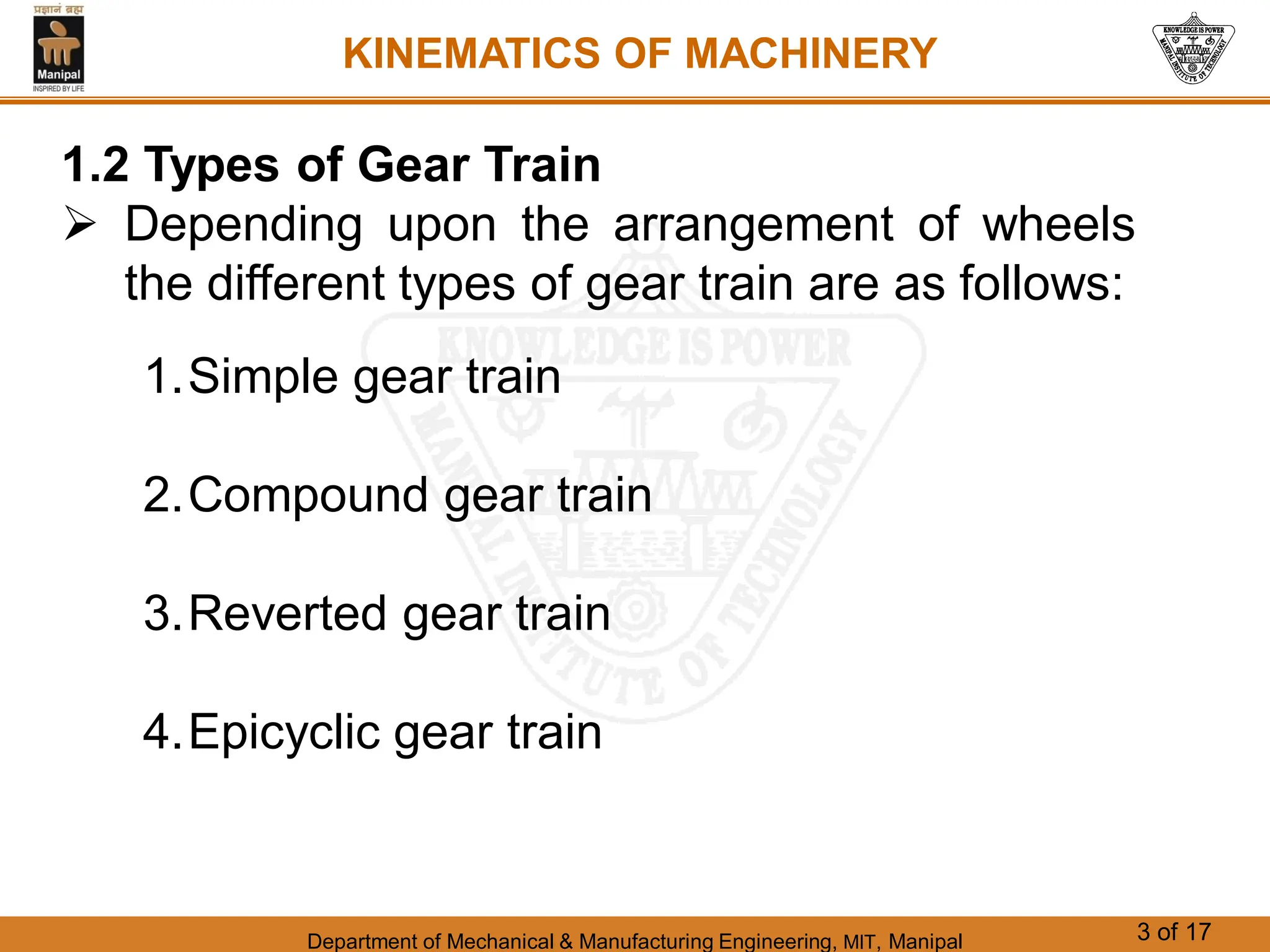
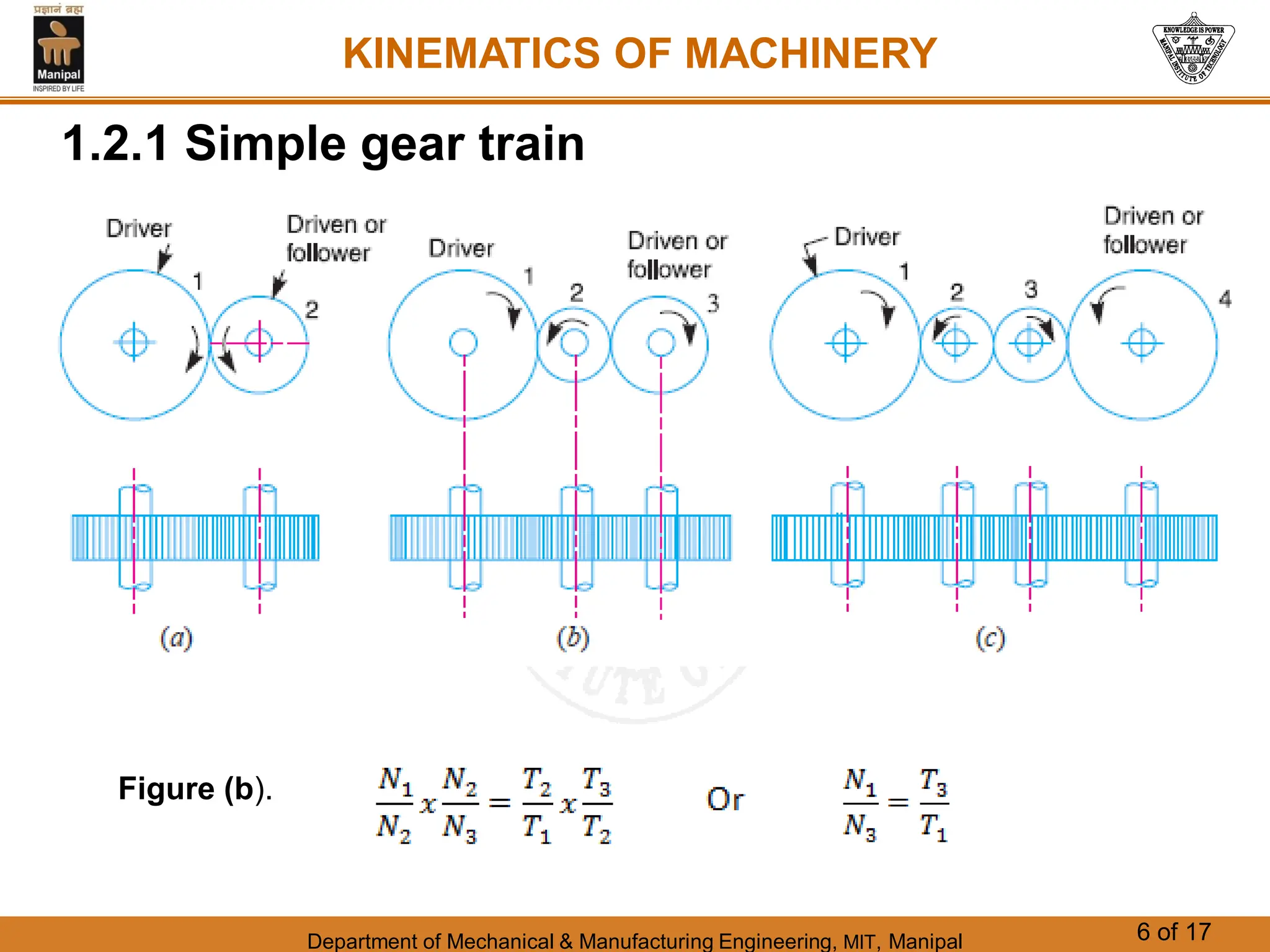
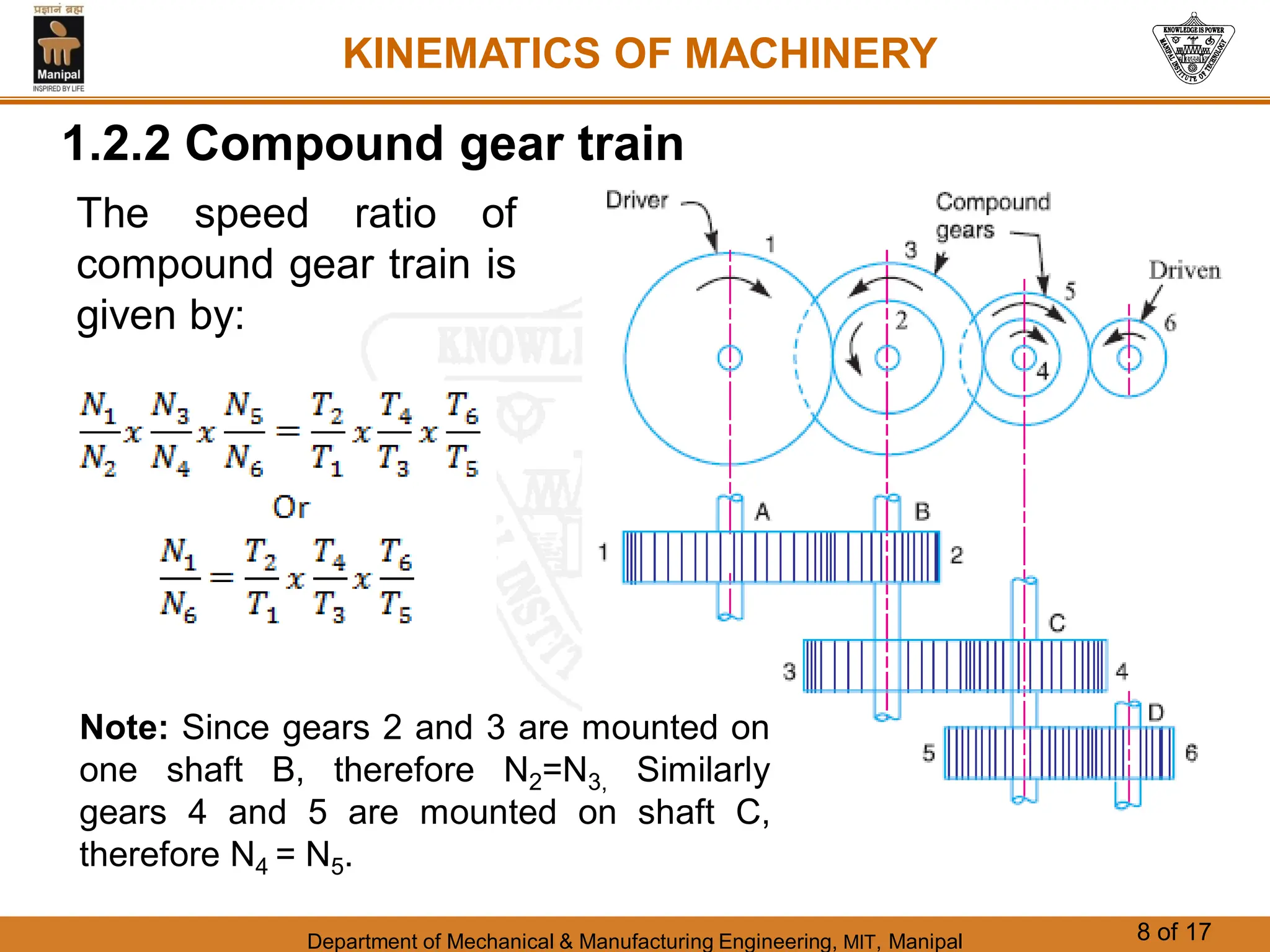
