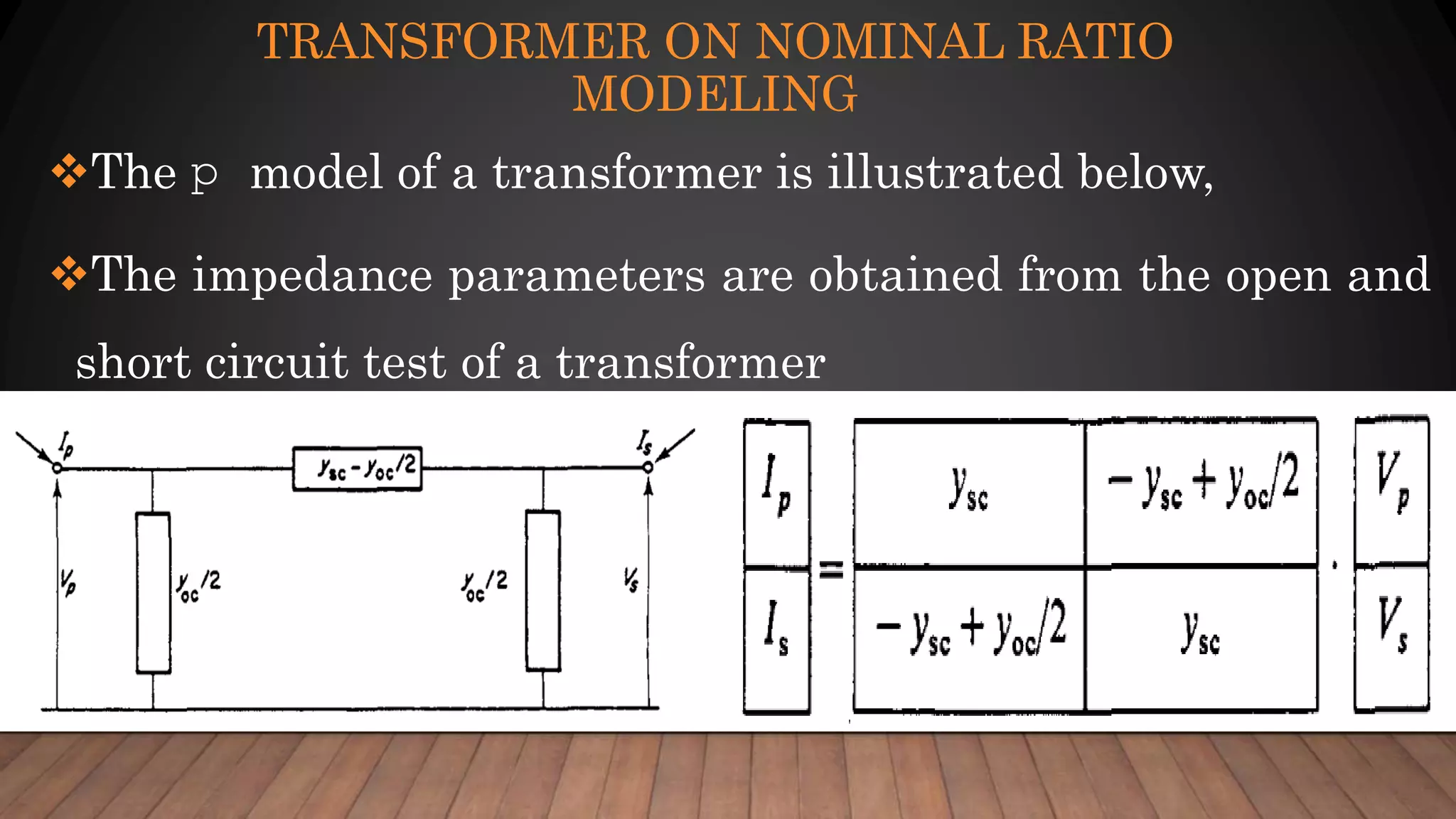
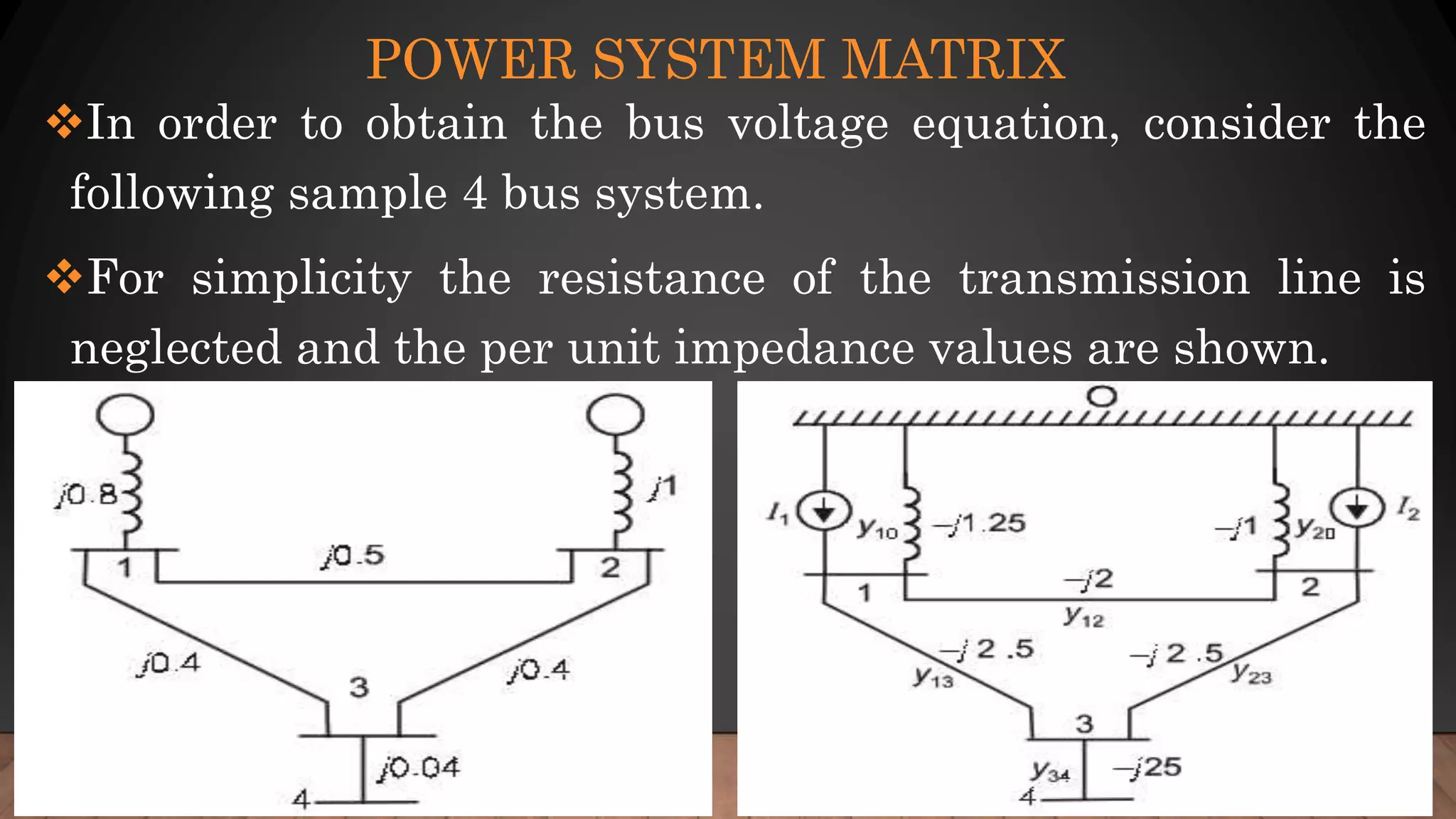
The document discusses load flow analysis necessary for determining the steady-state operating characteristics of power generation and transmission systems. It covers various aspects such as network modeling, transmission line modeling, and the basic nodal method, emphasizing the use of admittance matrices in power system analysis. Additionally, it introduces the decoupled method to handle sensitivity in power mismatch calculations related to voltage and phase angle changes.