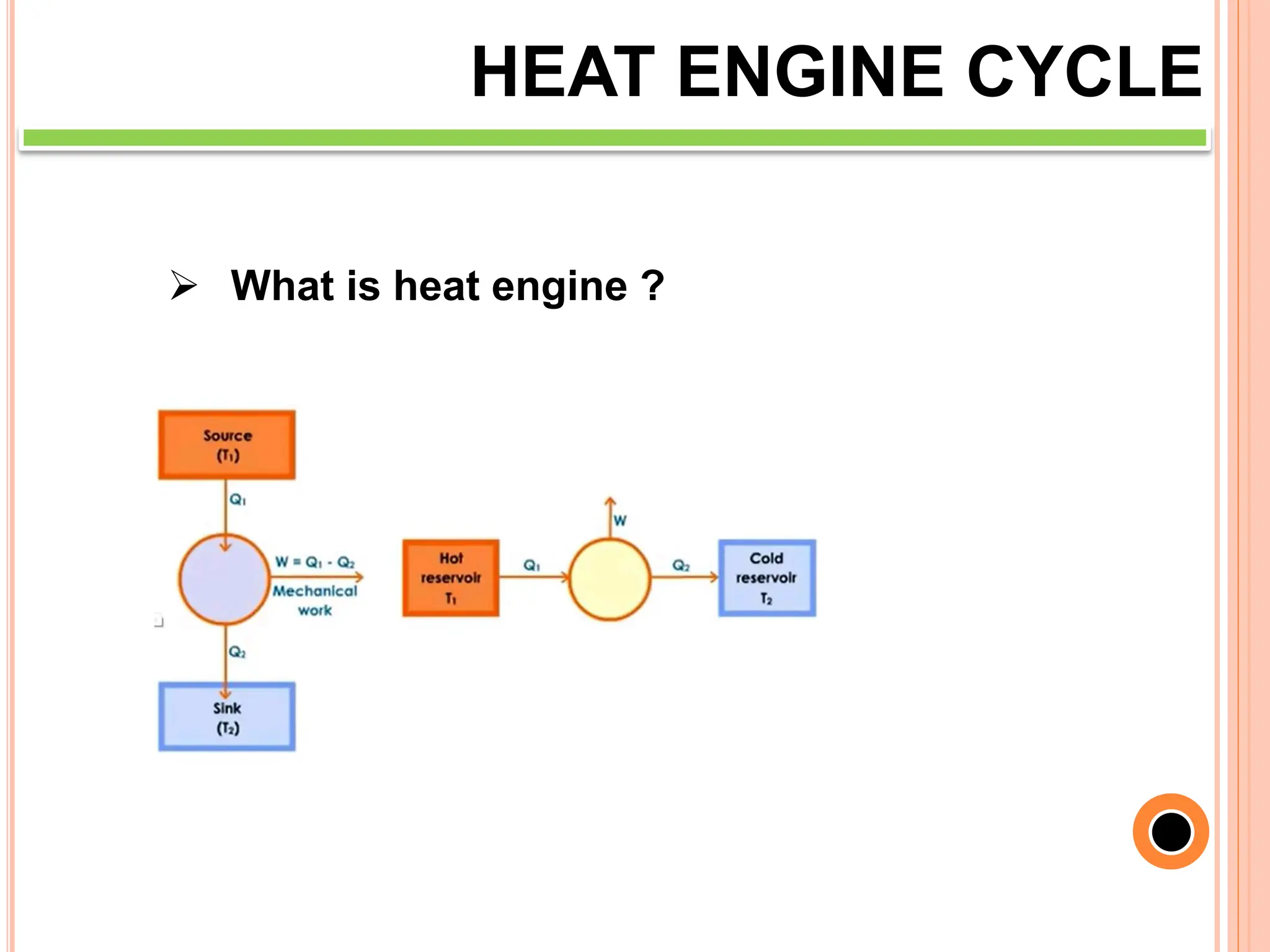
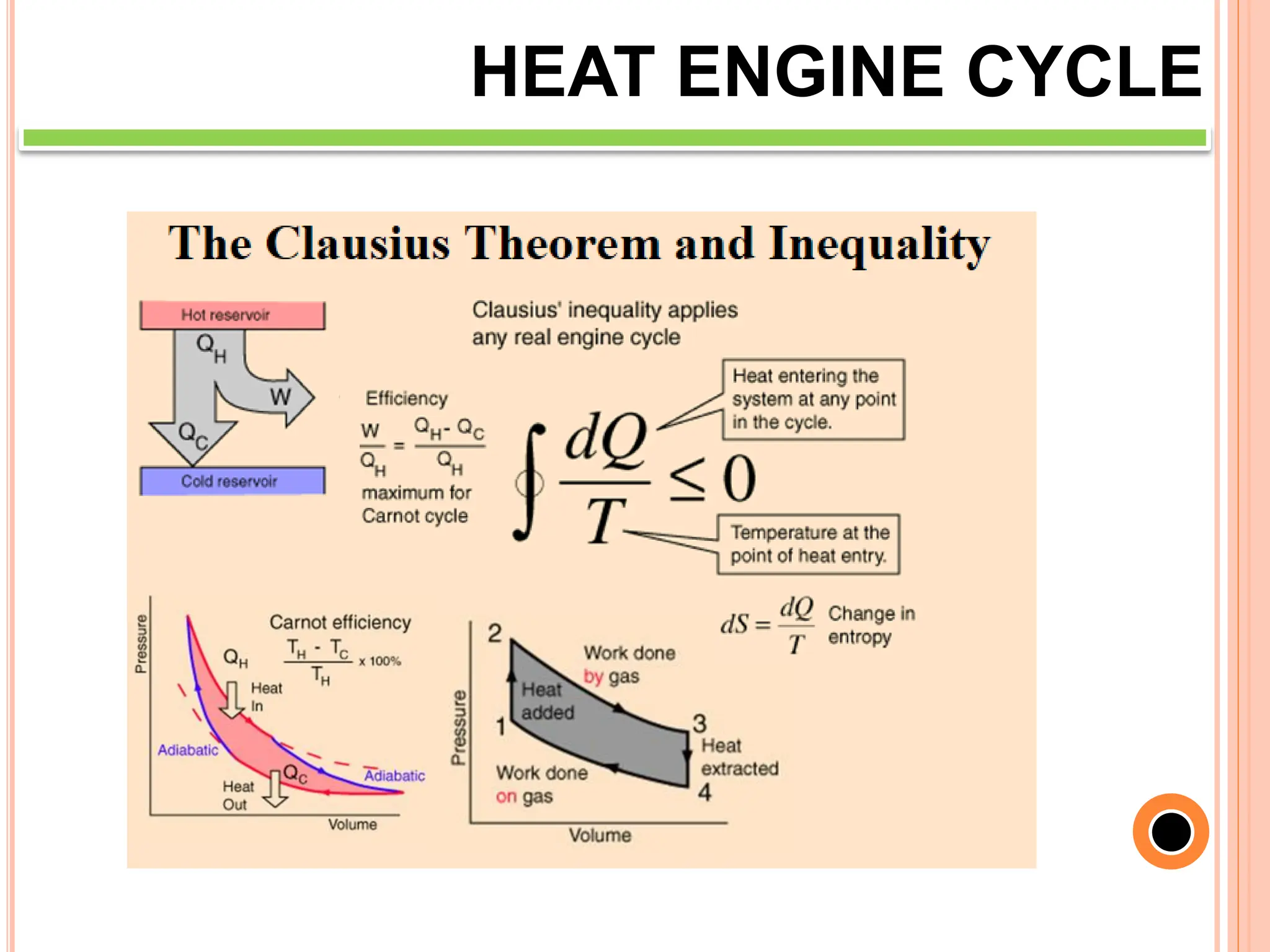
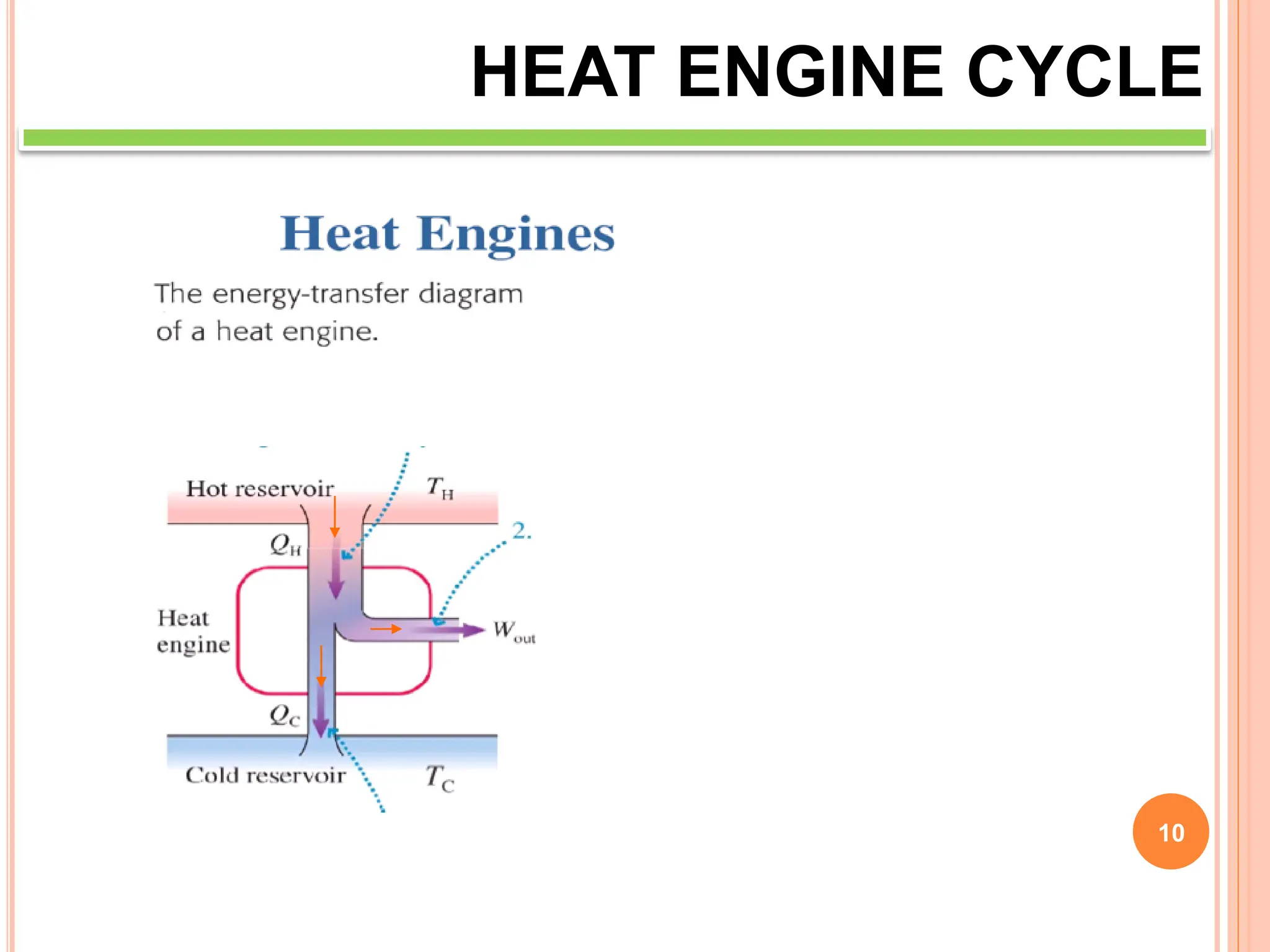