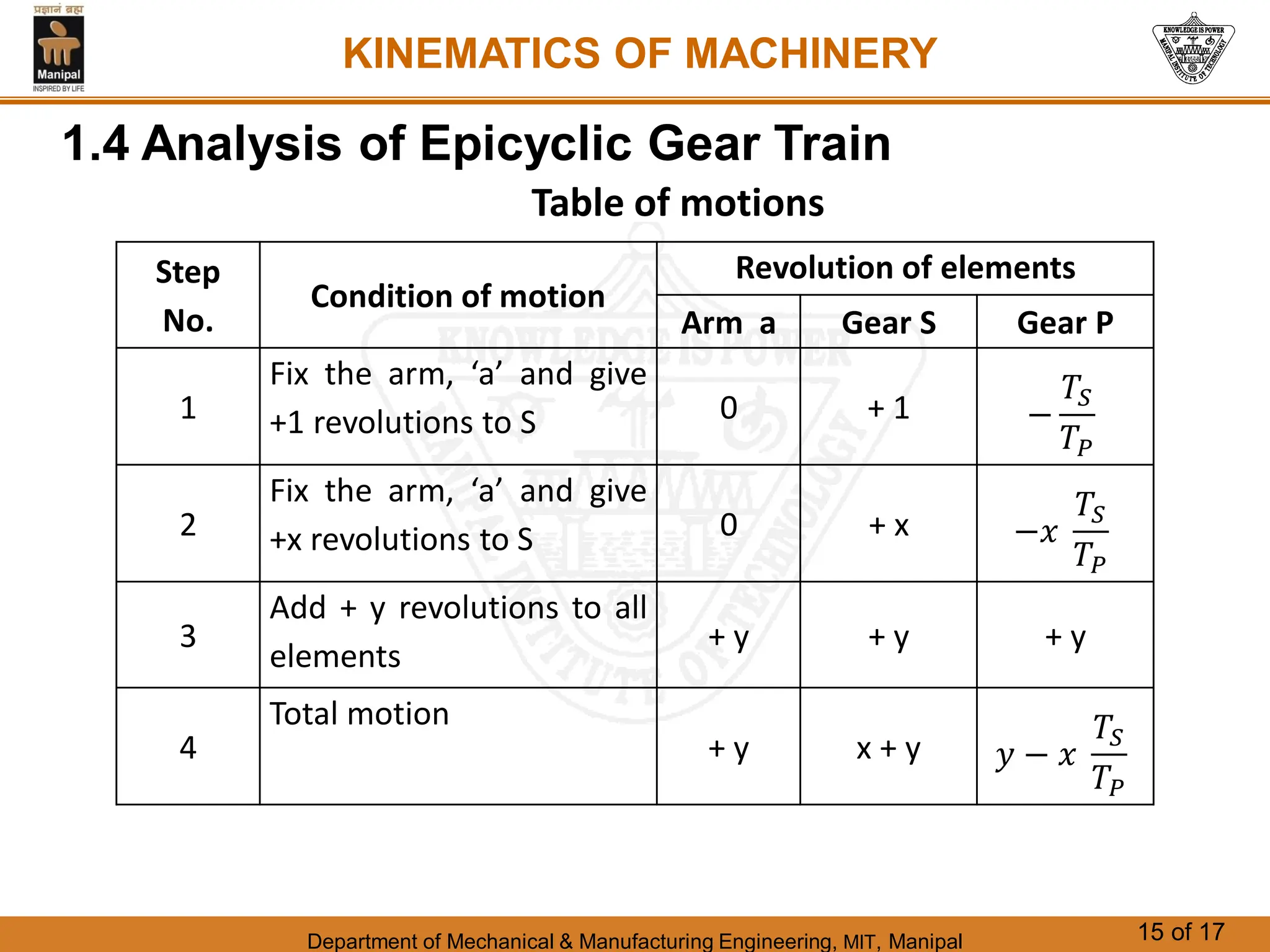
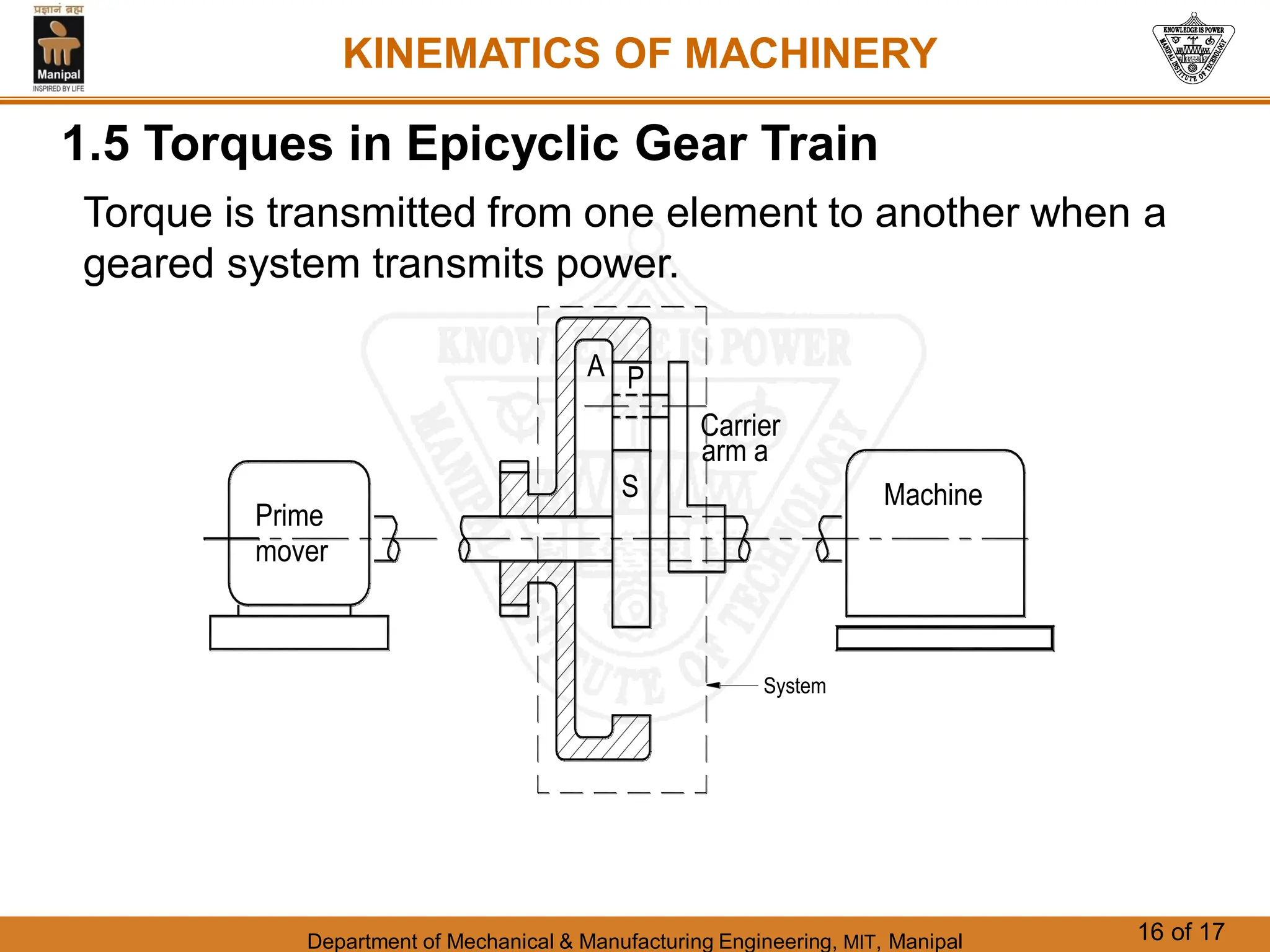
This document discusses different types of gear trains used to transmit power between shafts. It describes simple, compound, reverted, and epicyclic gear trains. Epicyclic gear trains allow for high velocity ratios within a compact space by using gears mounted on shafts that can move relative to a central axis. The document also examines the automobile differential mechanism and methods for analyzing kinematics and torques in epicyclic gear trains.