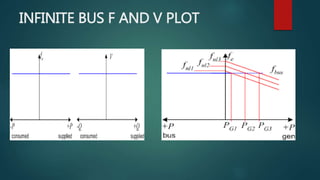
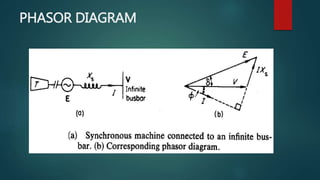
An infinite bus bar maintains constant voltage and frequency despite load variations, functioning like a voltage source with zero impedance. It is exemplified by interconnected alternators where the addition or removal of alternators does not affect system voltage or frequency. Synchronous machines connected to such a bus can be analyzed using phasor diagrams and mathematical expressions for power delivery.