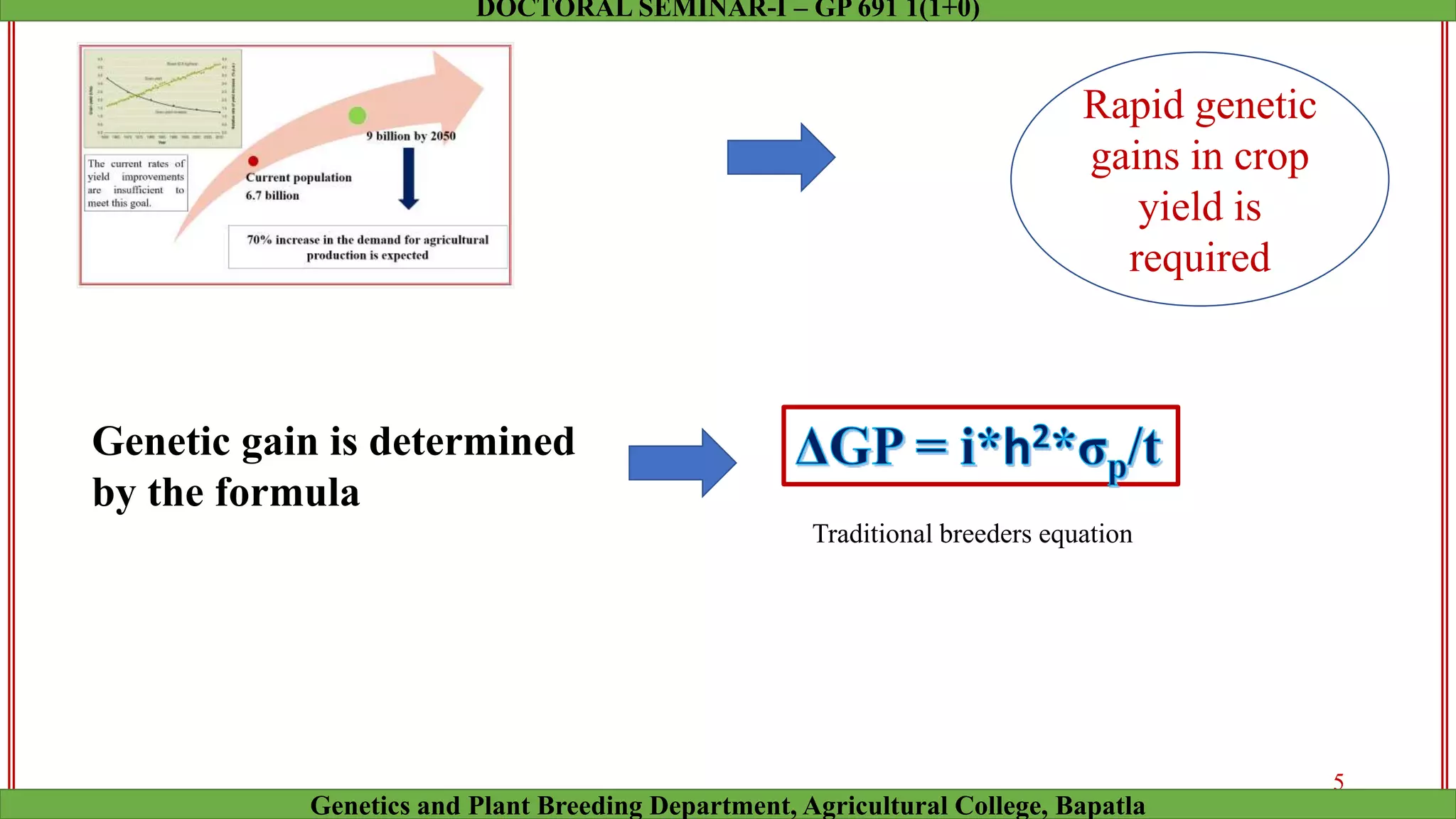
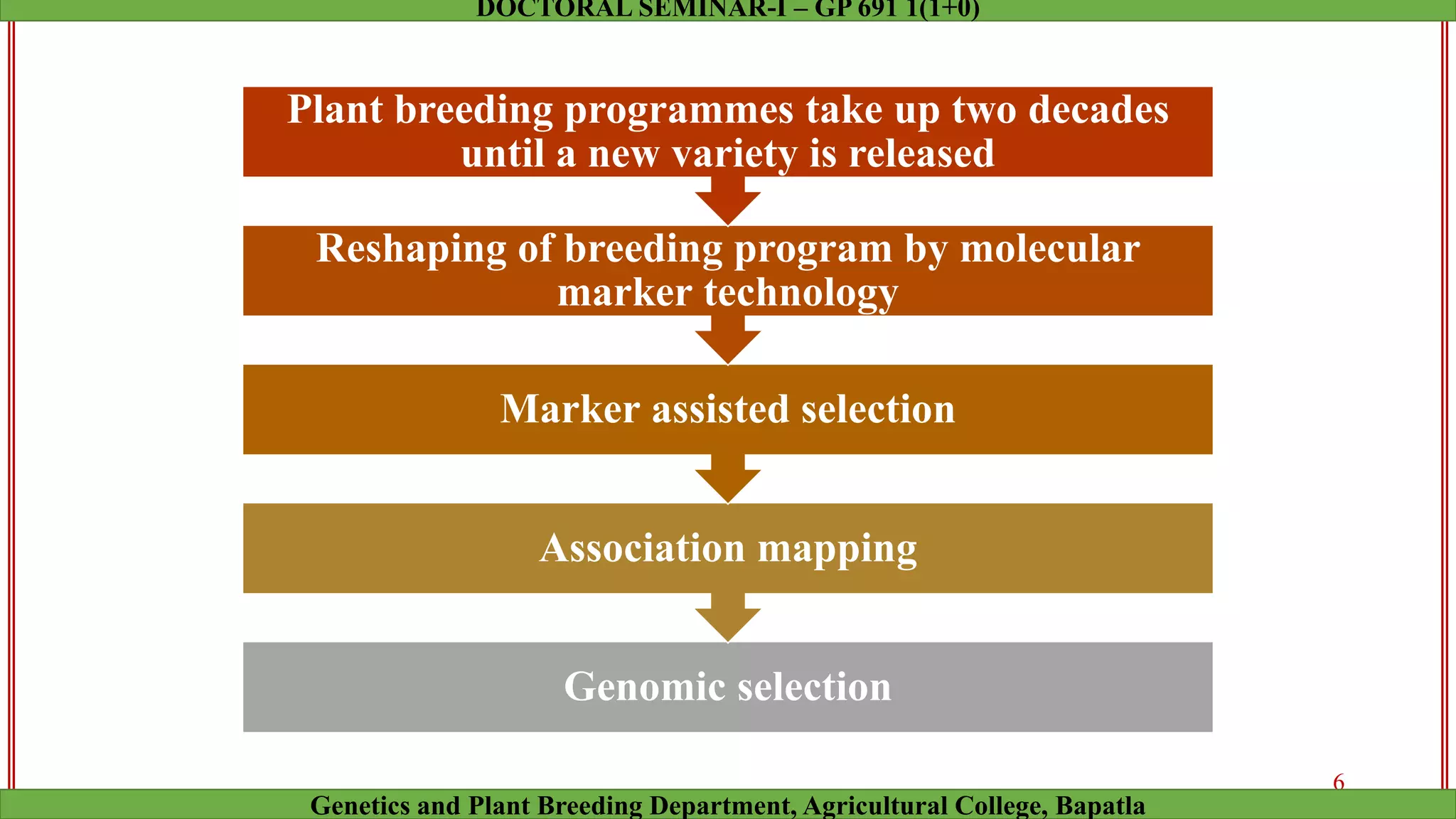
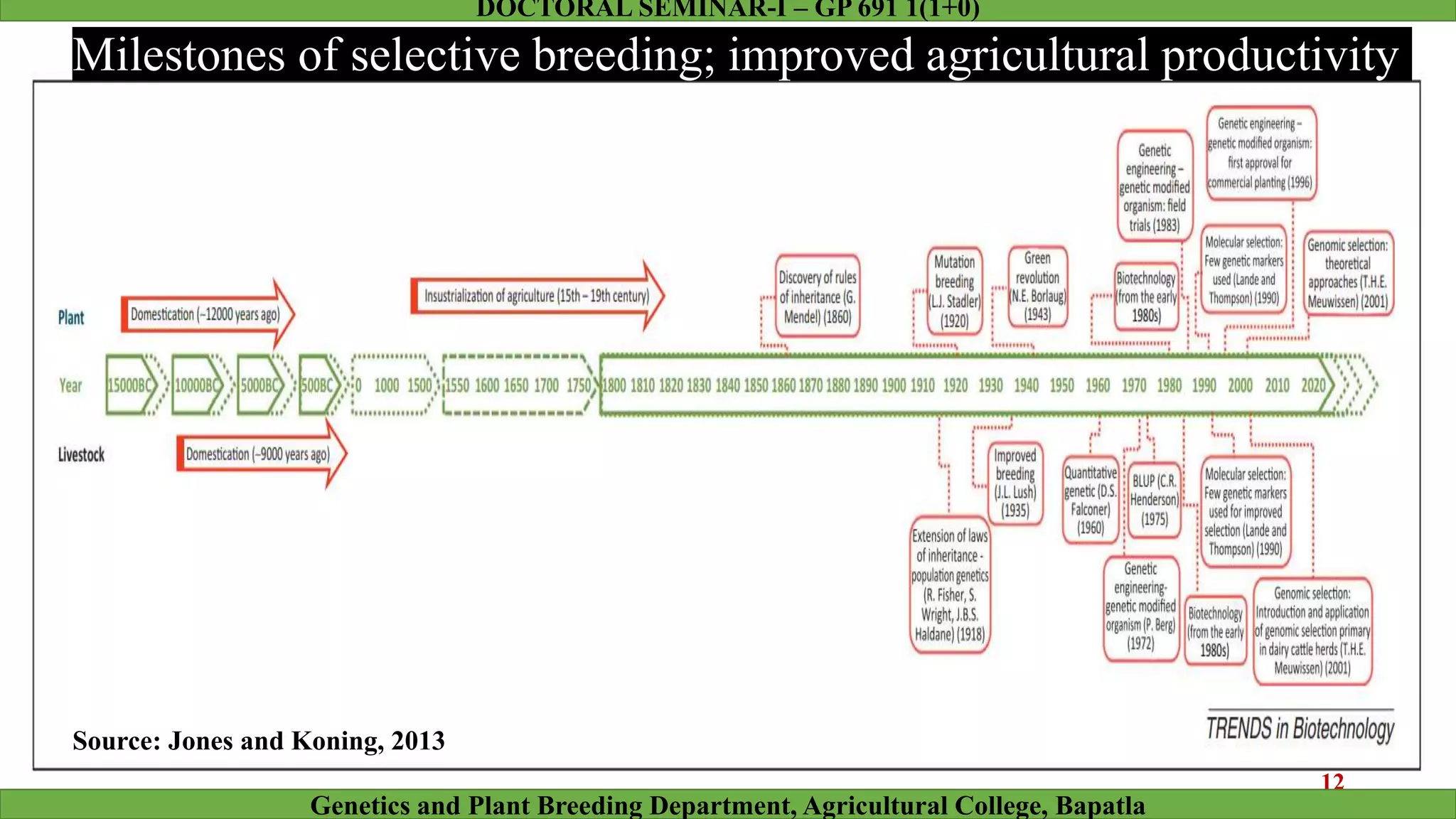
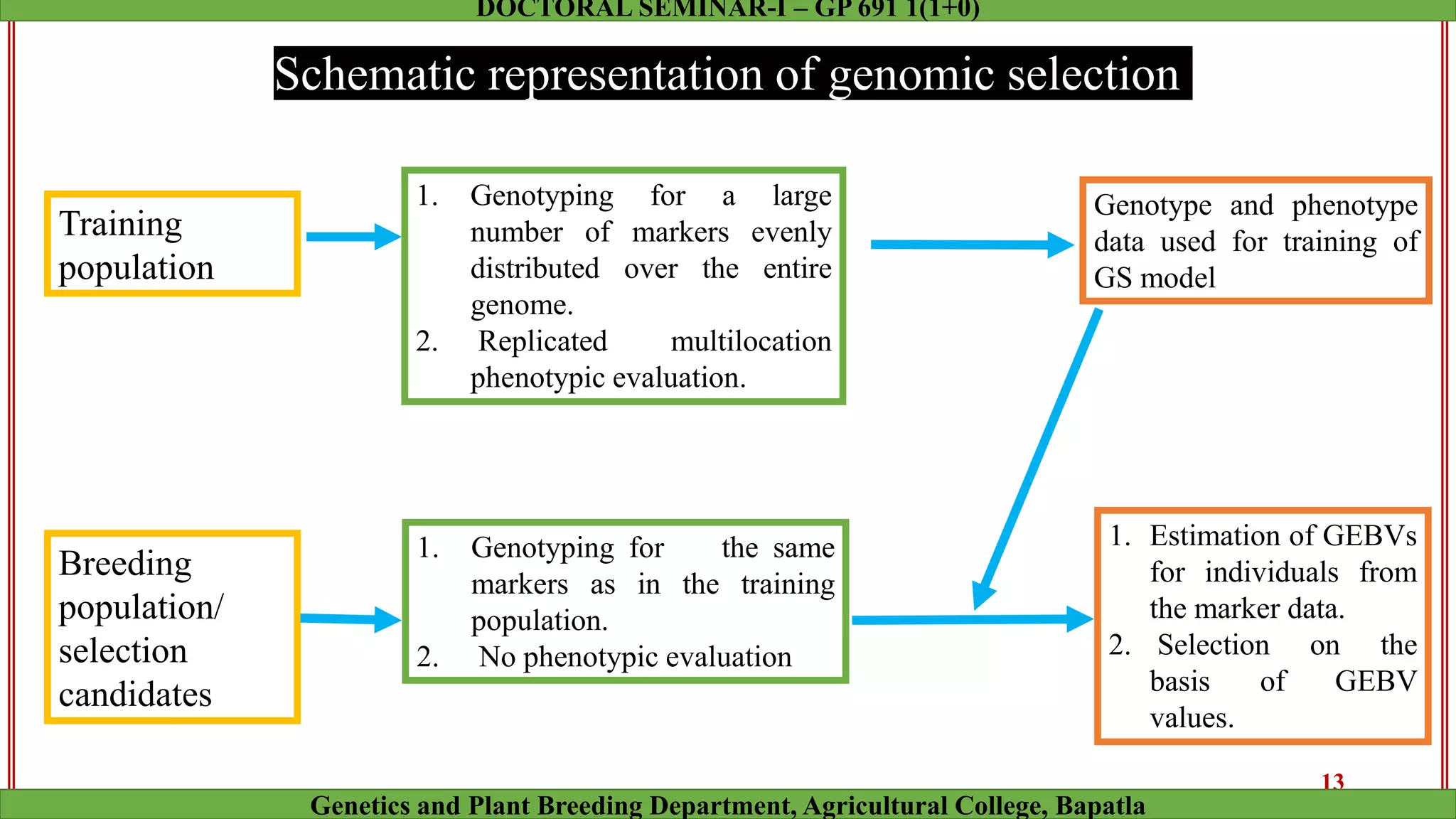
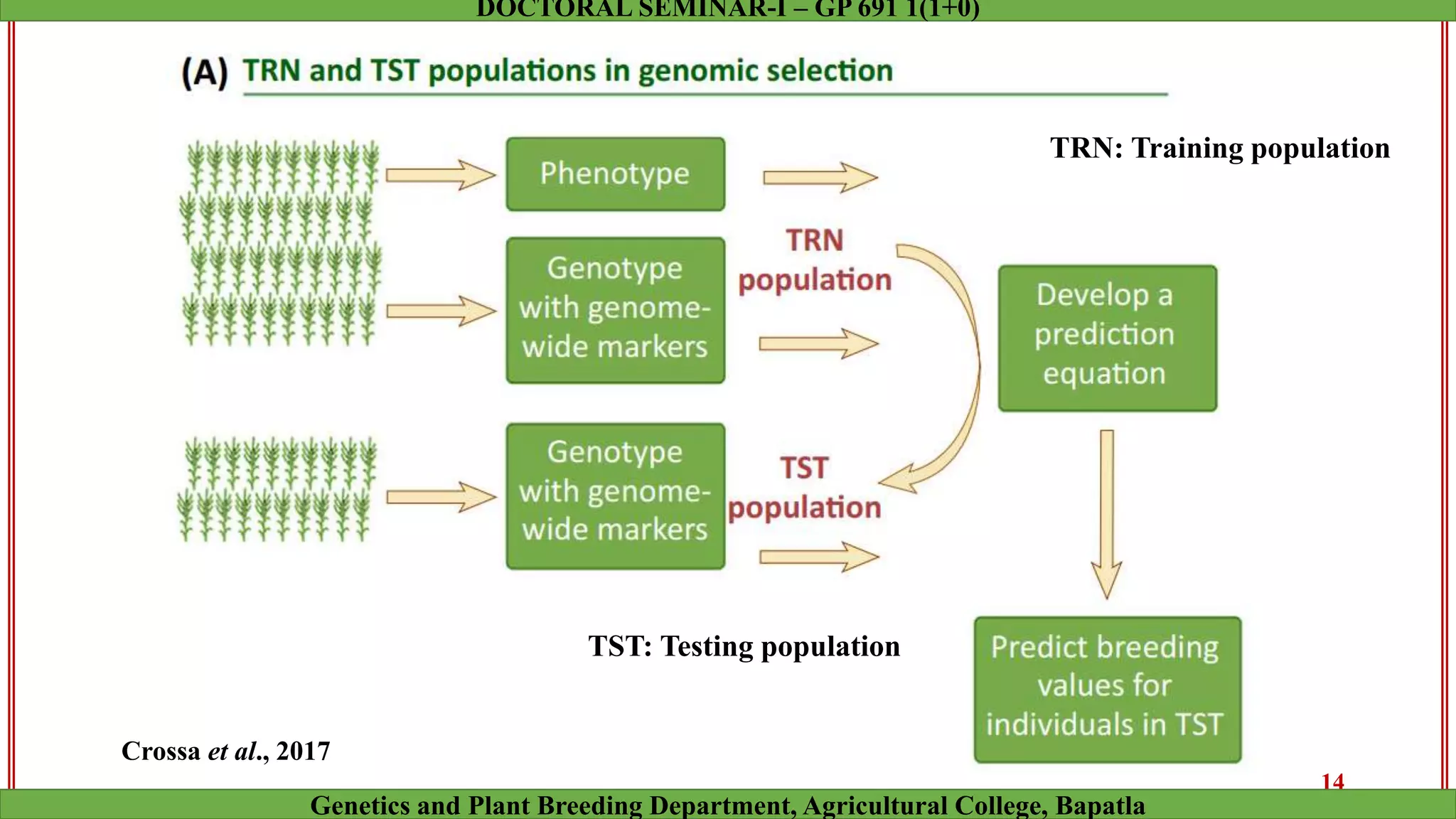