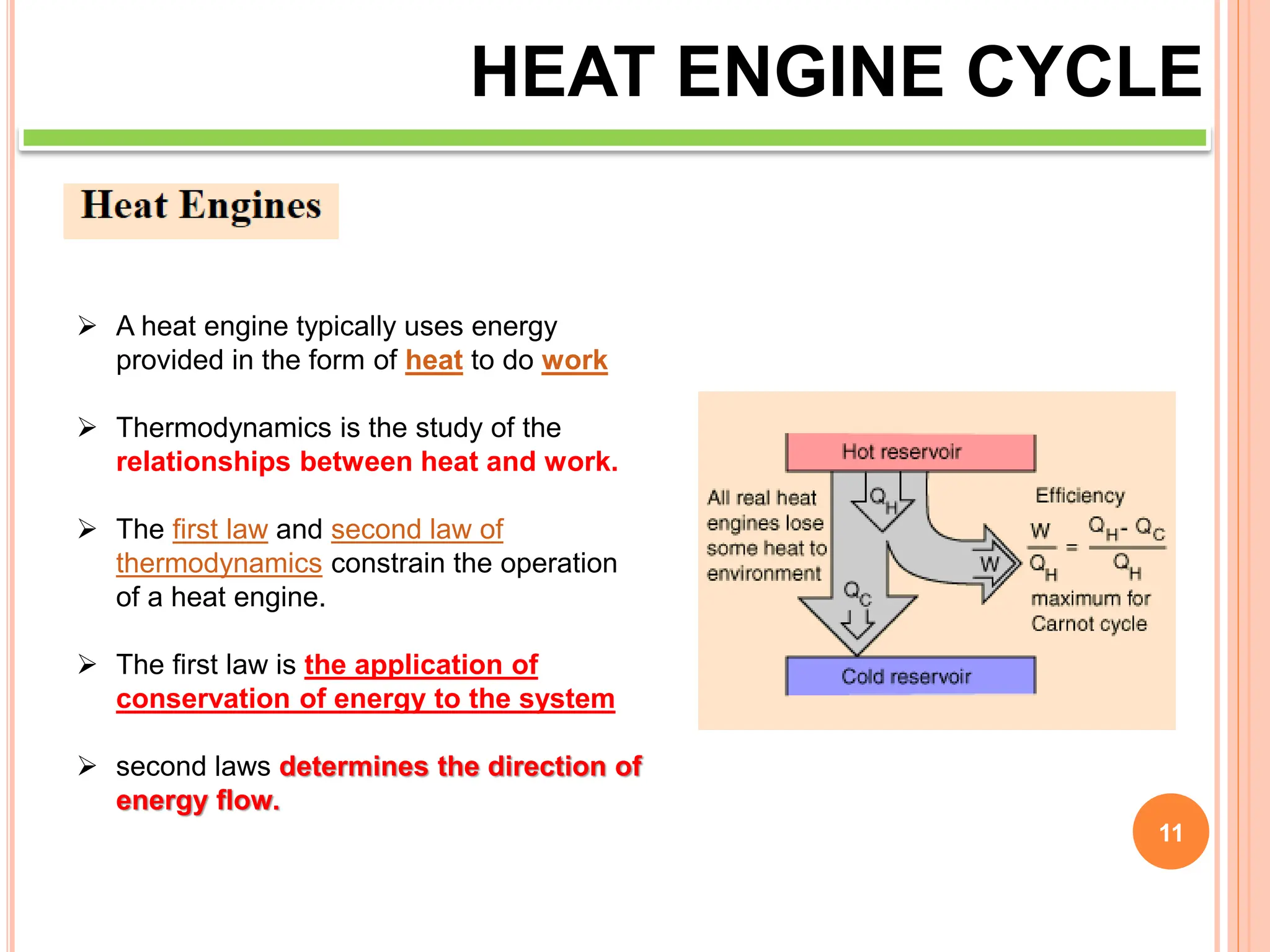
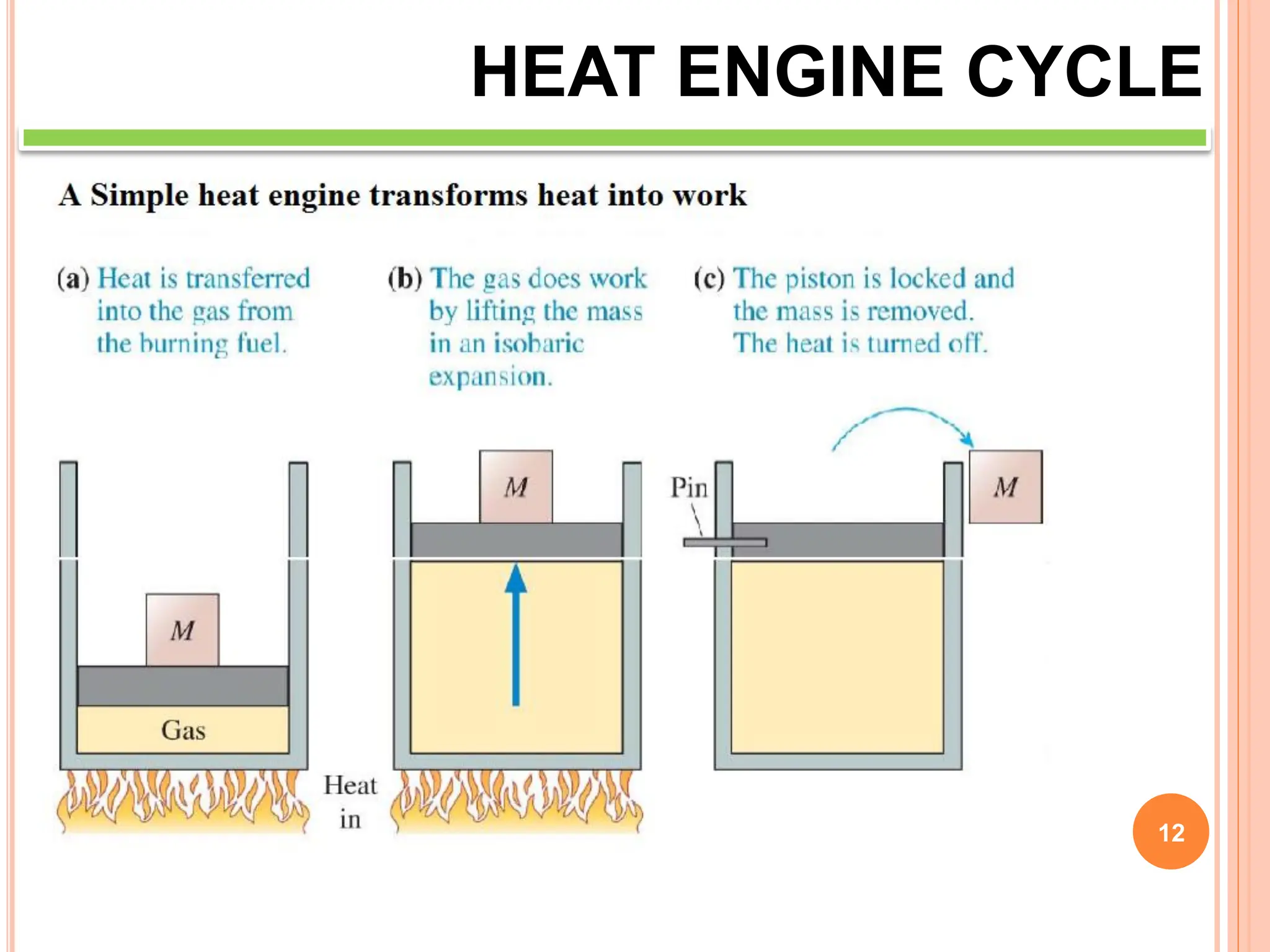
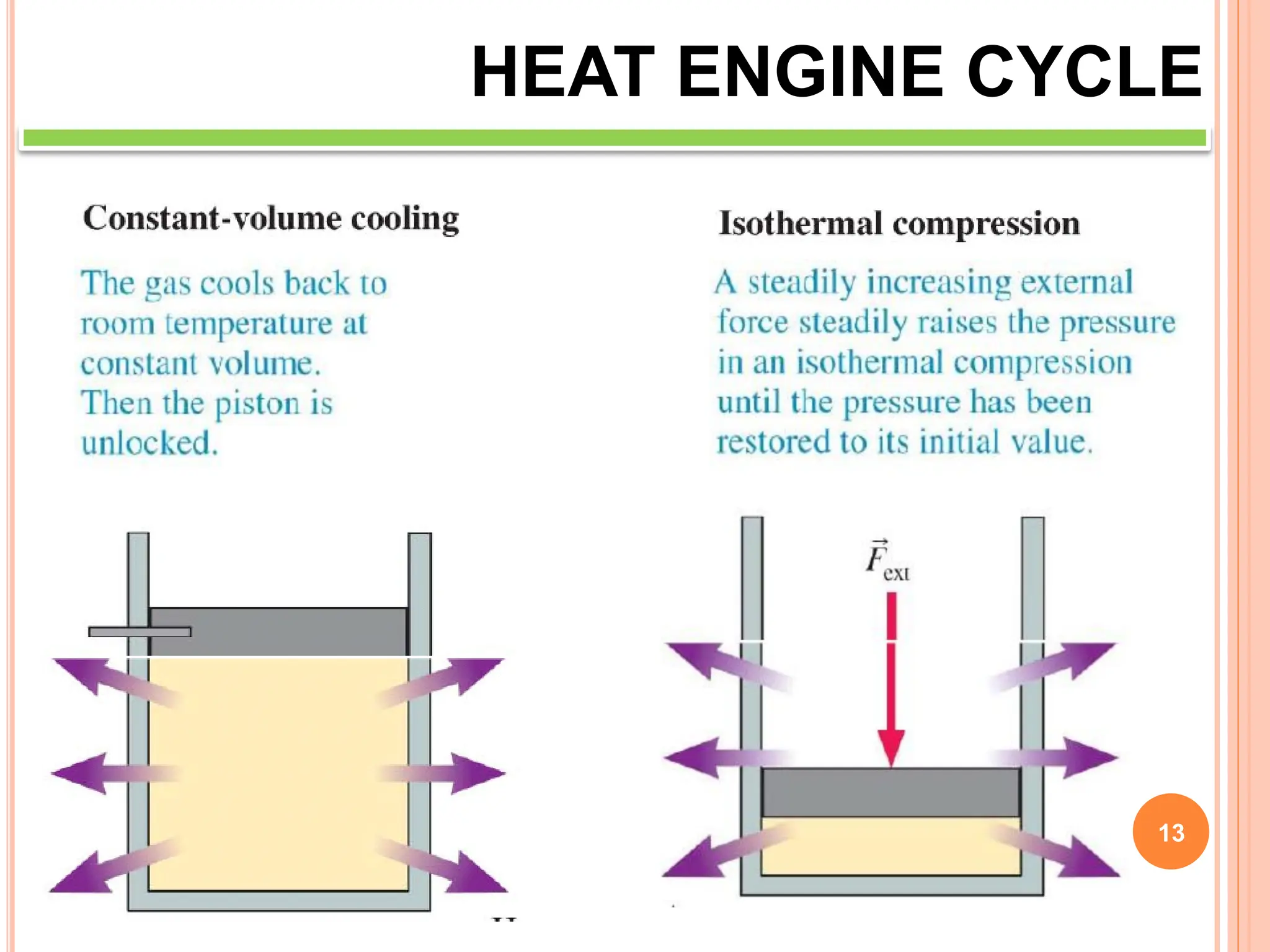
