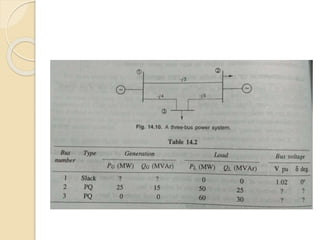
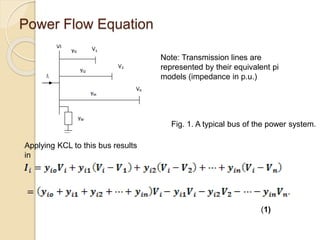
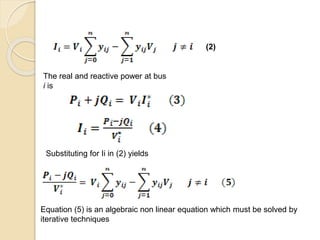
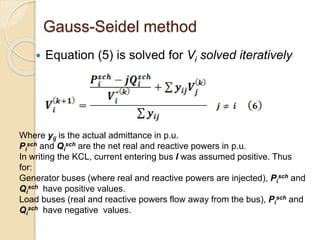
The document discusses load flow studies and the Gauss-Siedel method for solving power flow equations. Load flow studies calculate voltage drops, bus voltages, and power flows under various conditions to determine if voltages remain within limits and equipment is not overloaded. The Gauss-Siedel method iteratively solves power flow equations represented by a non-linear algebraic equation using the bus admittance matrix and known real and reactive power values at buses to calculate unknown bus voltages until converging on a solution. An example applies the Gauss-Siedel method with an acceleration factor to a three bus system to calculate voltages after the first iteration.


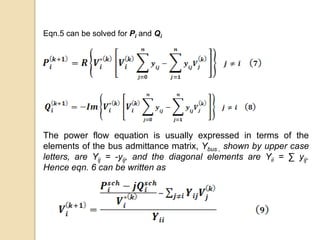
![Iterative steps:
•Slack bus: both components of the voltage are specified. 2(n-1)
equations to be solved iteratively.
• Flat voltage start: initial voltage of 1.0+j0 for unknown voltages.
• PQ buses: Pi and Qi are known. with flat voltage start, Eqn. 9 is solved
for real and imaginary components of Voltage.
•PV buses: Pi
sch and [Vi] are known. Eqn. 11 is solved for Qi
k+1 which is
then substituted in Eqn. 9 to solve for Vi
k+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myslides-170304190200/85/Gauss-Siedel-method-of-Load-Flow-7-320.jpg)