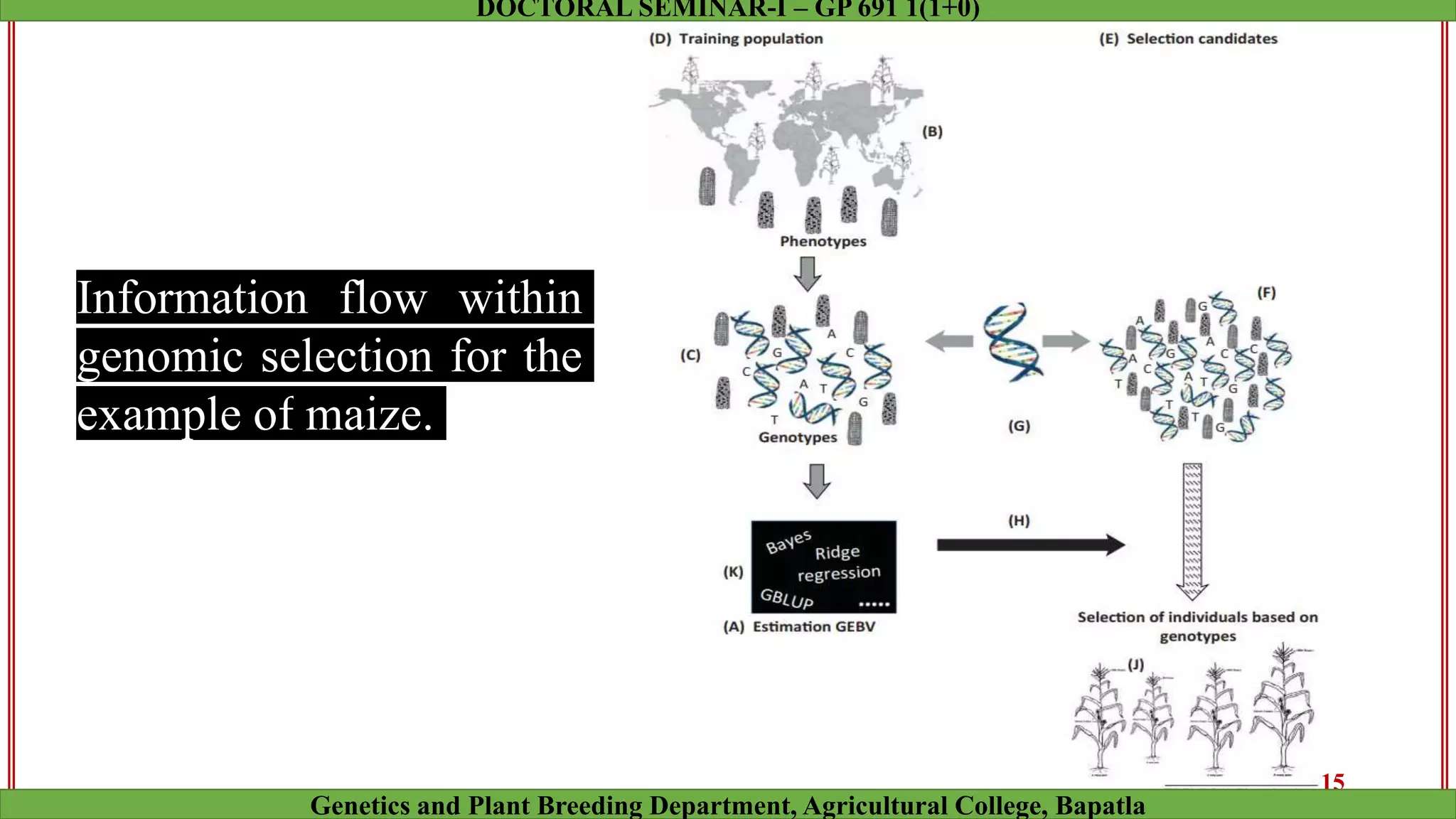
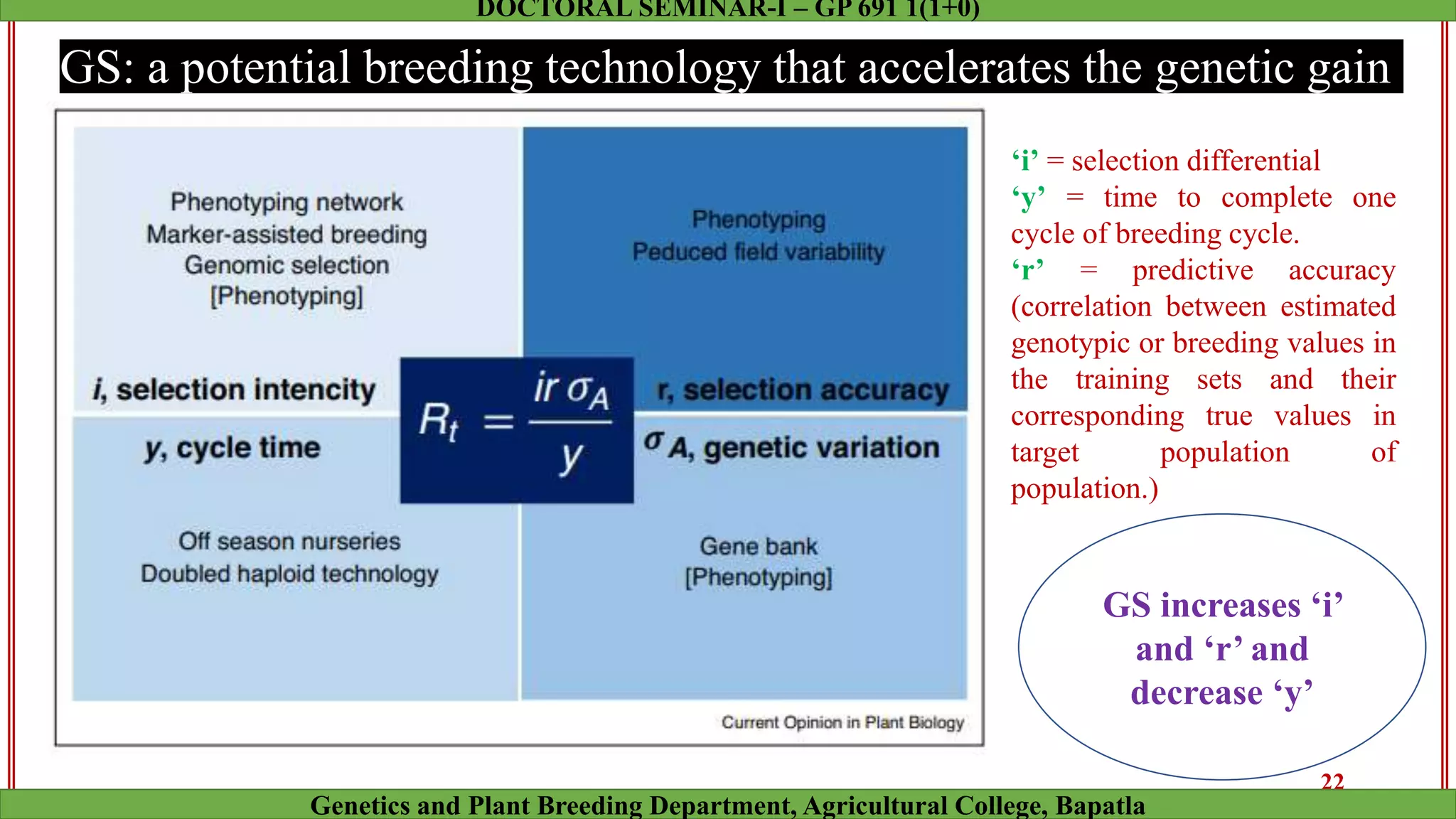
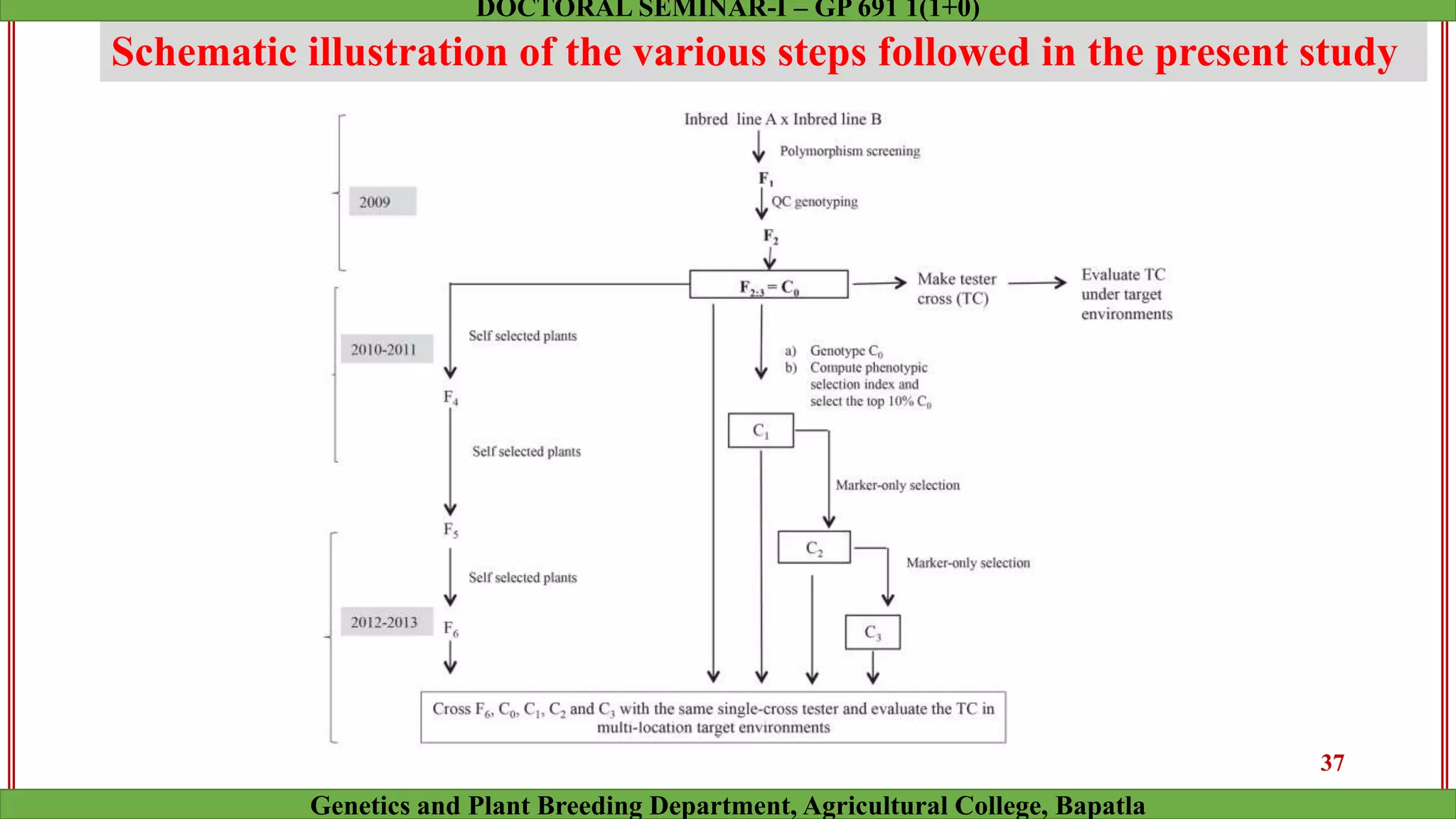
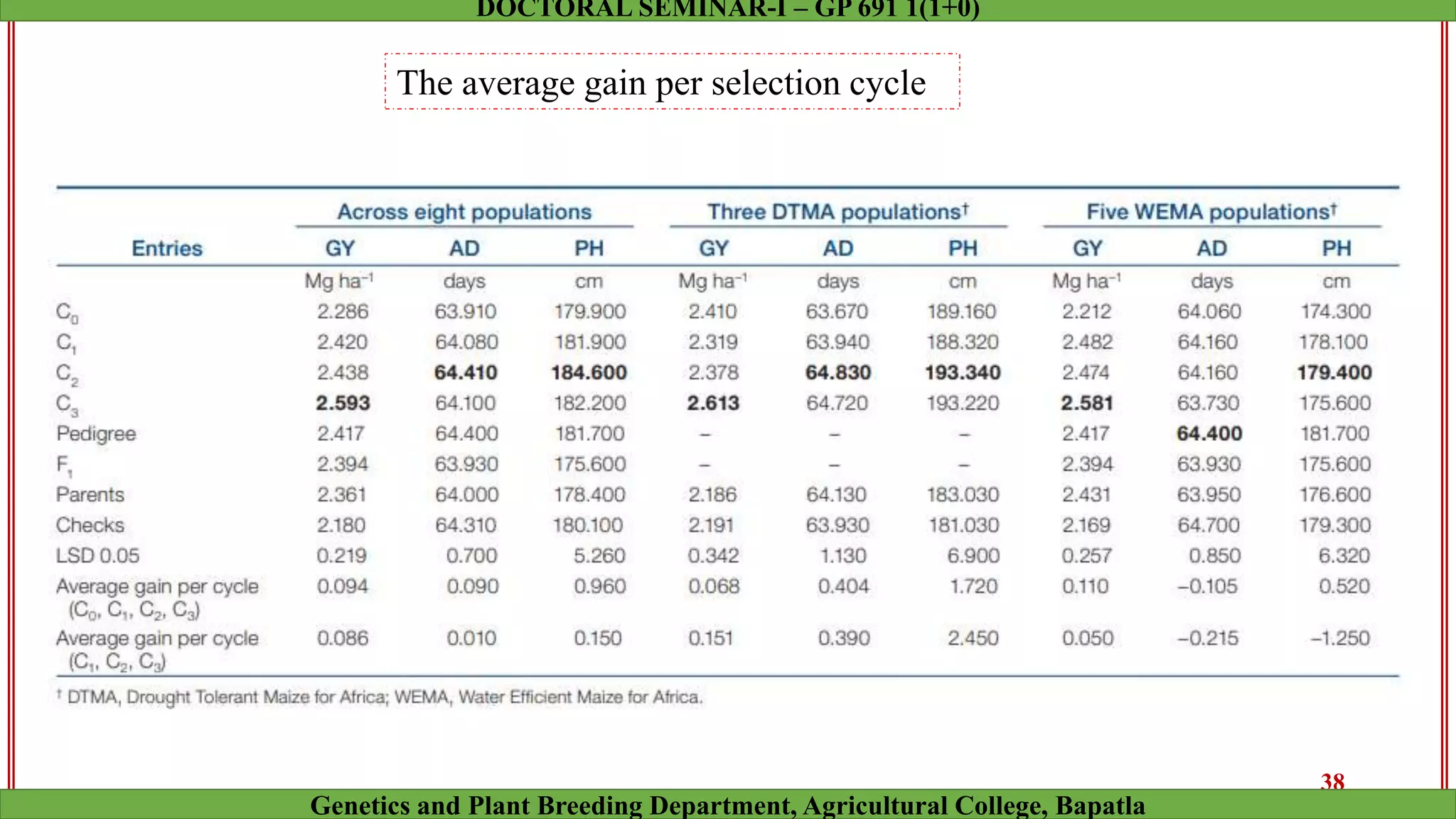
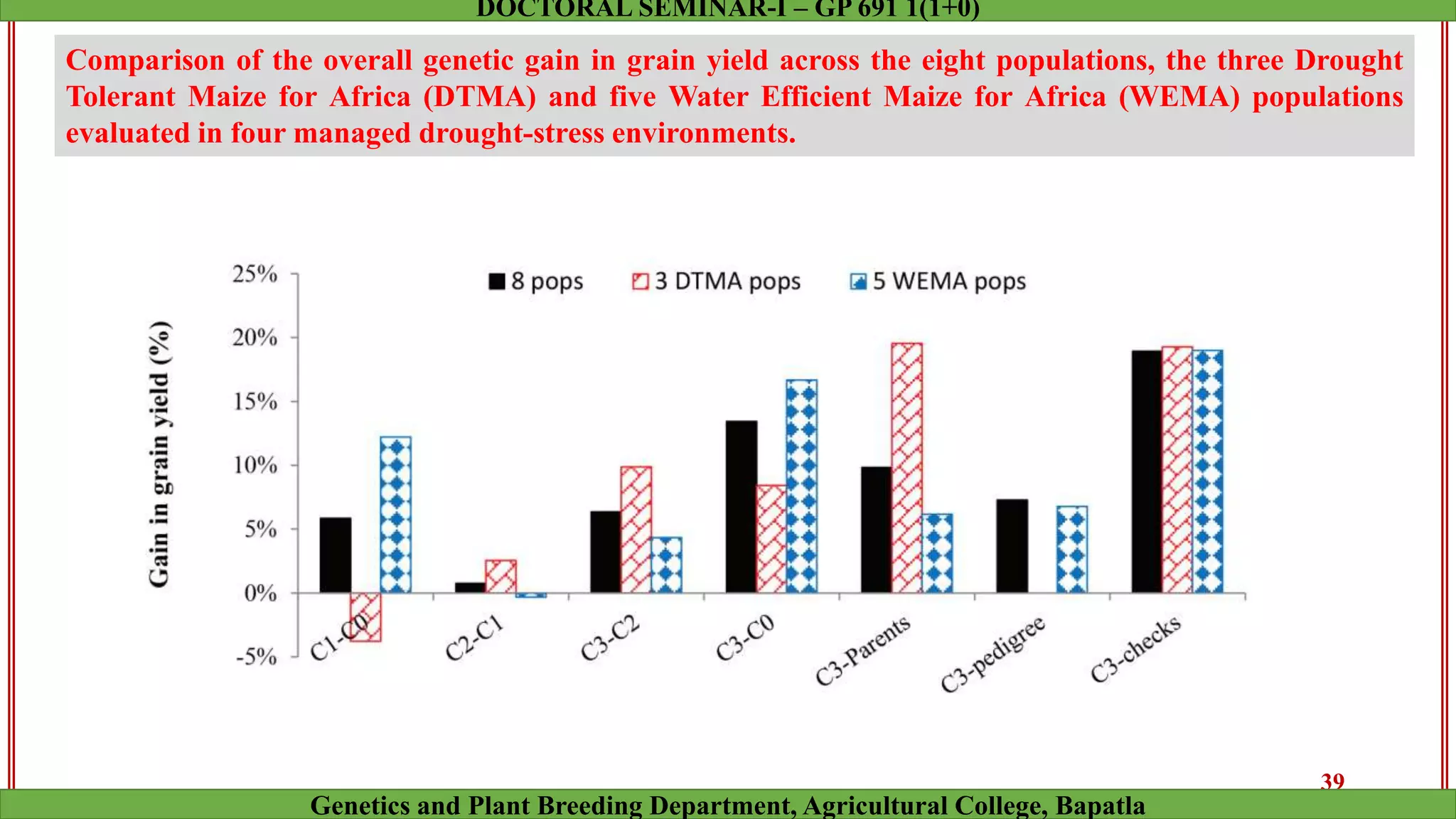
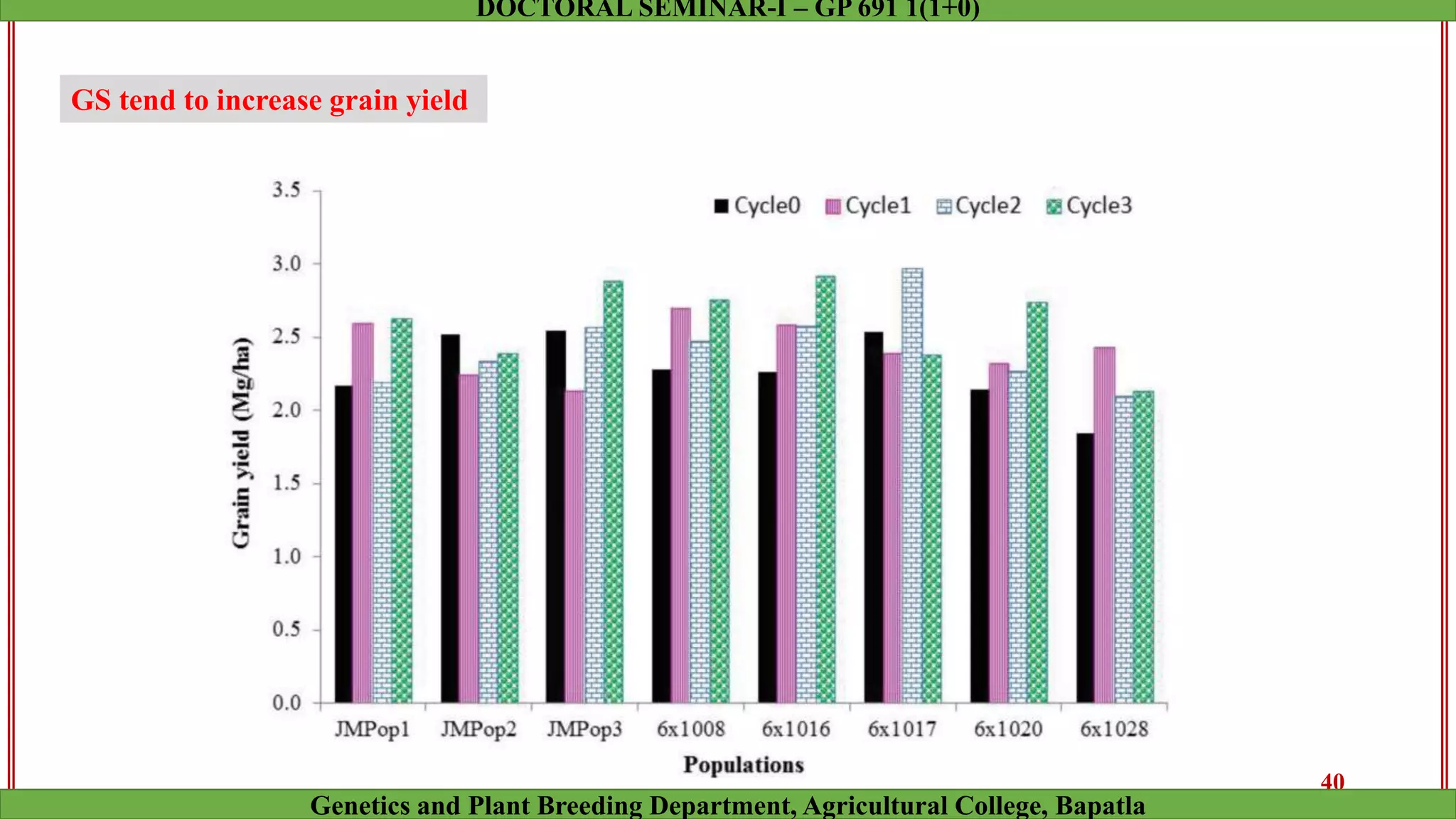