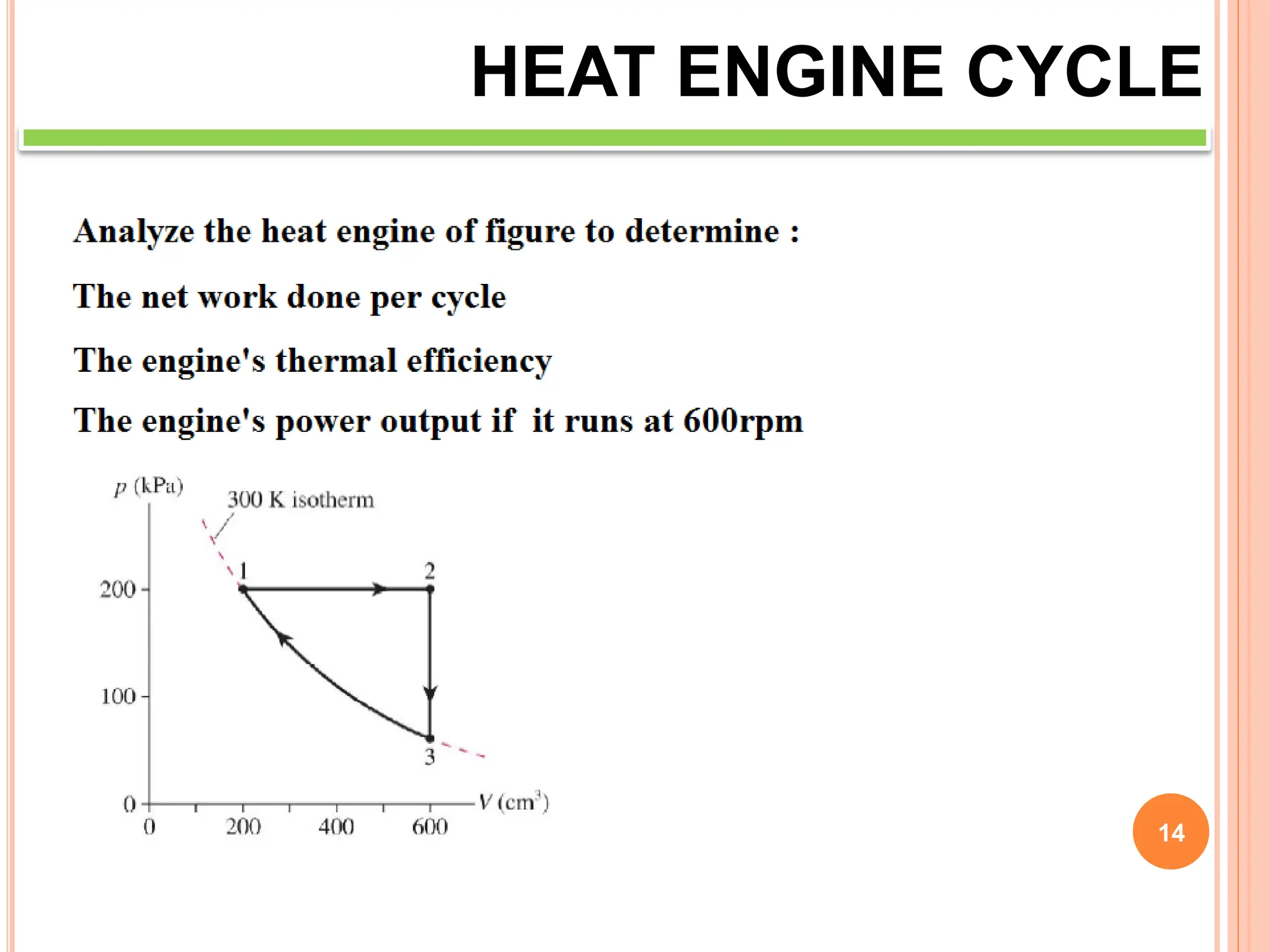
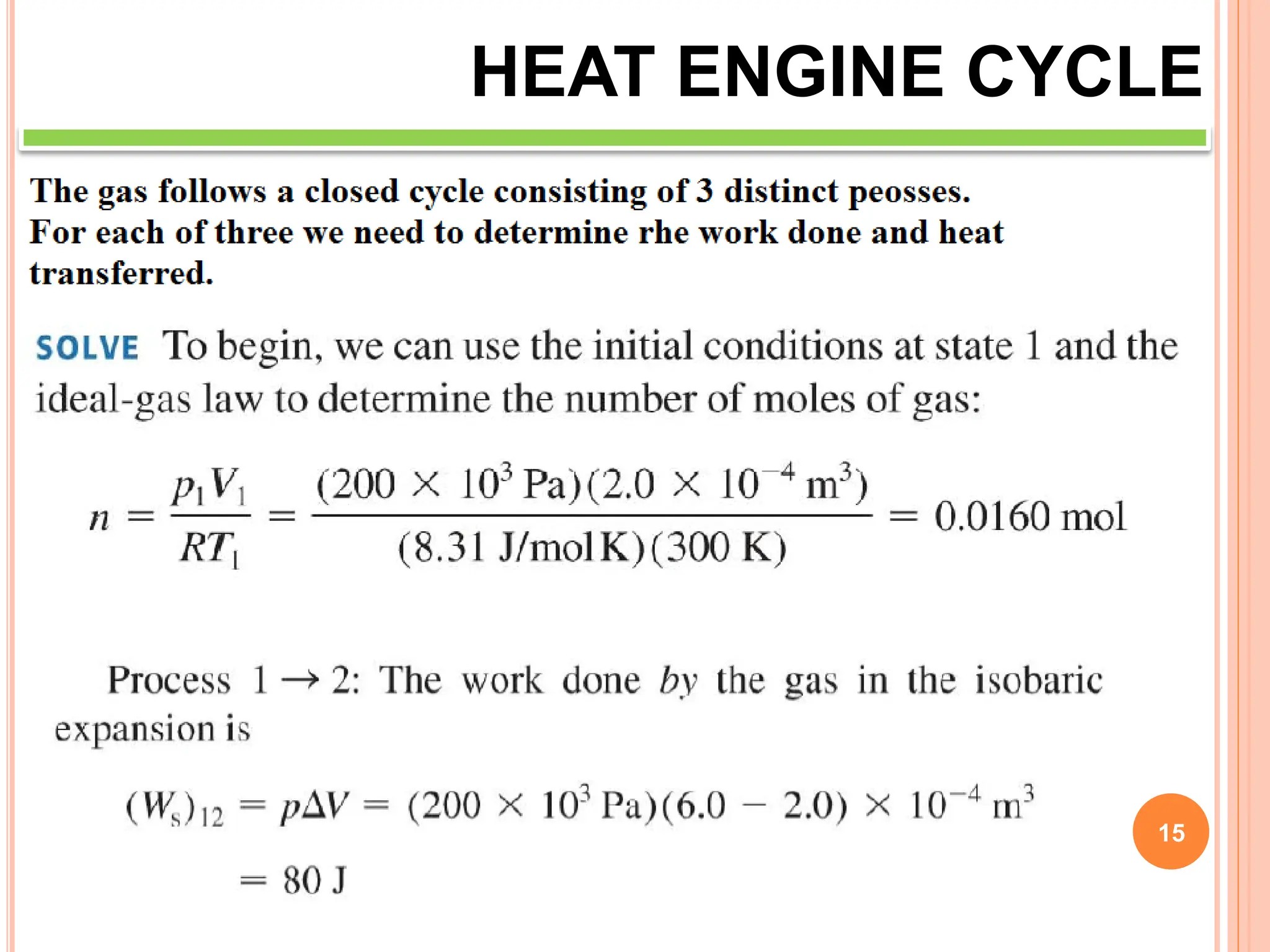
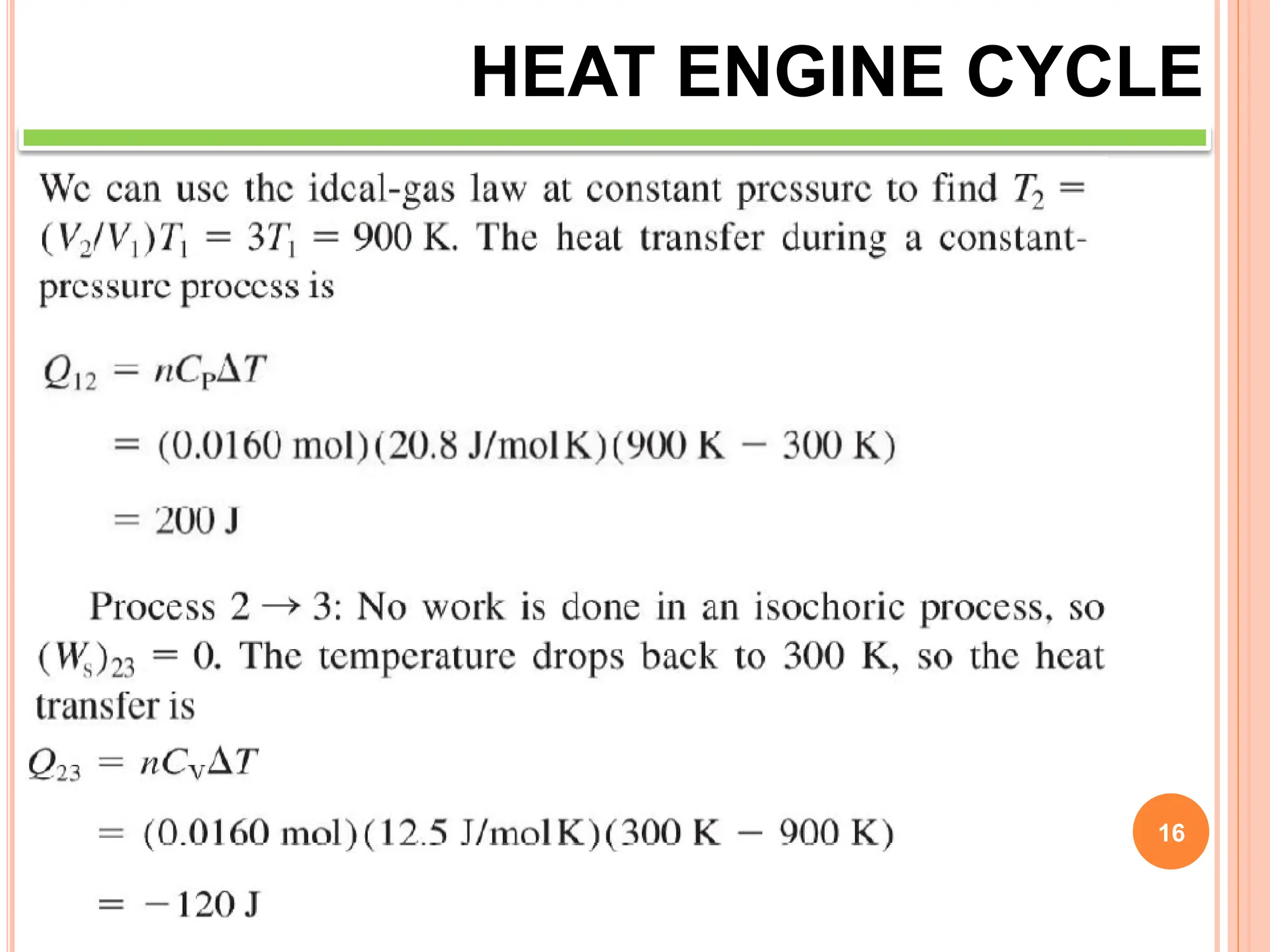
