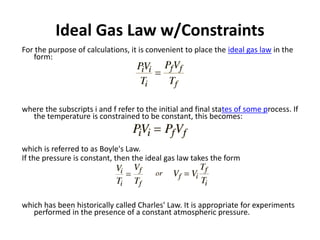
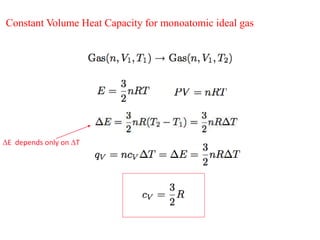
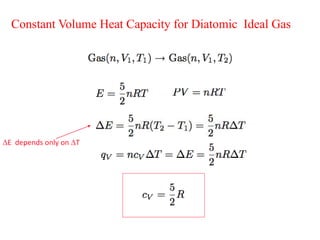
The document discusses gas laws and the ideal gas law. It defines an ideal gas as having perfectly elastic collisions between molecules with no intermolecular forces. The ideal gas law relates pressure, volume, amount of gas, and temperature. It also discusses:
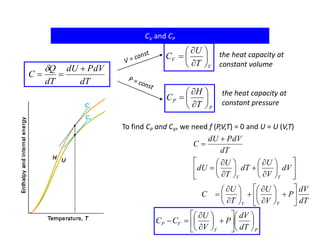
- Constant volume heat capacity (CV) which is the heat required to change temperature with constant volume
- Constant pressure heat capacity (CP) which is the heat required to change temperature with constant pressure
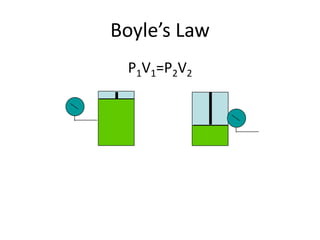
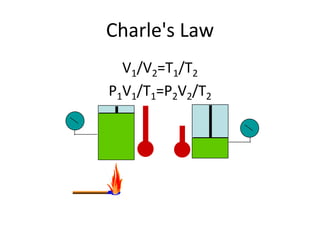
- Derivations of Boyle's law (inverse relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature) and Charles' law (direct relationship between volume and temperature at constant pressure) from the ideal gas law
- Heat capacities of monoatomic and diatomic ideal gases depend only on