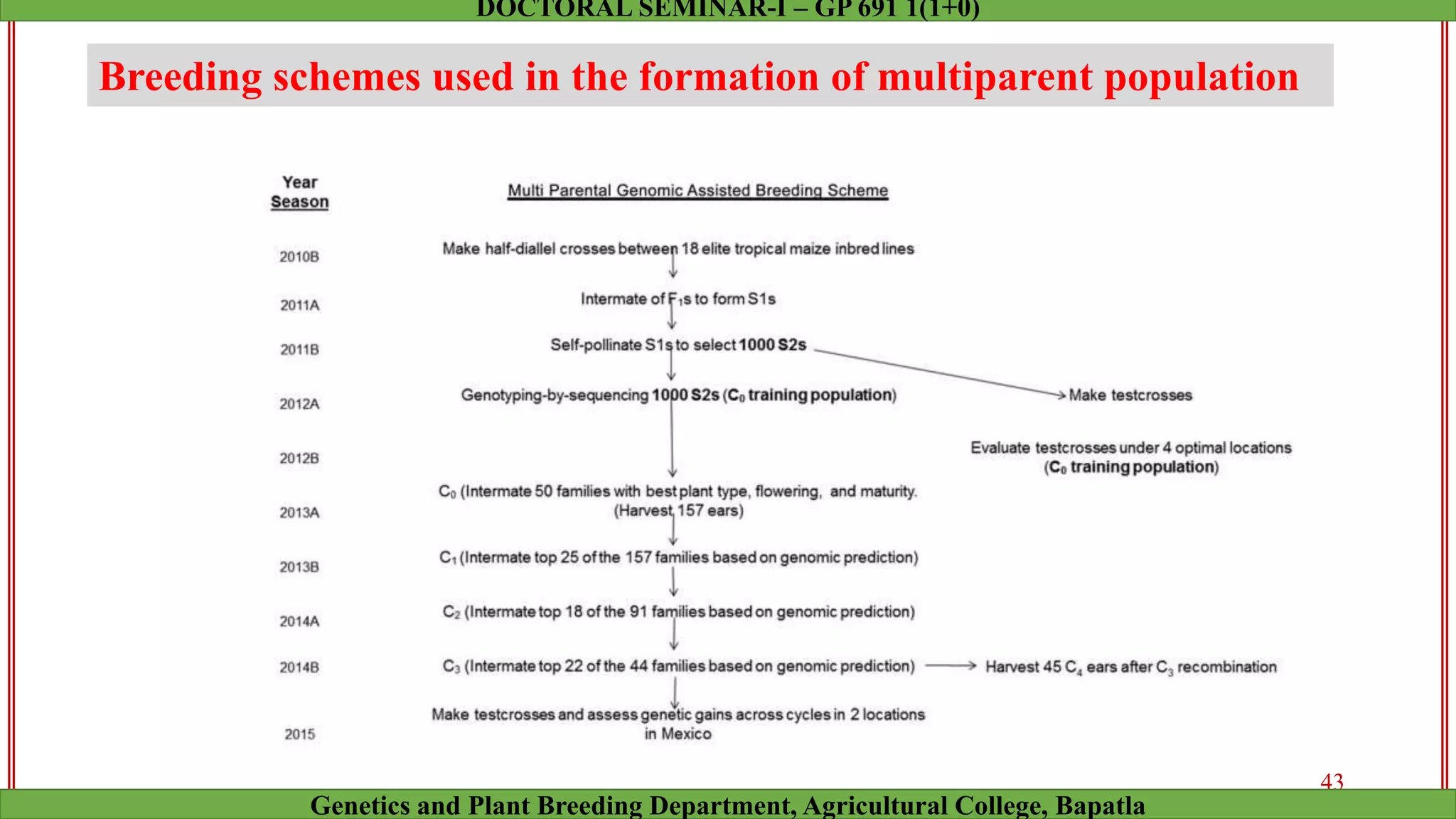
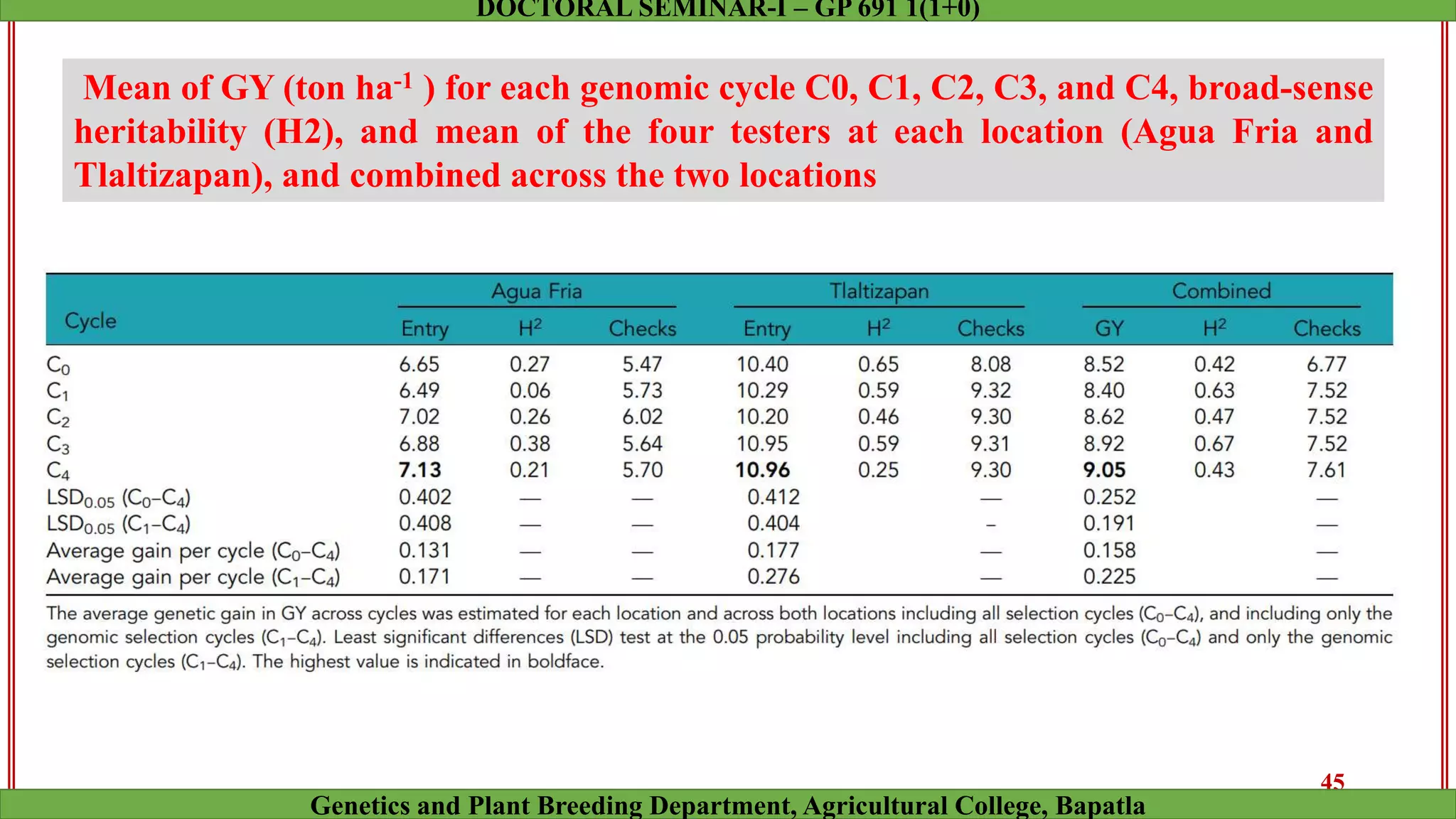
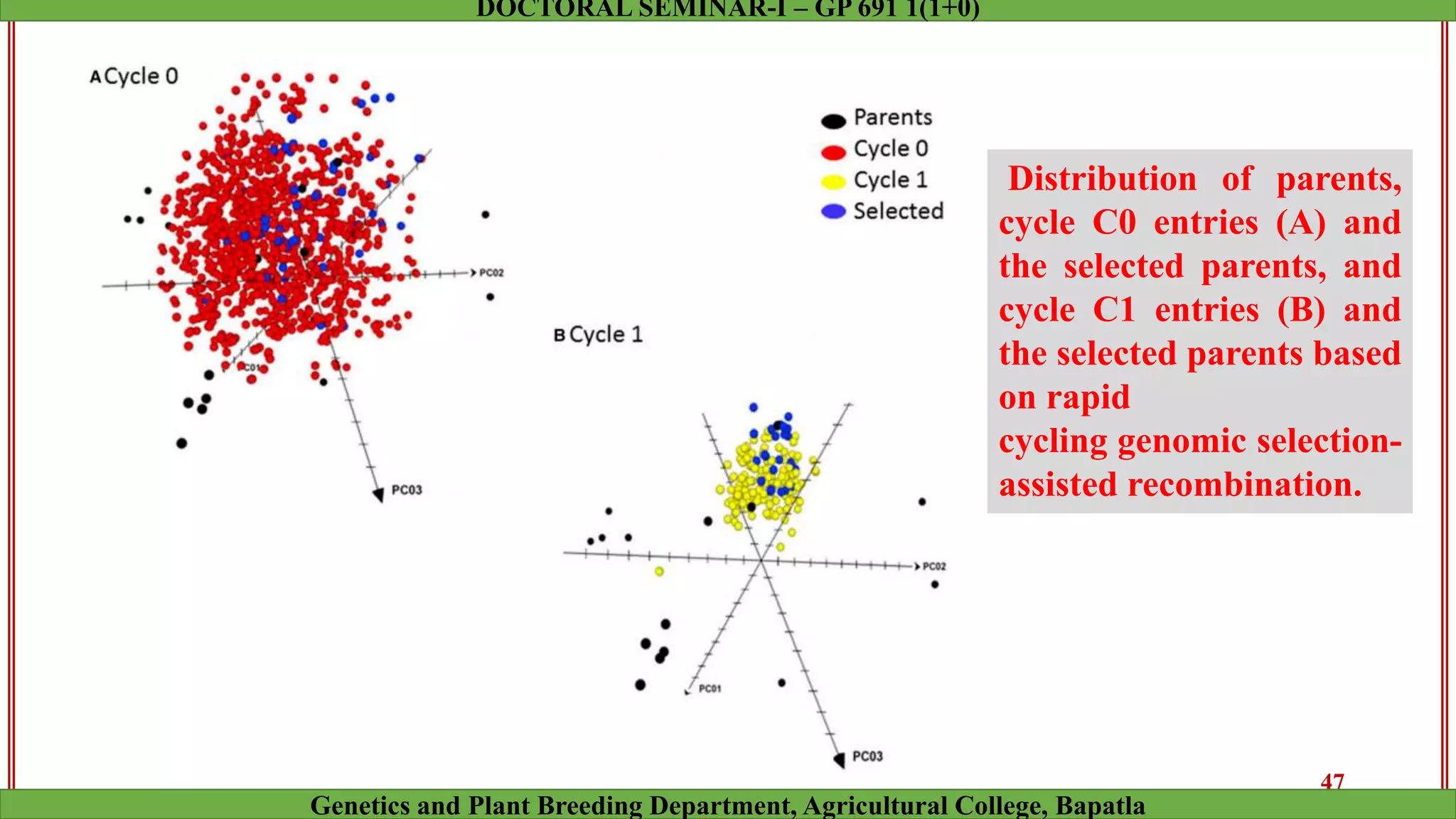
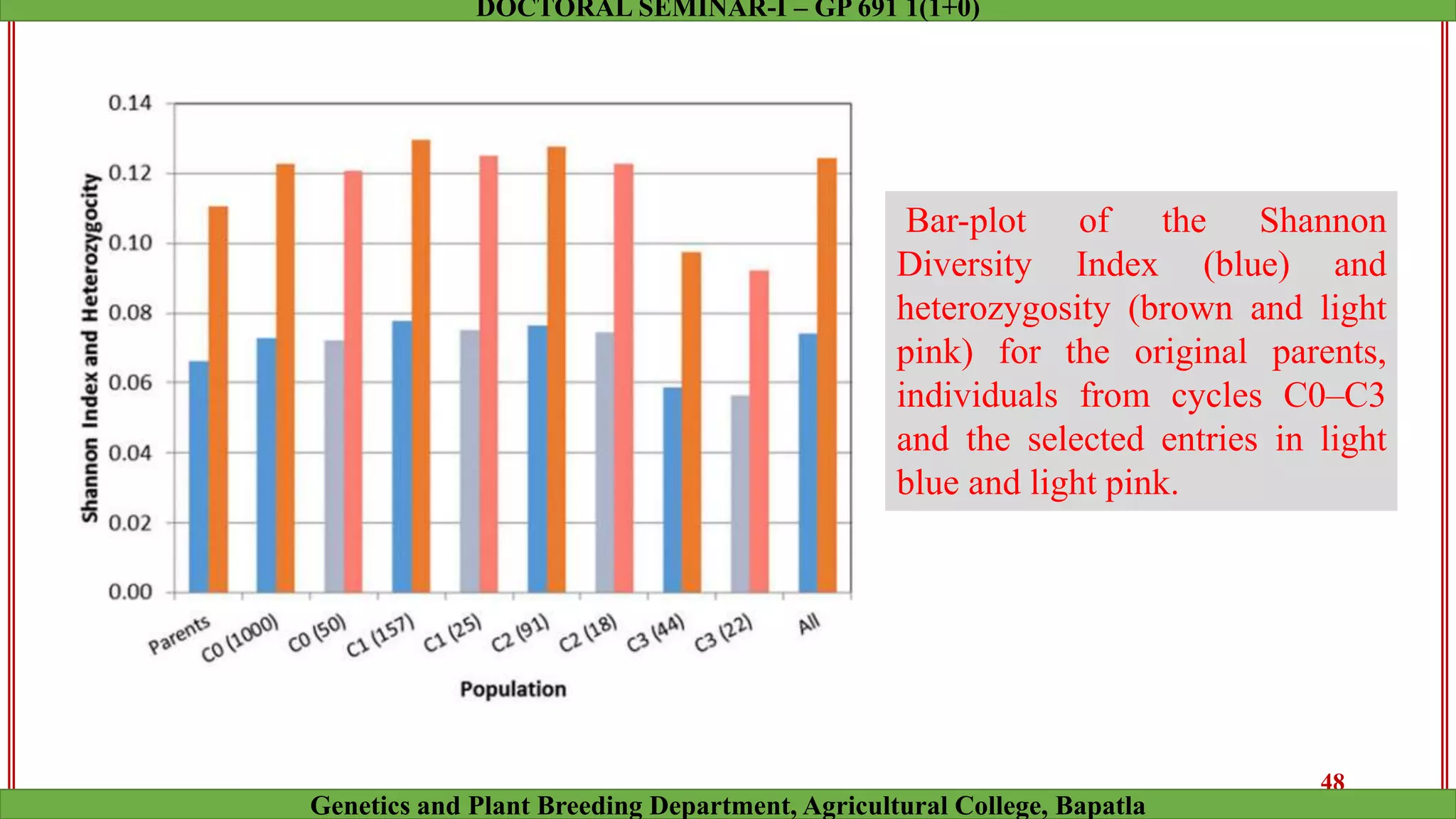
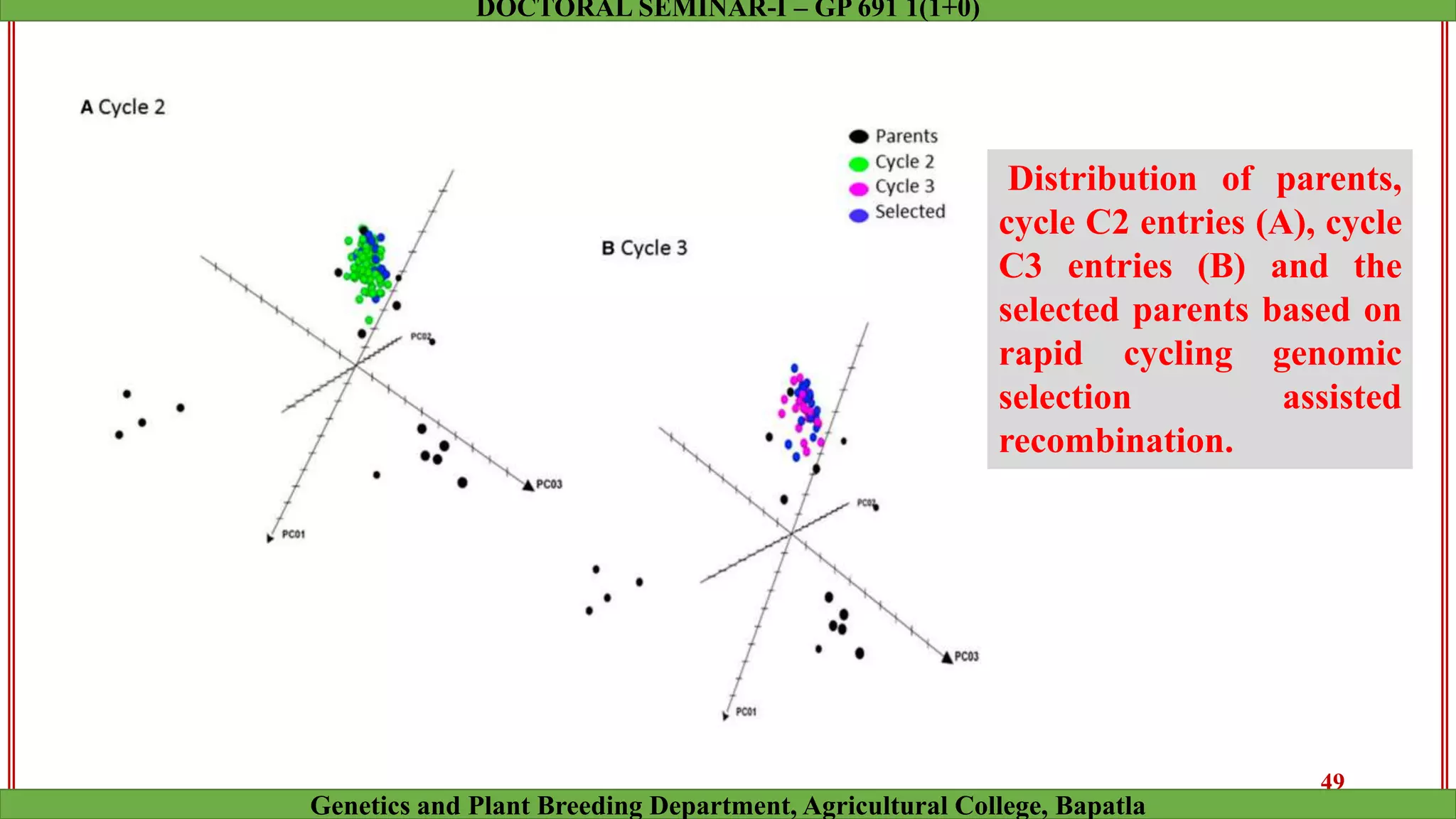