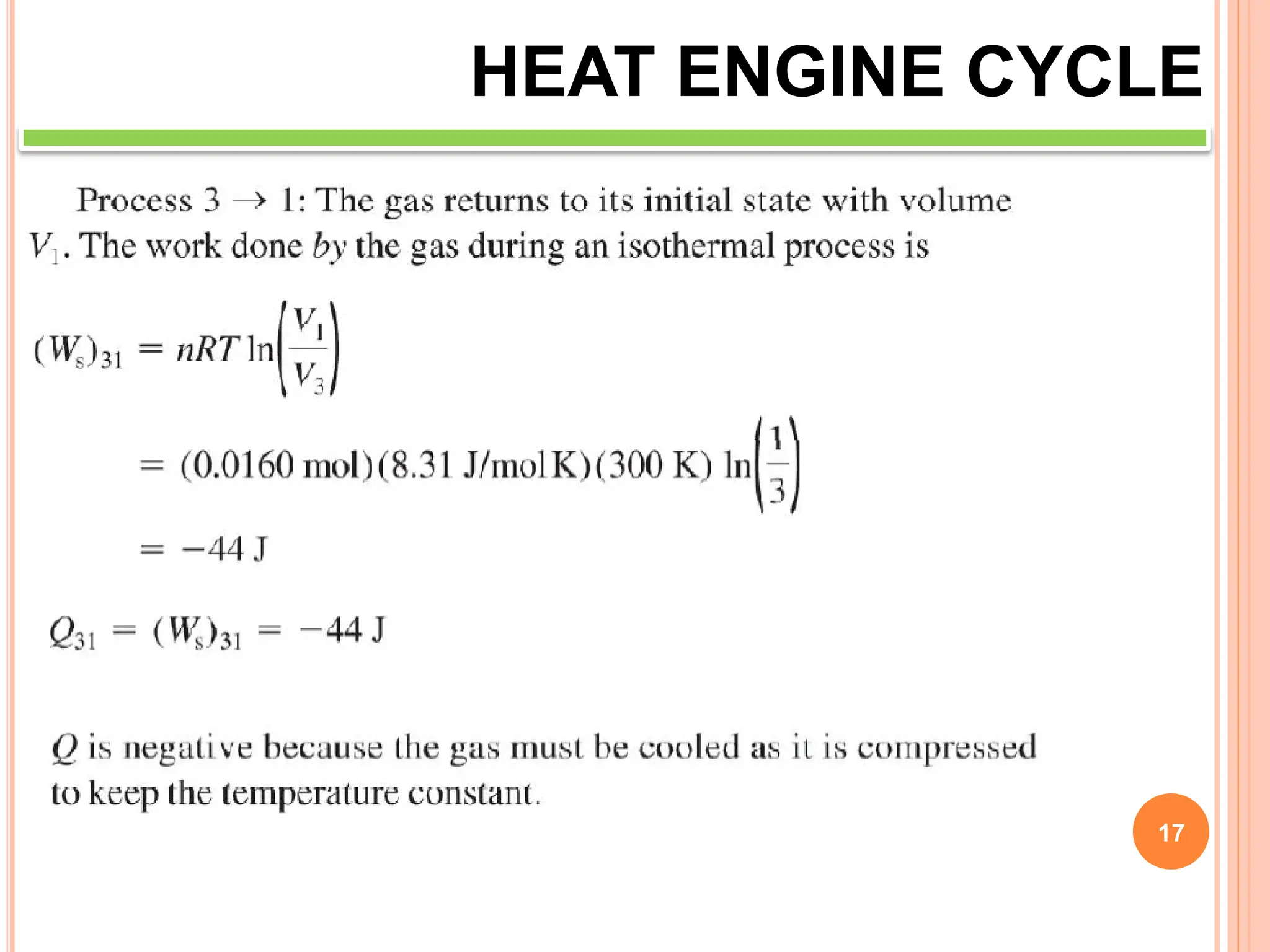
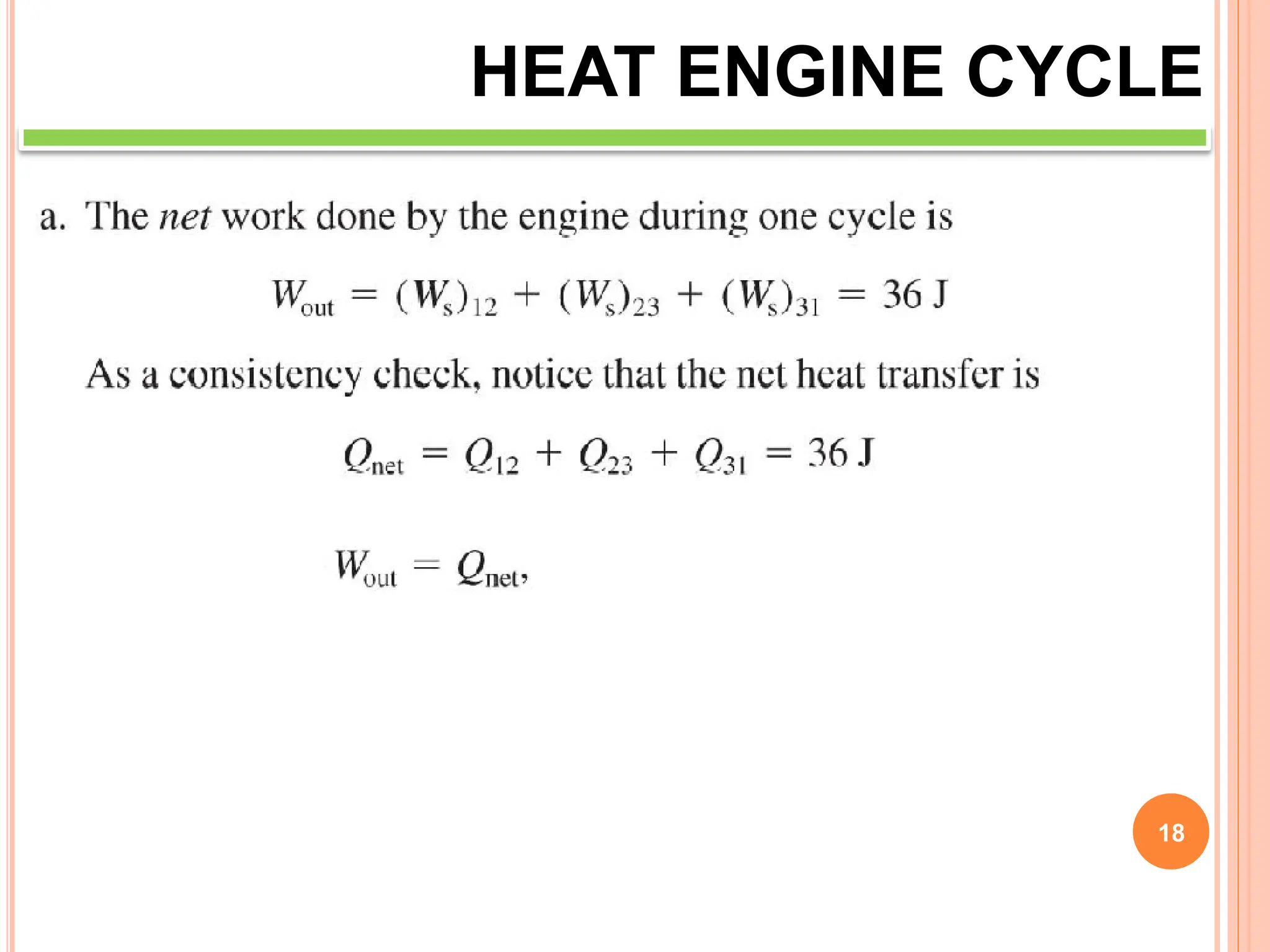
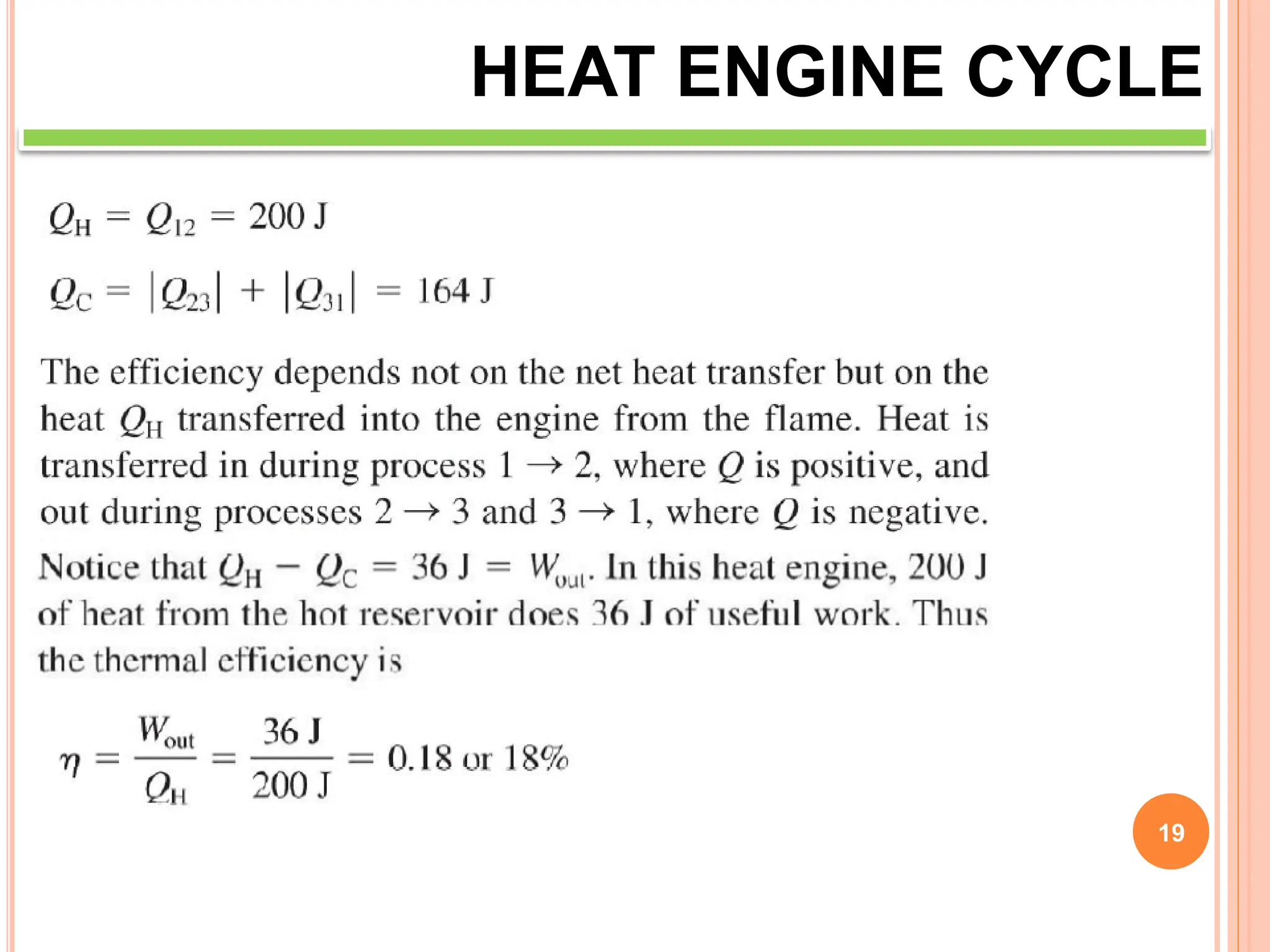
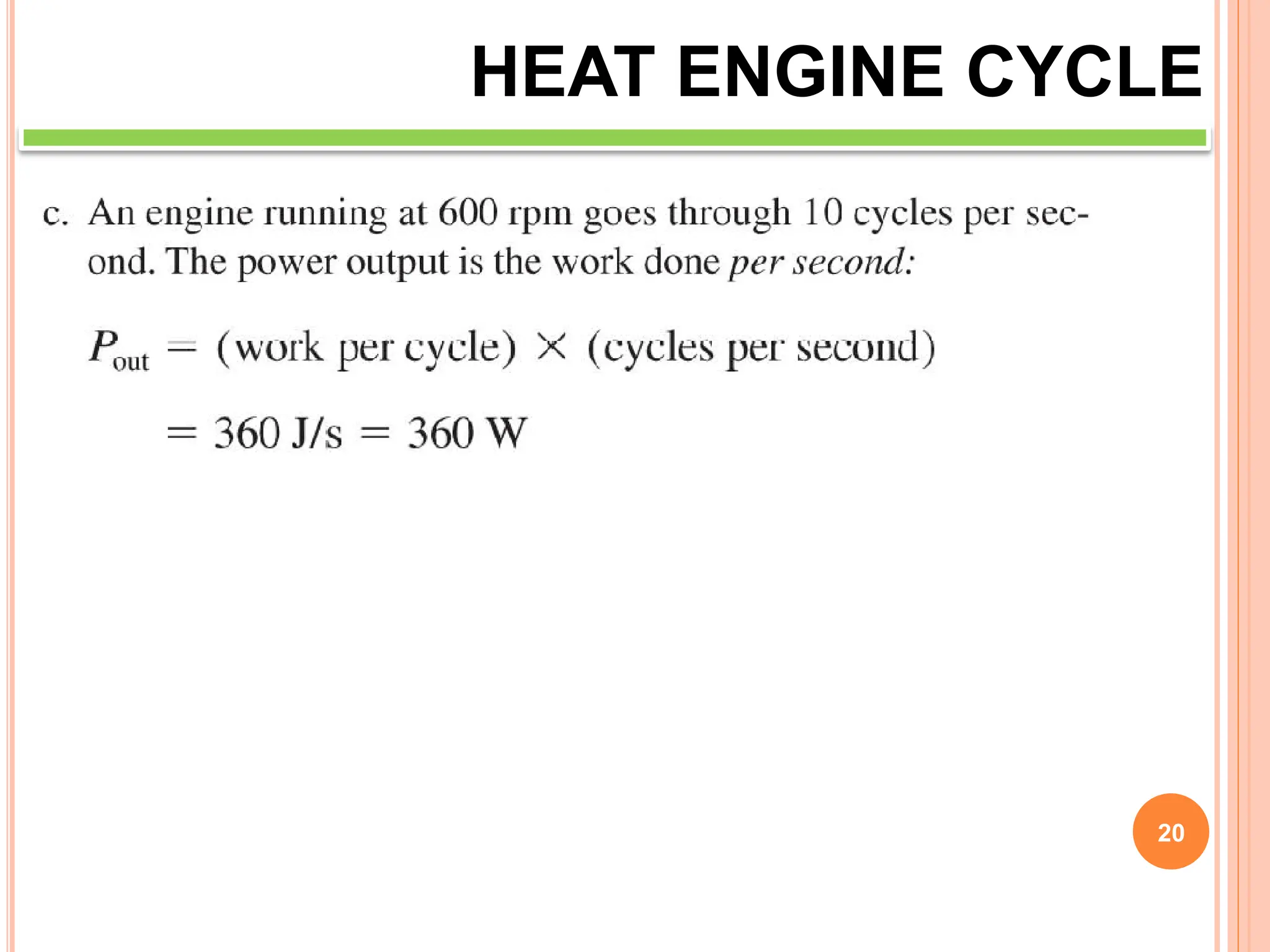
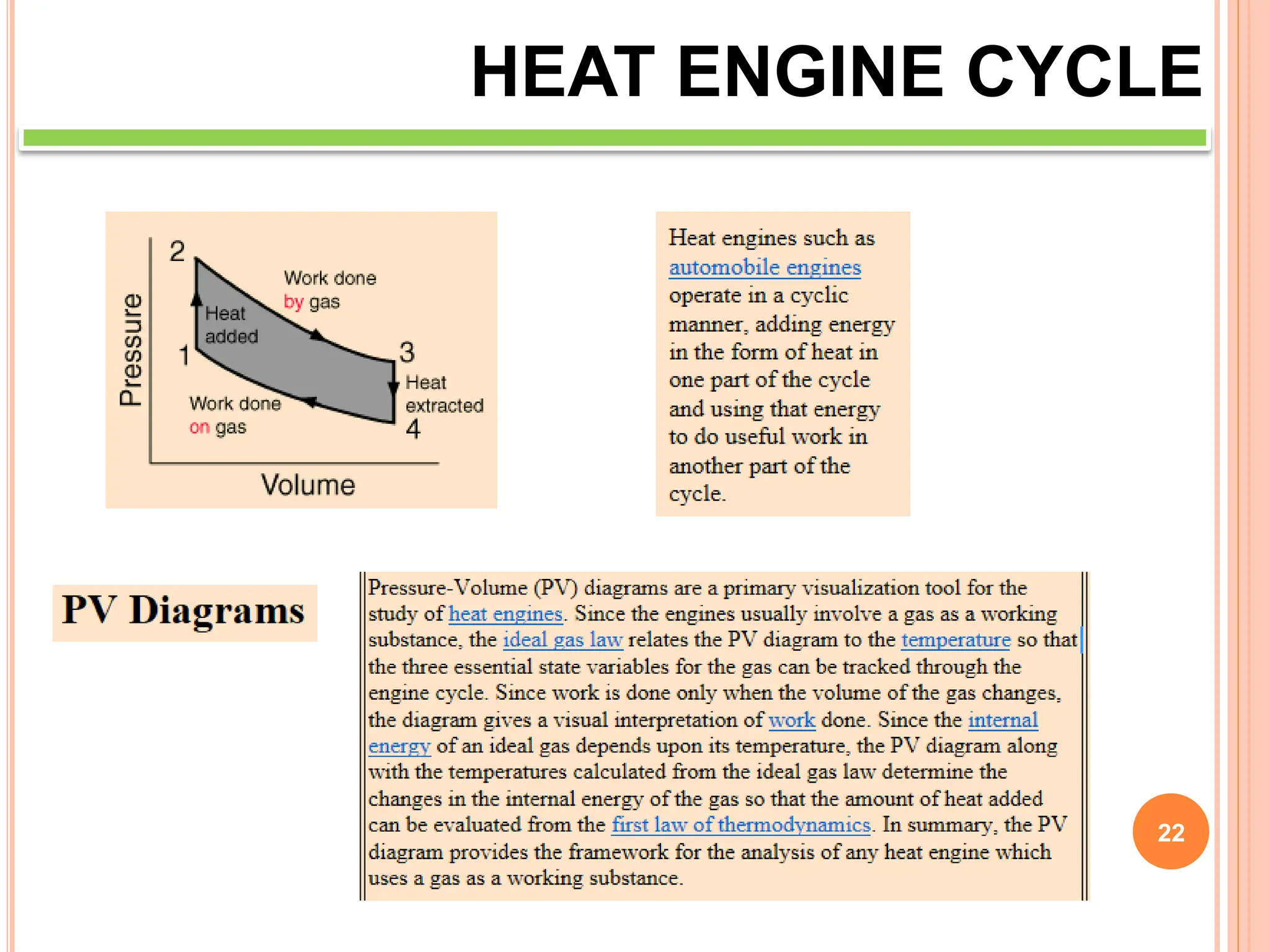
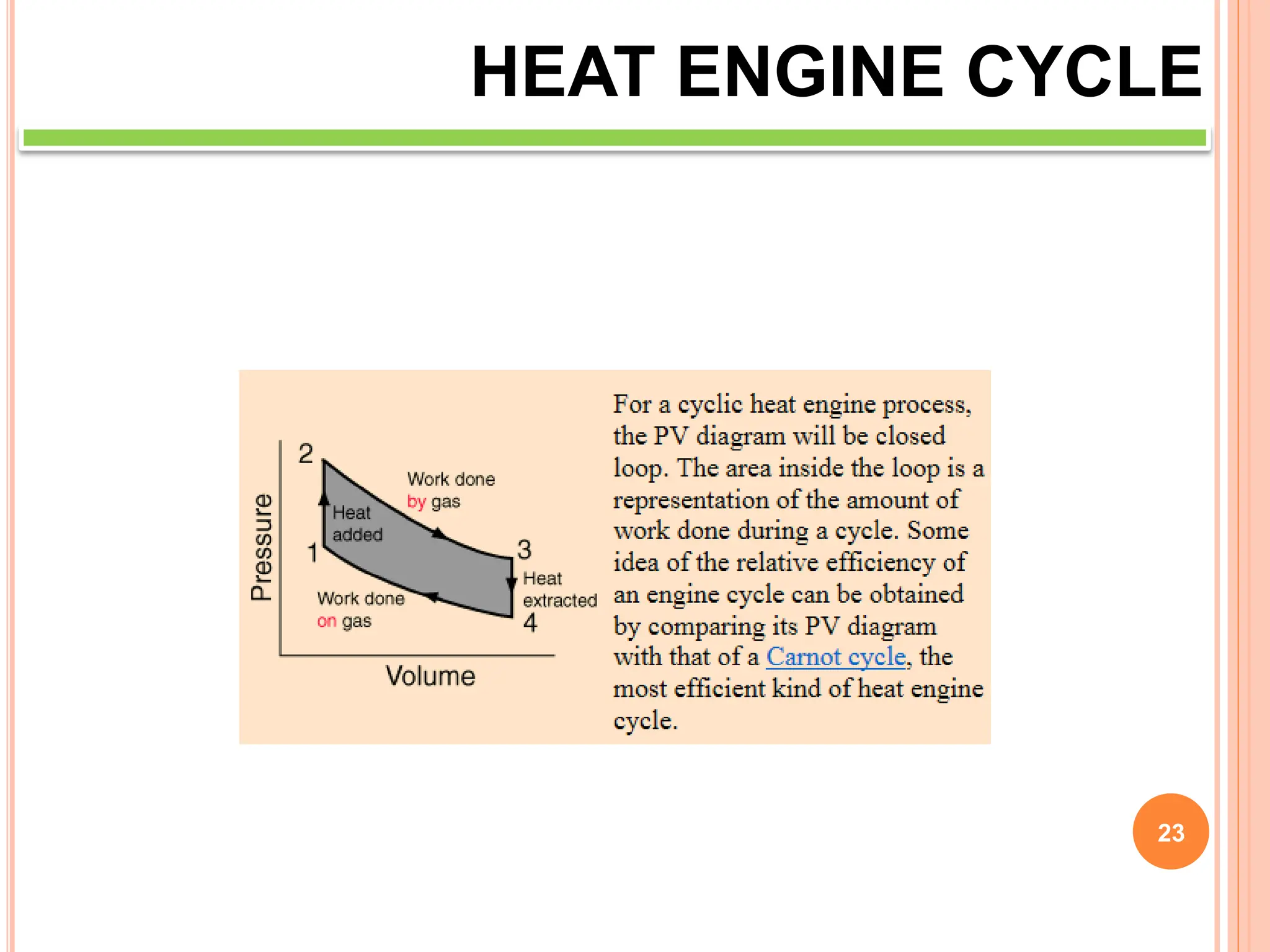