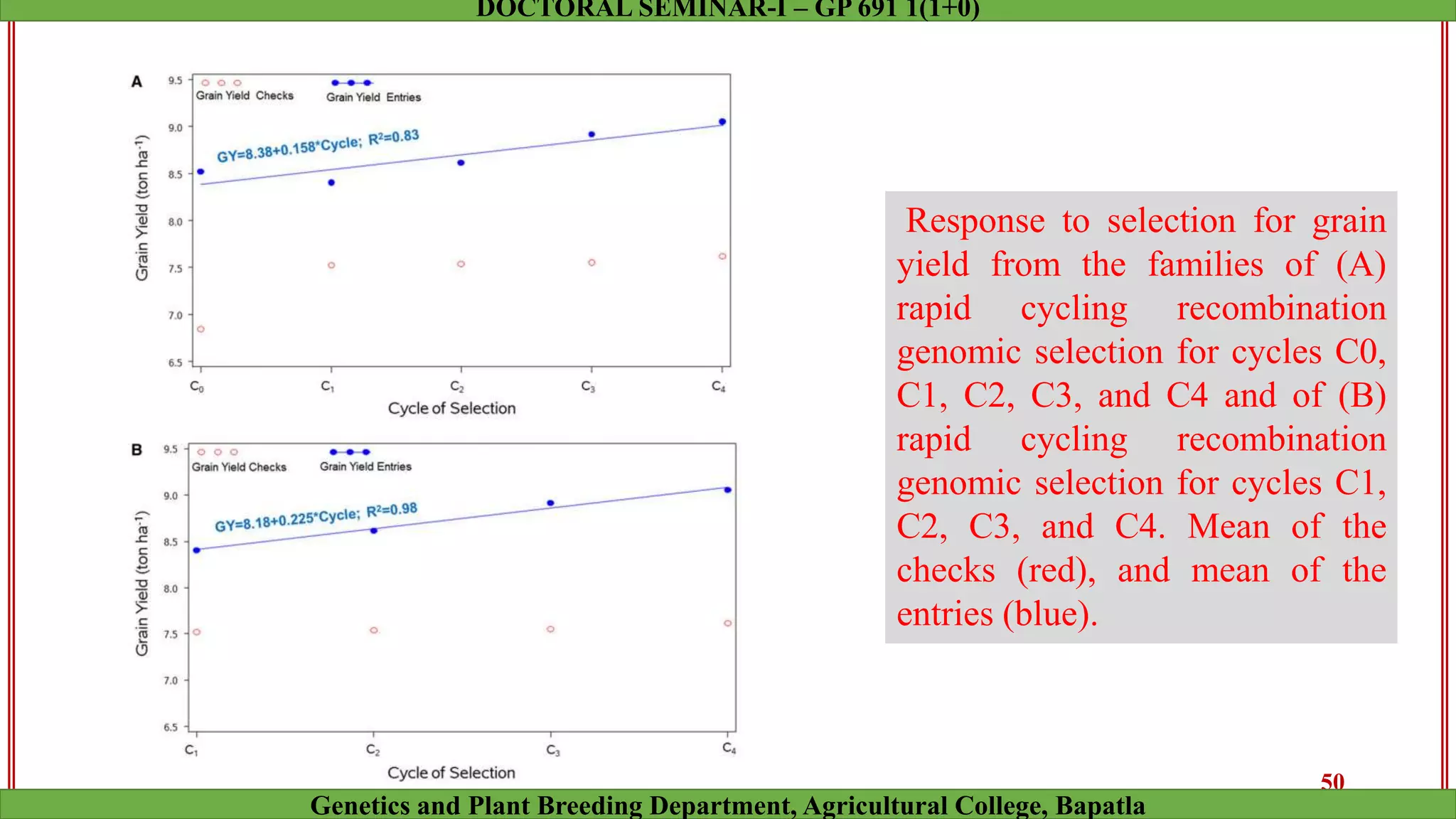
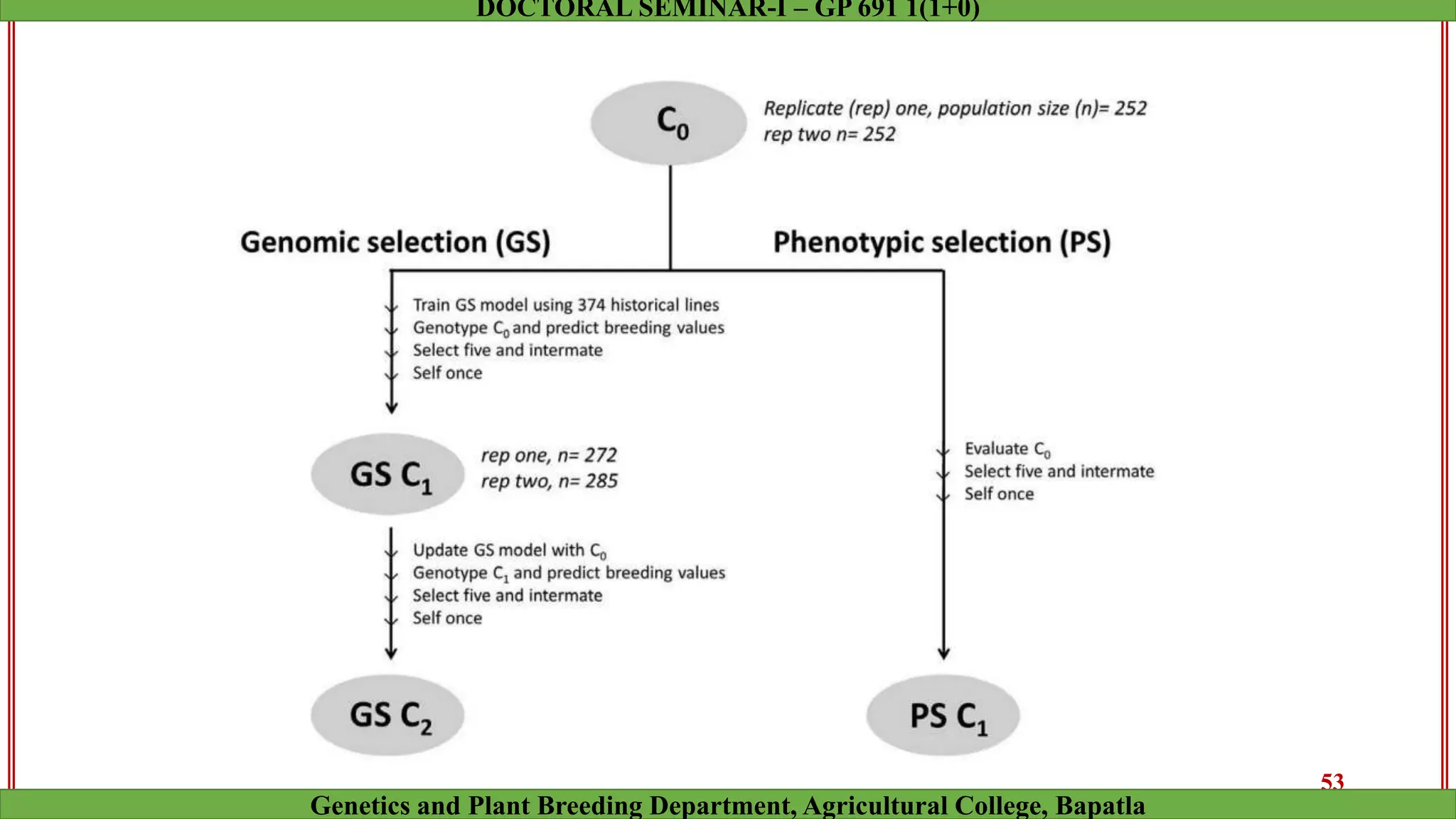
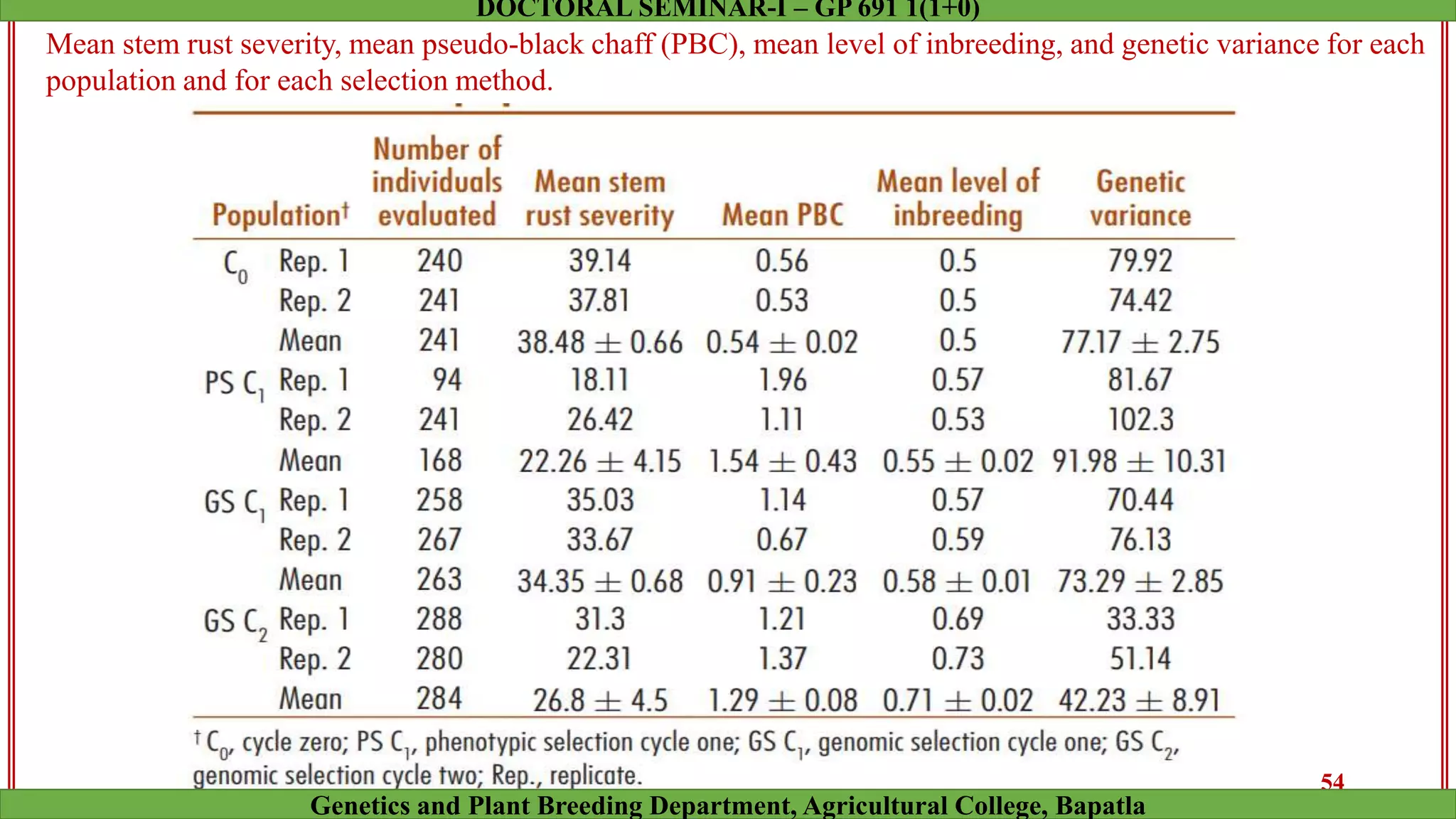
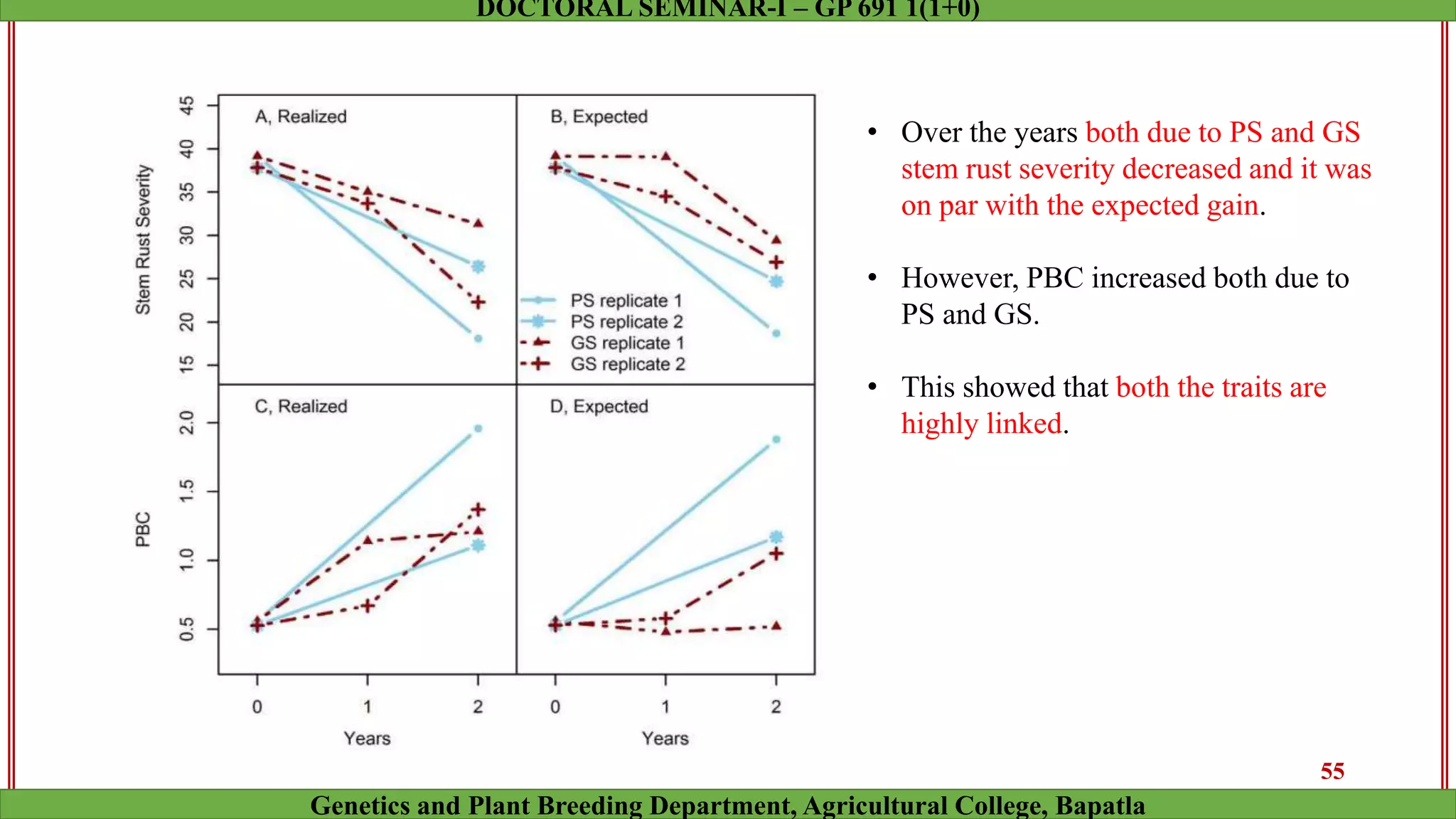
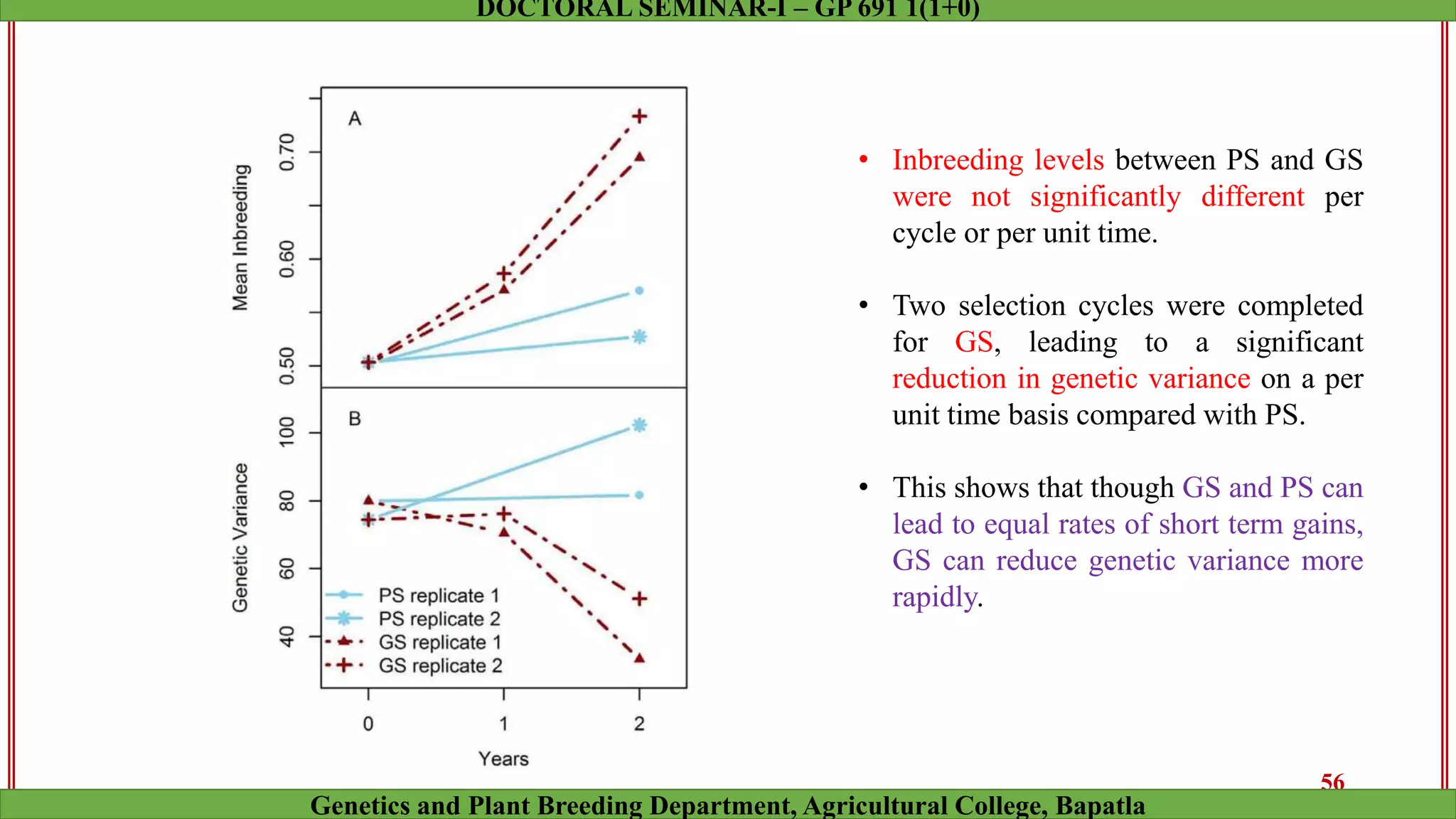