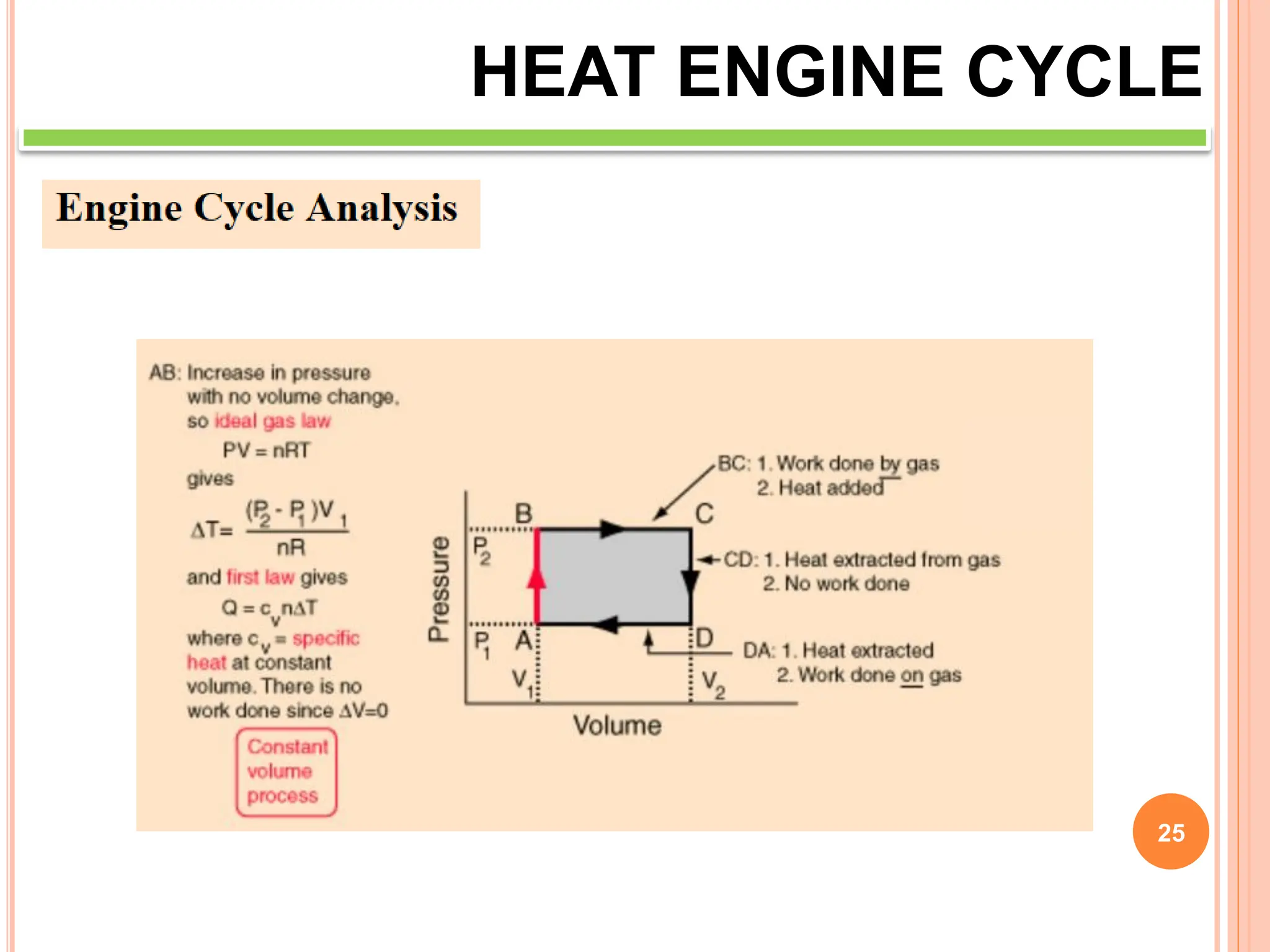
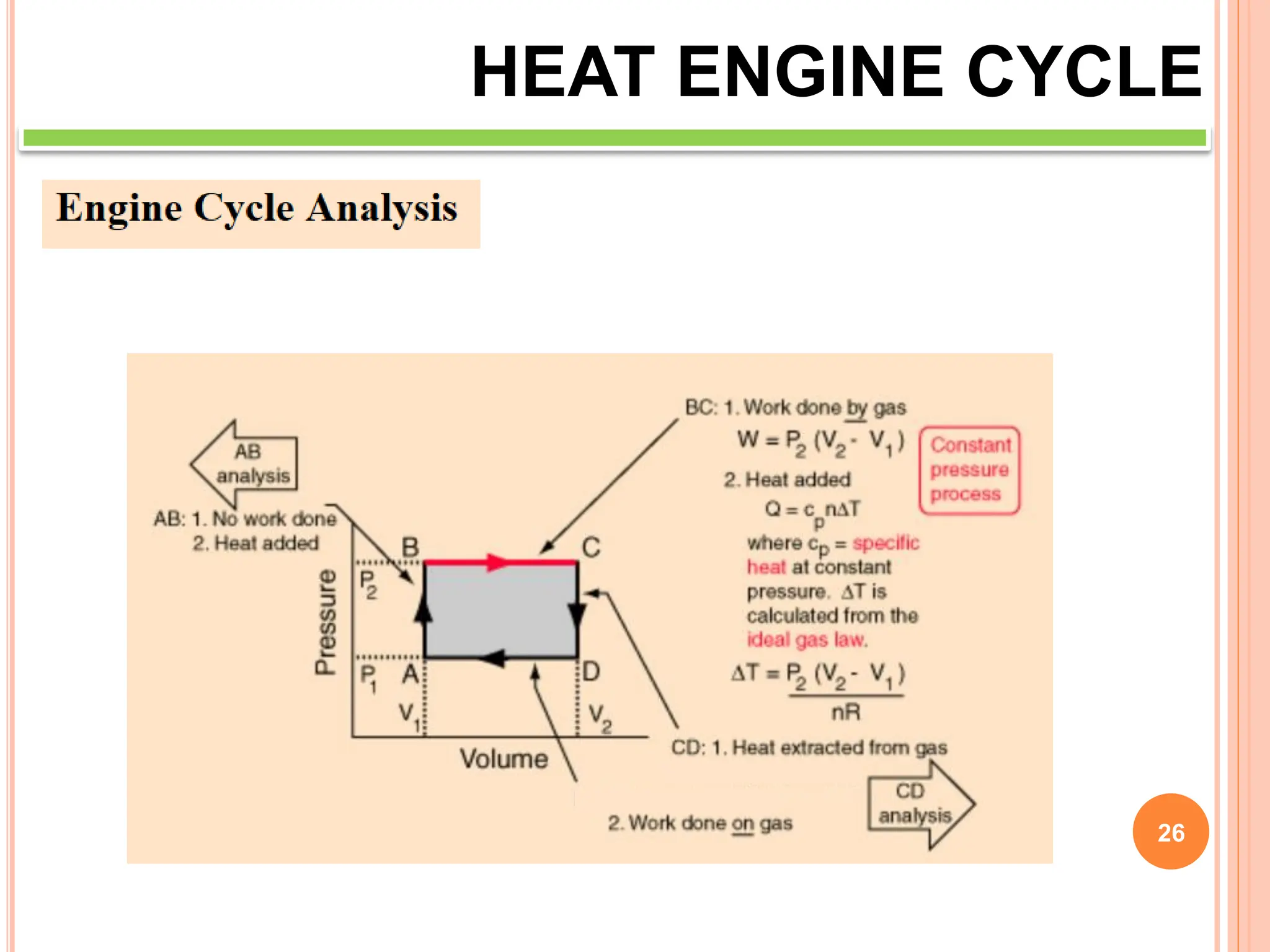
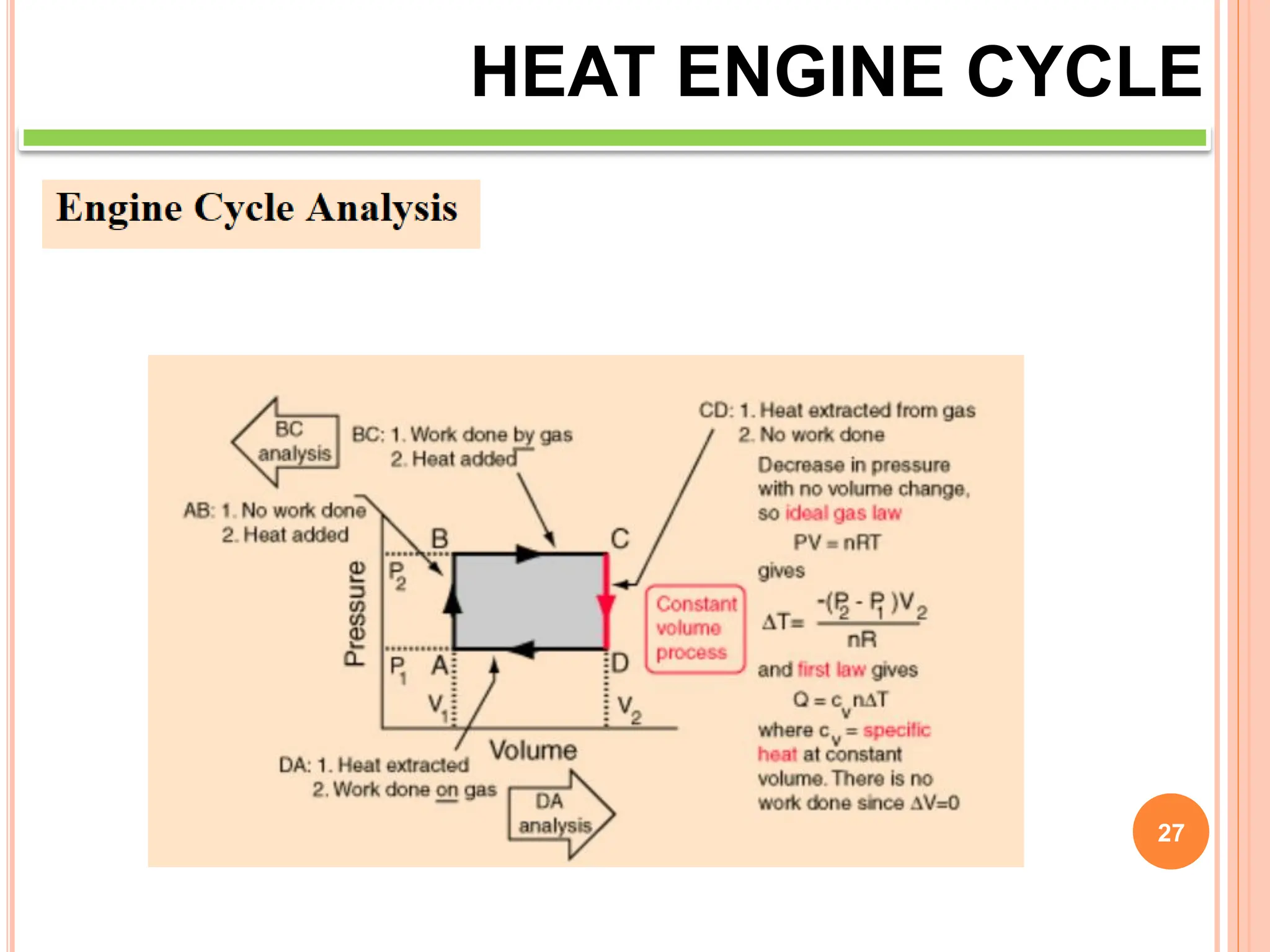