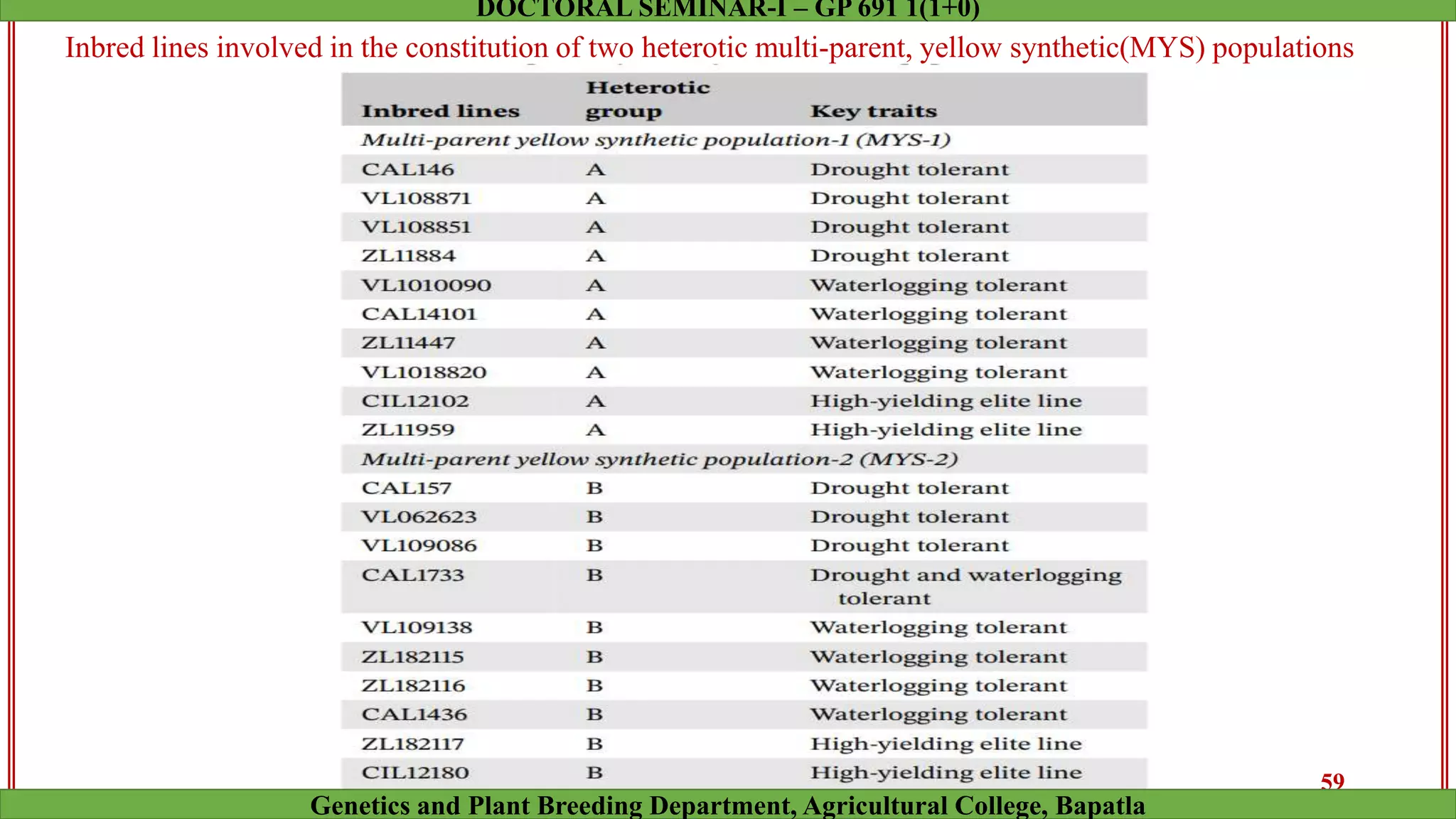
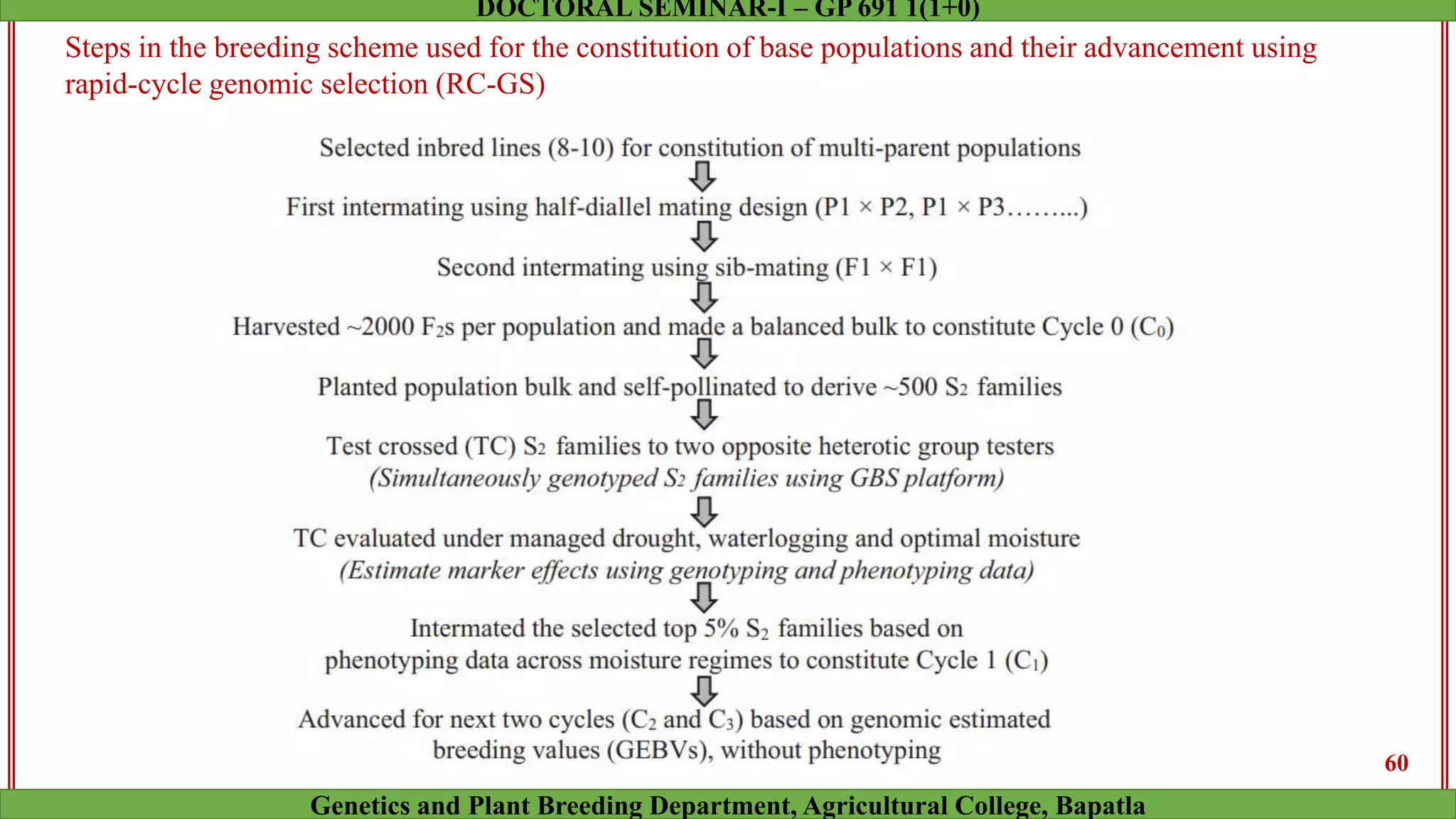
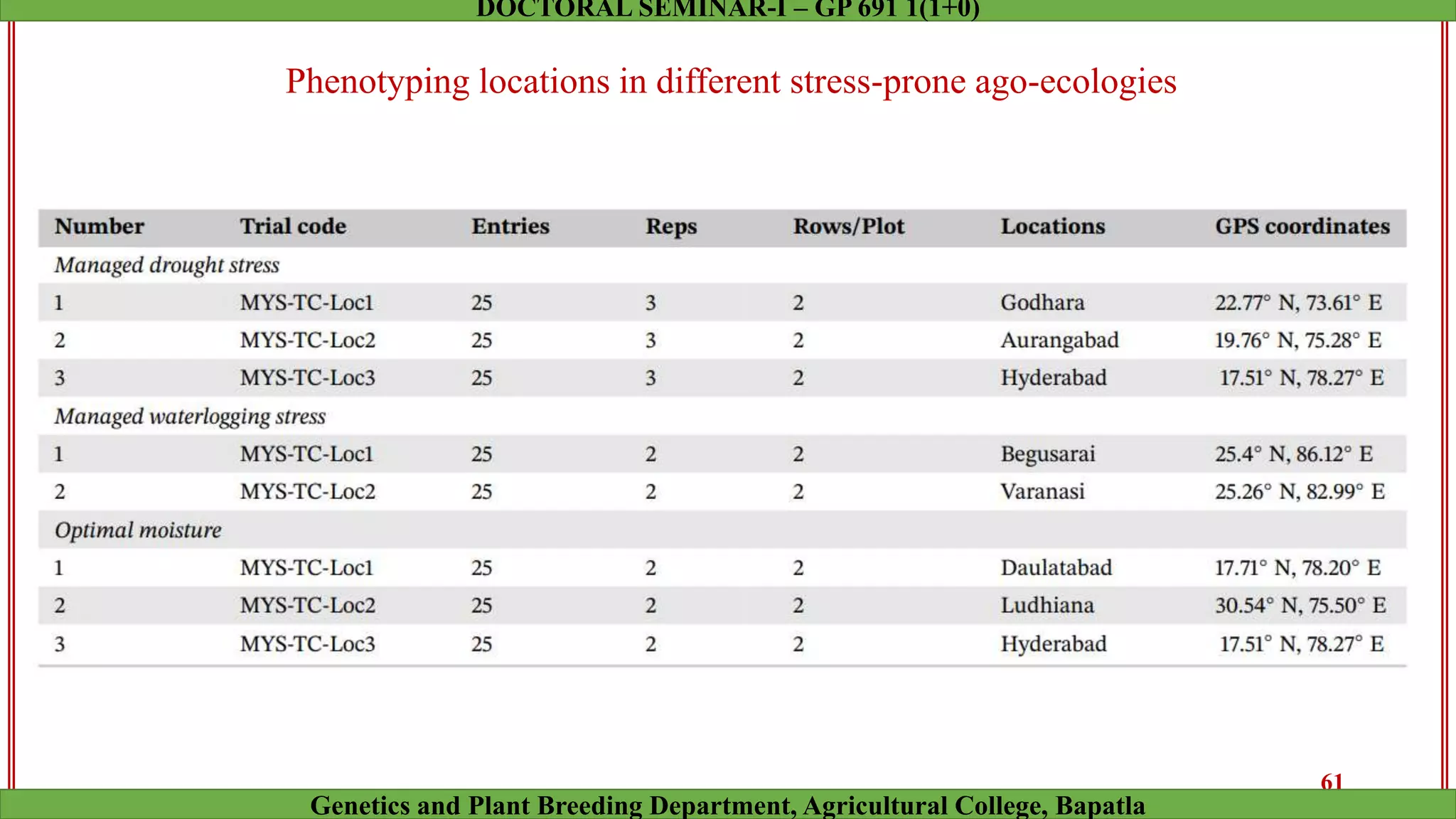
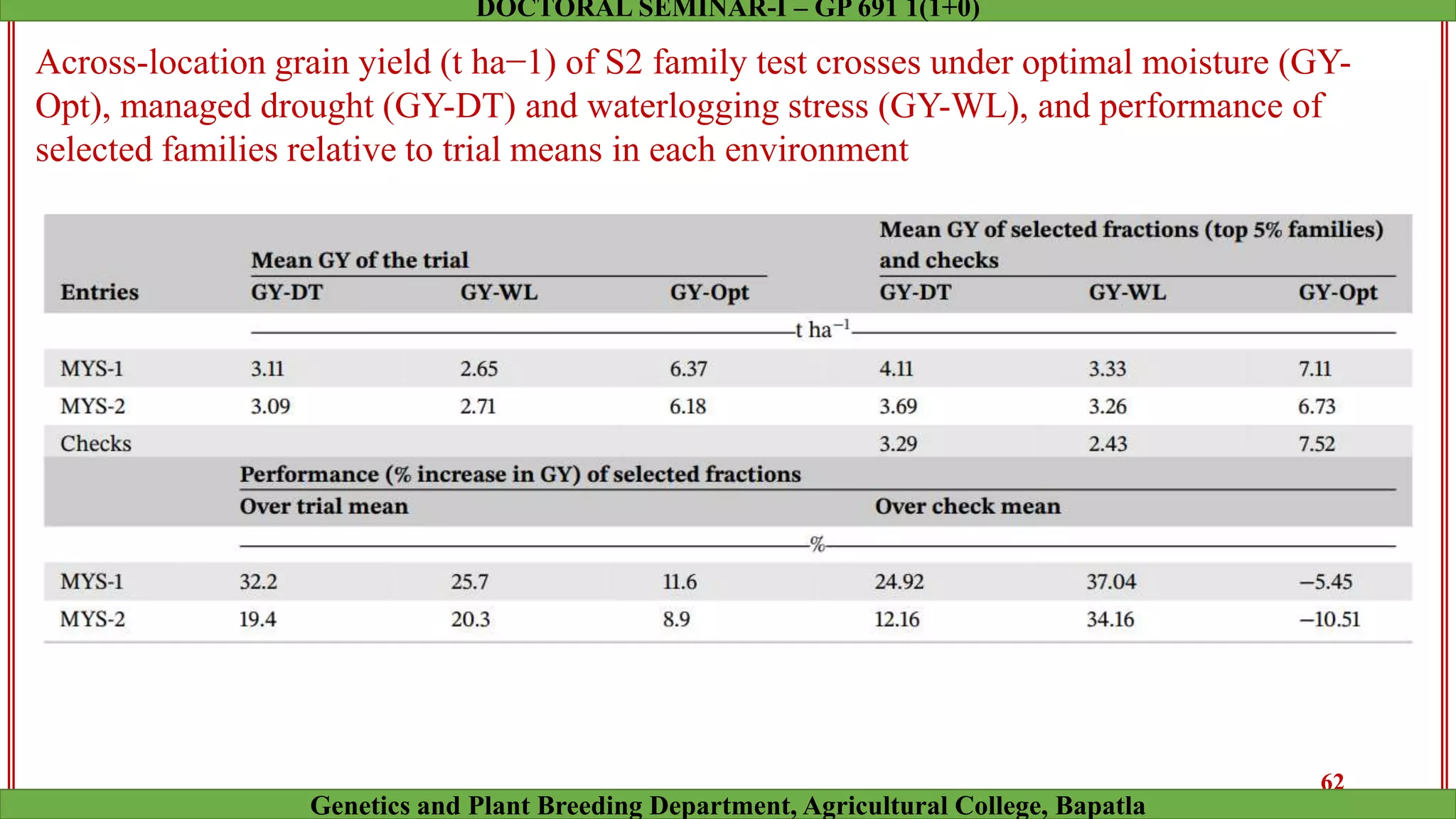
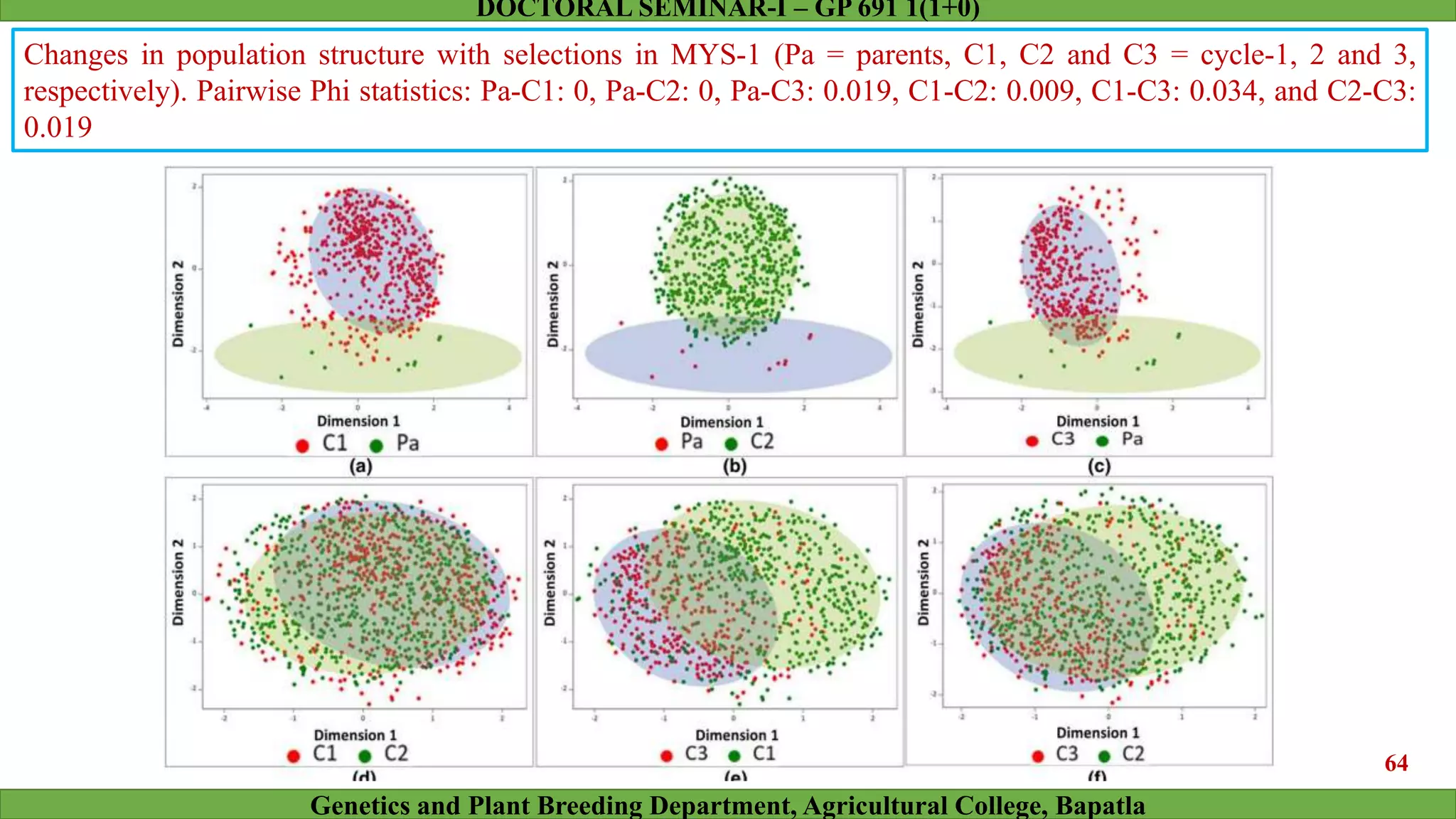
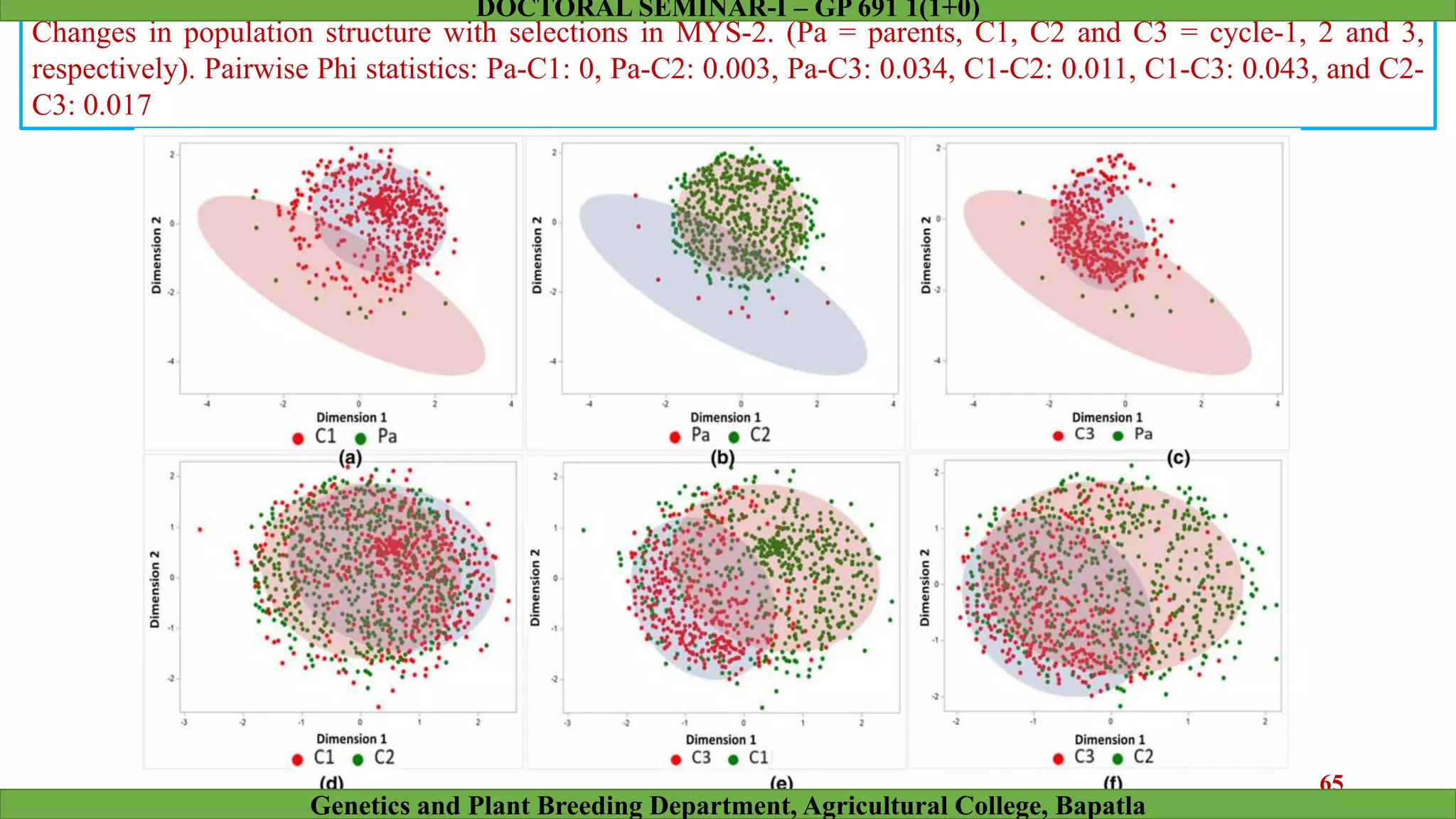