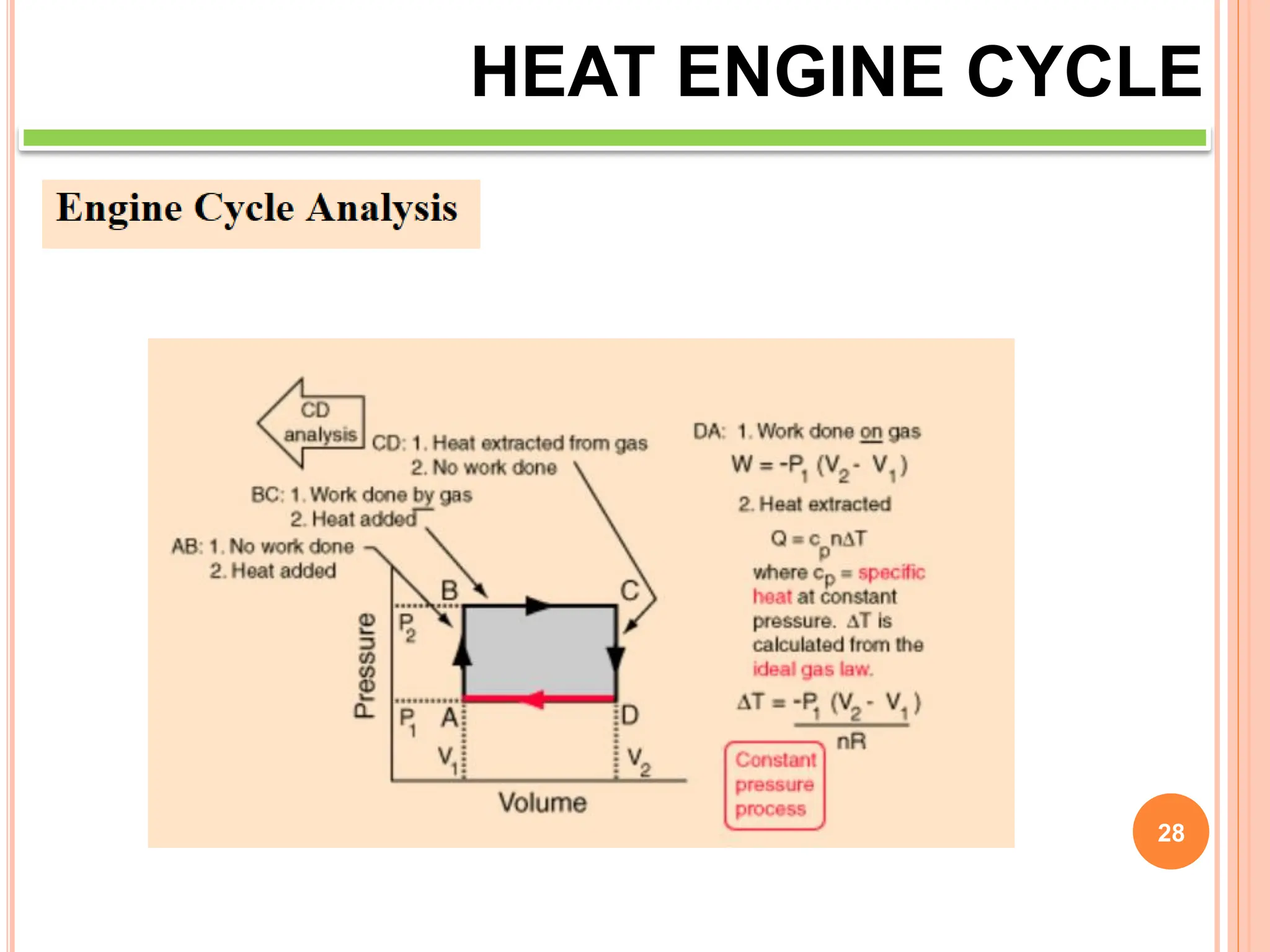
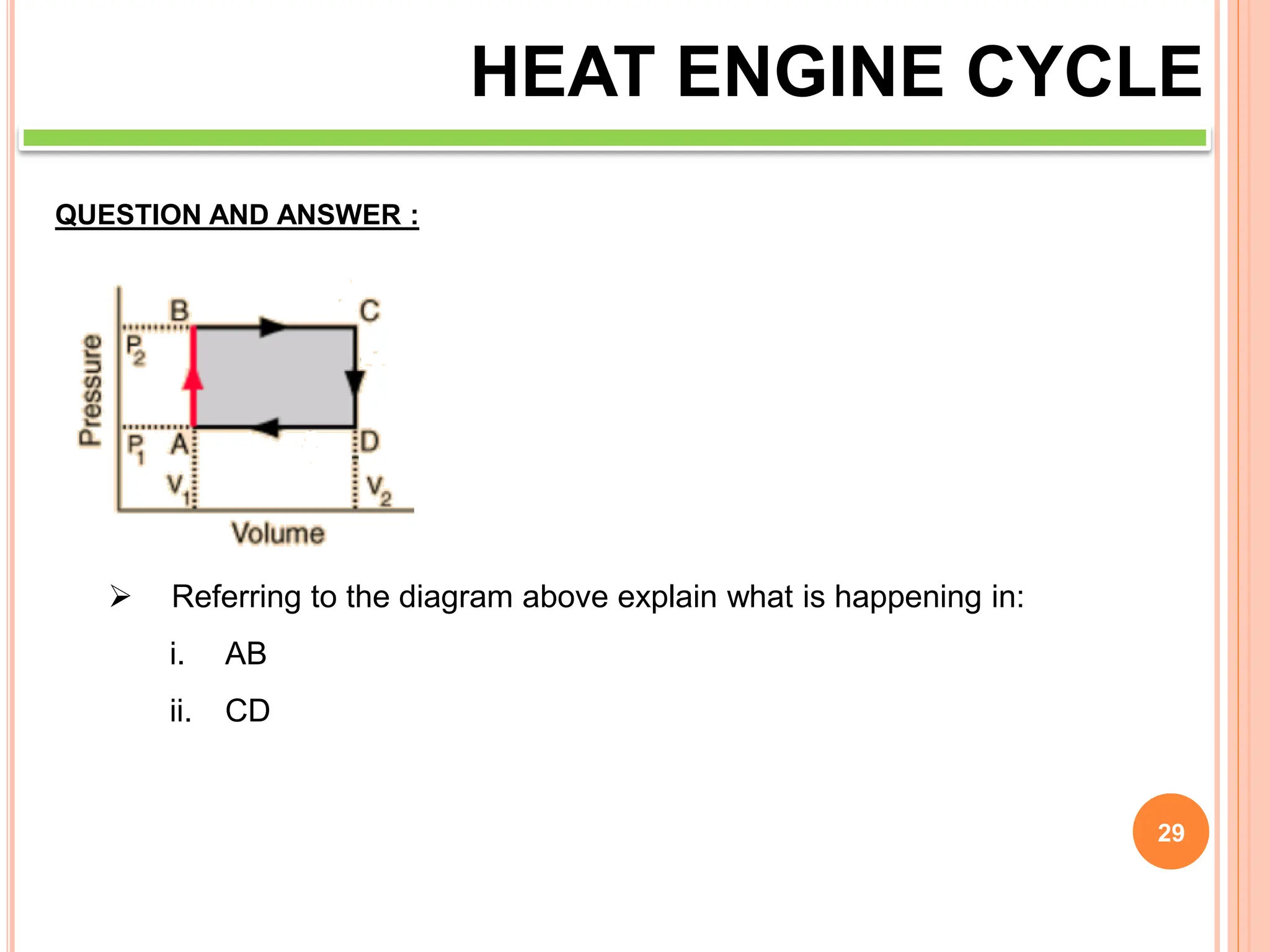
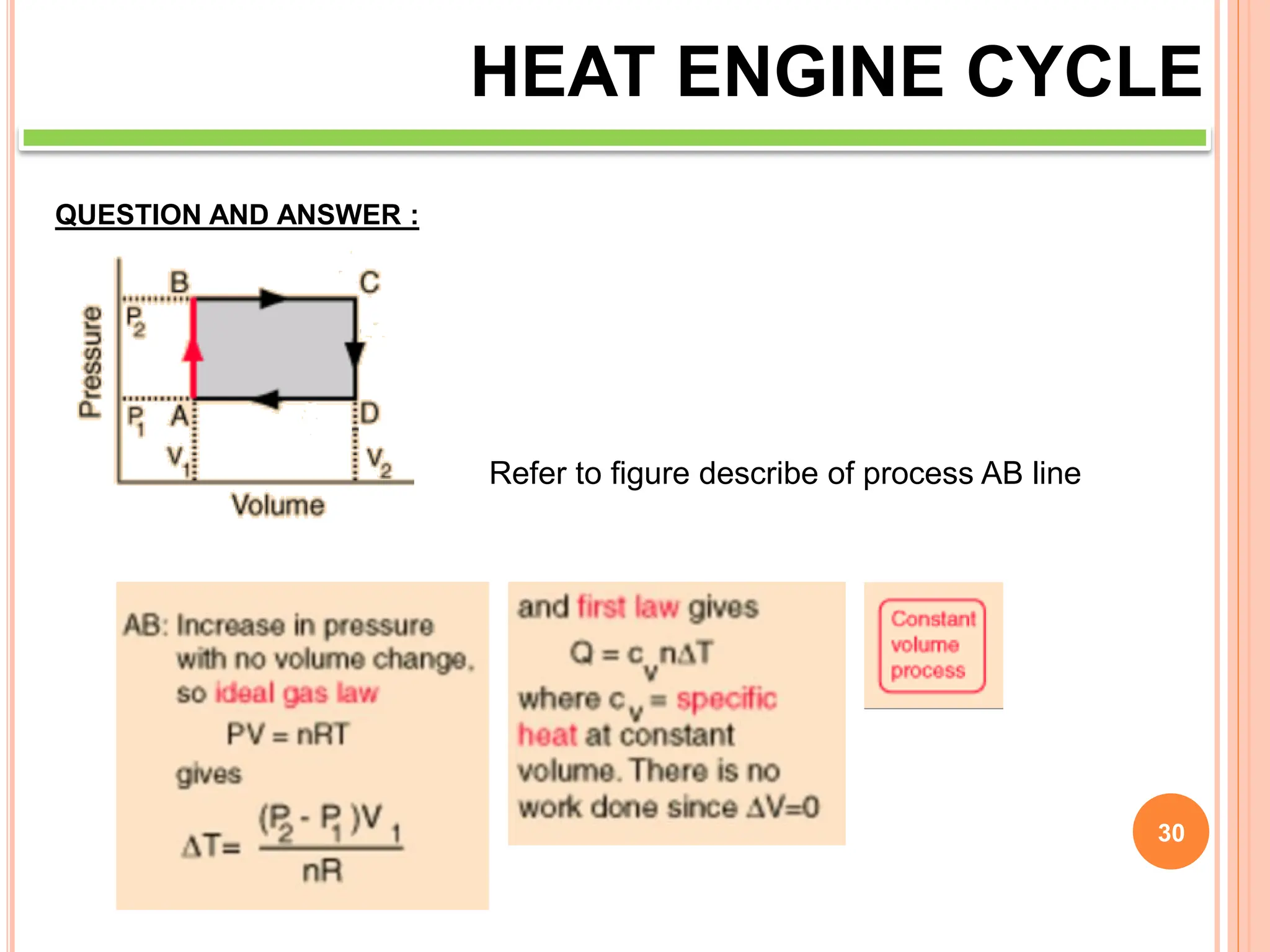