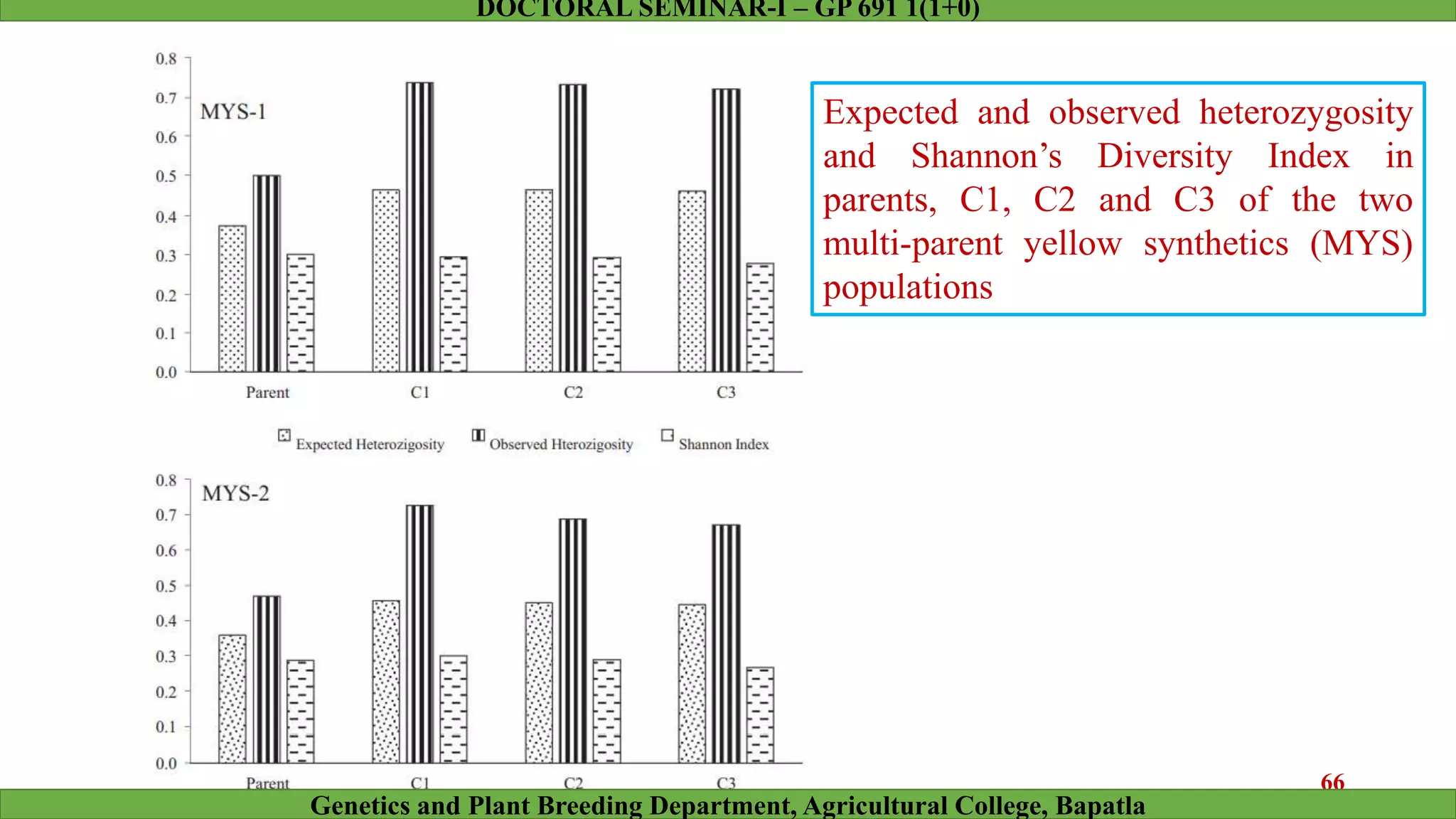
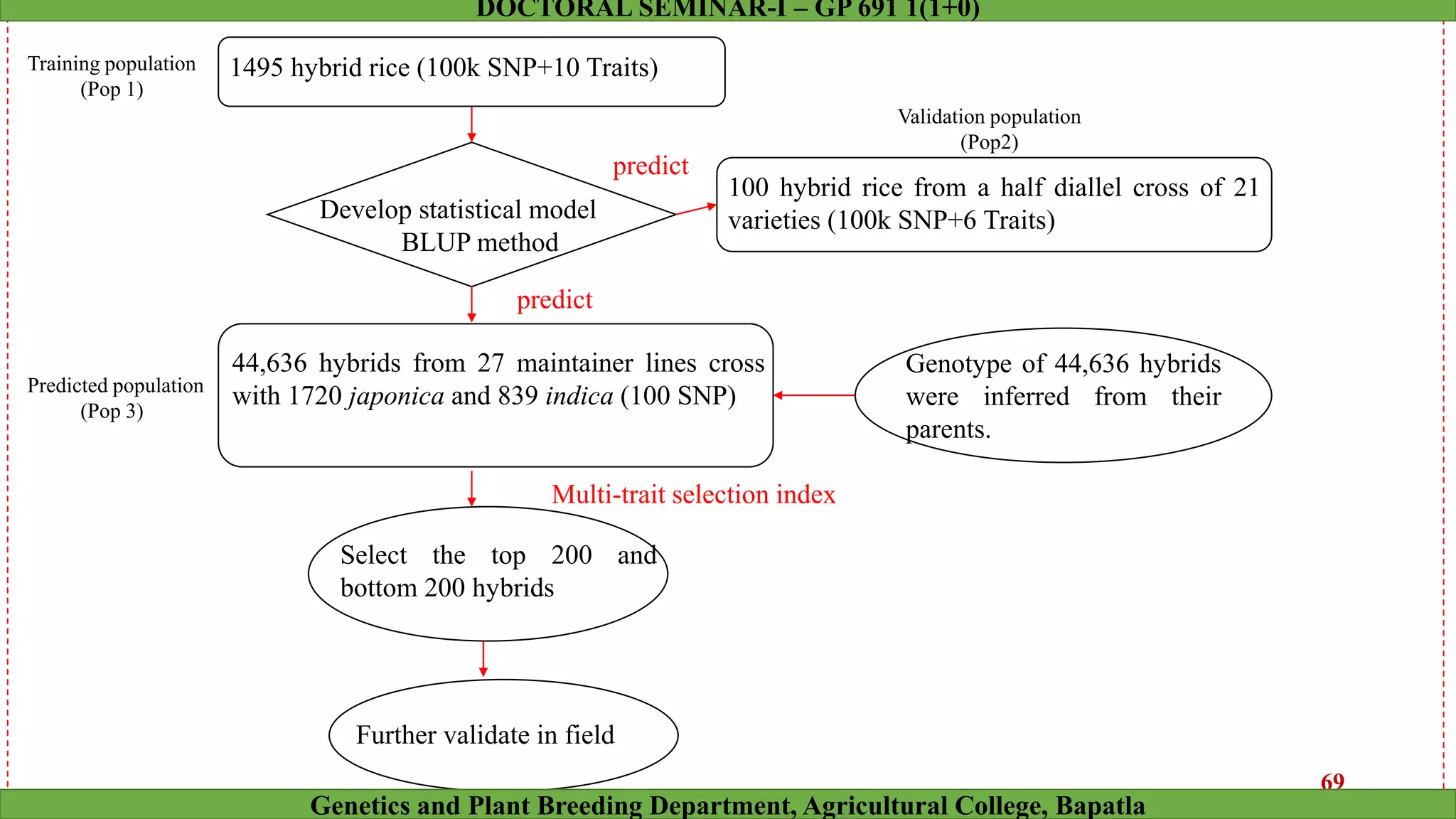
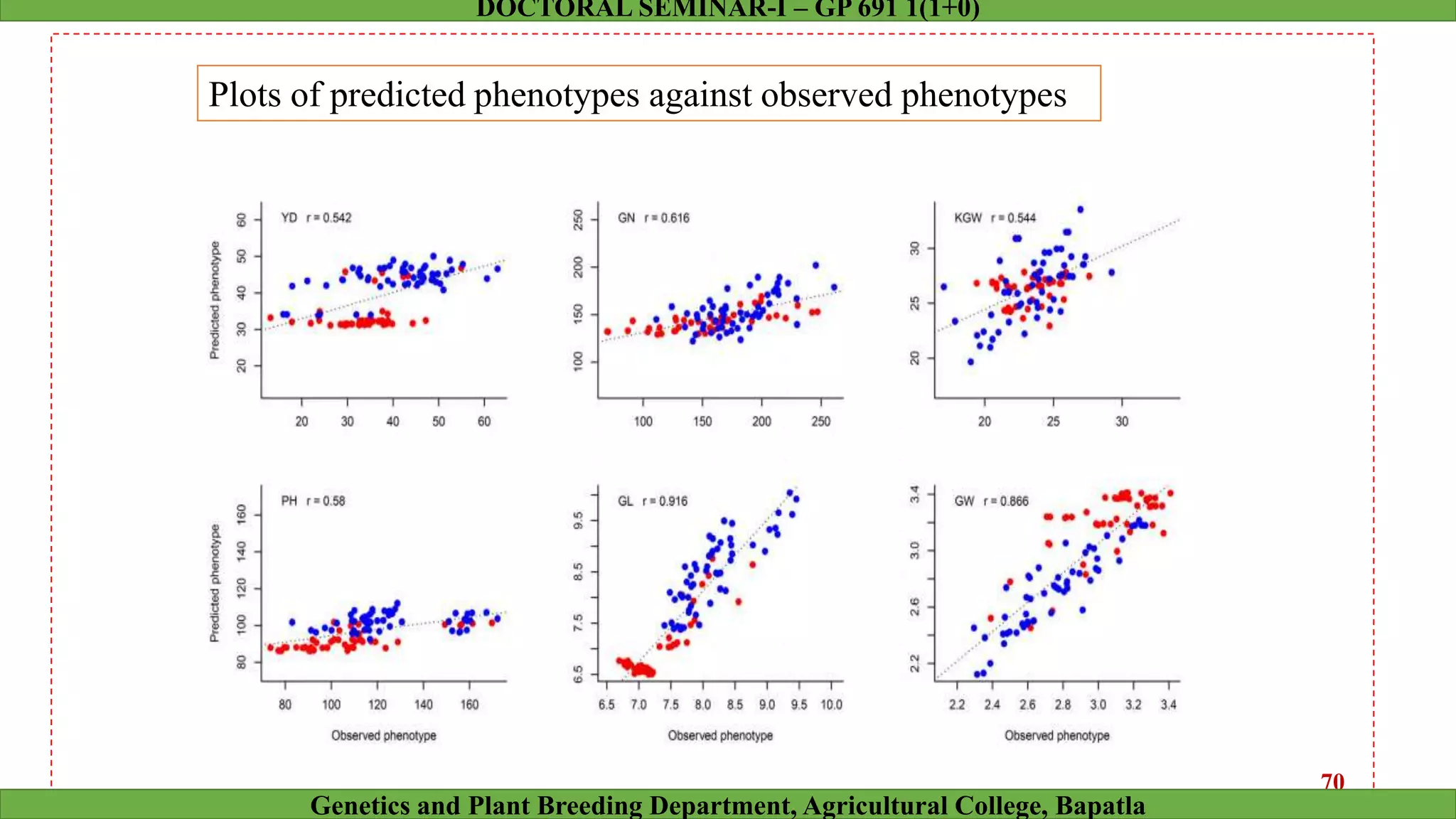
This document discusses genomic selection (GS), a plant and animal breeding technique that uses genome-wide molecular markers to predict and select for an individual's genetic merit or breeding value. GS can accelerate genetic gain compared to traditional breeding by increasing selection intensity and accuracy. Key points covered include: how GS works, factors affecting its accuracy, challenges like genotype-environment interaction, and examples of its successful application in maize and wheat breeding programs.