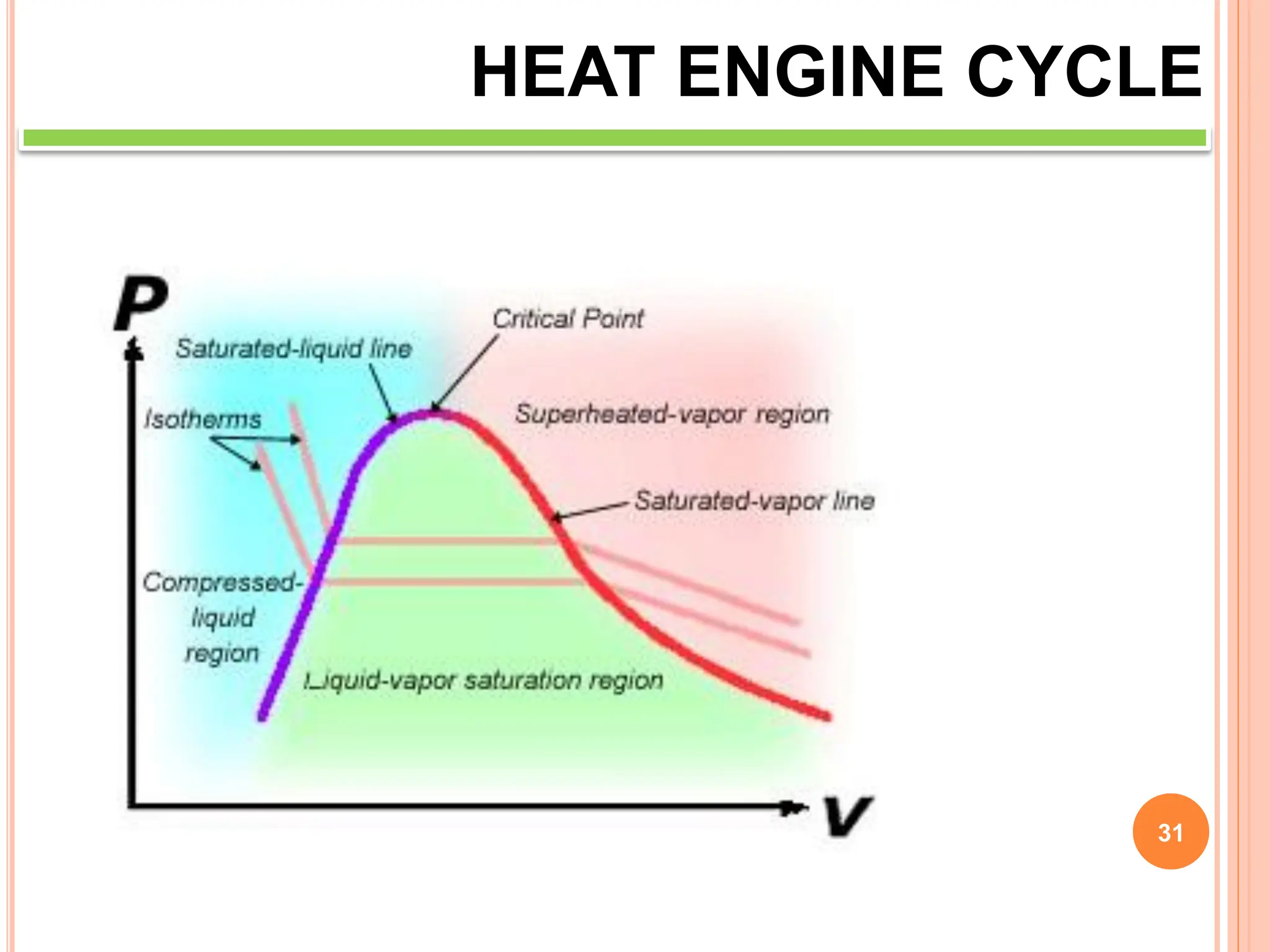
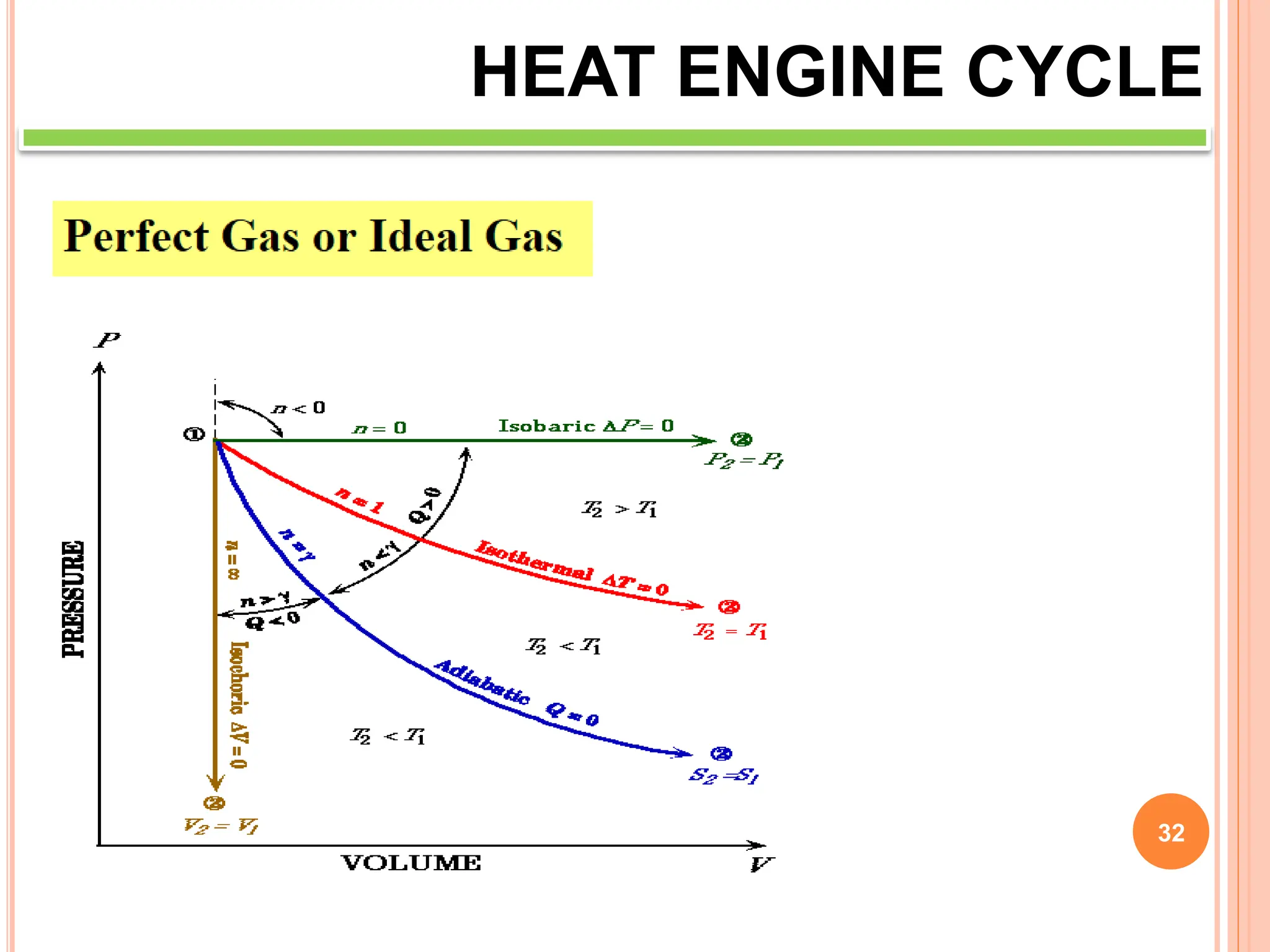
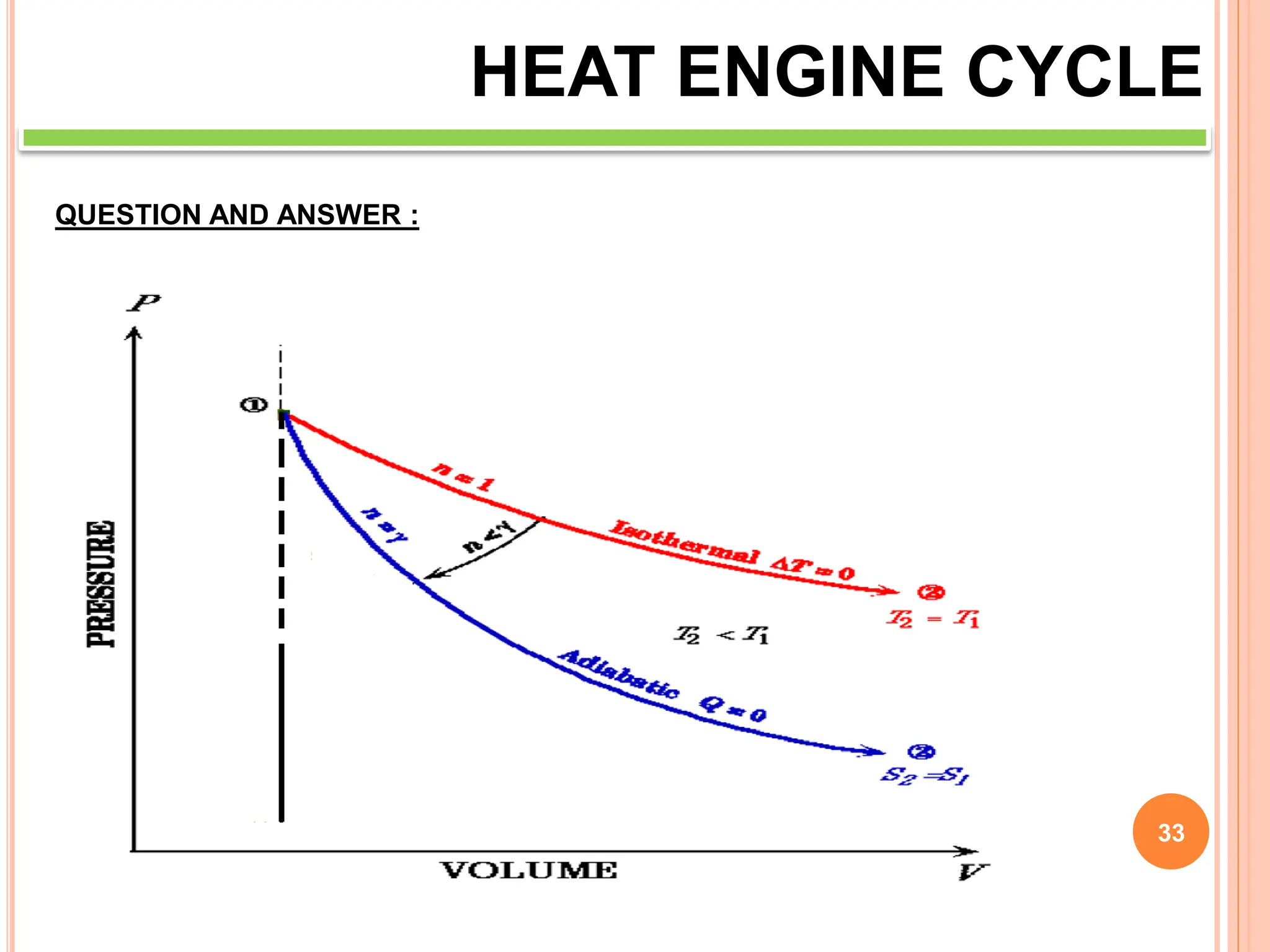
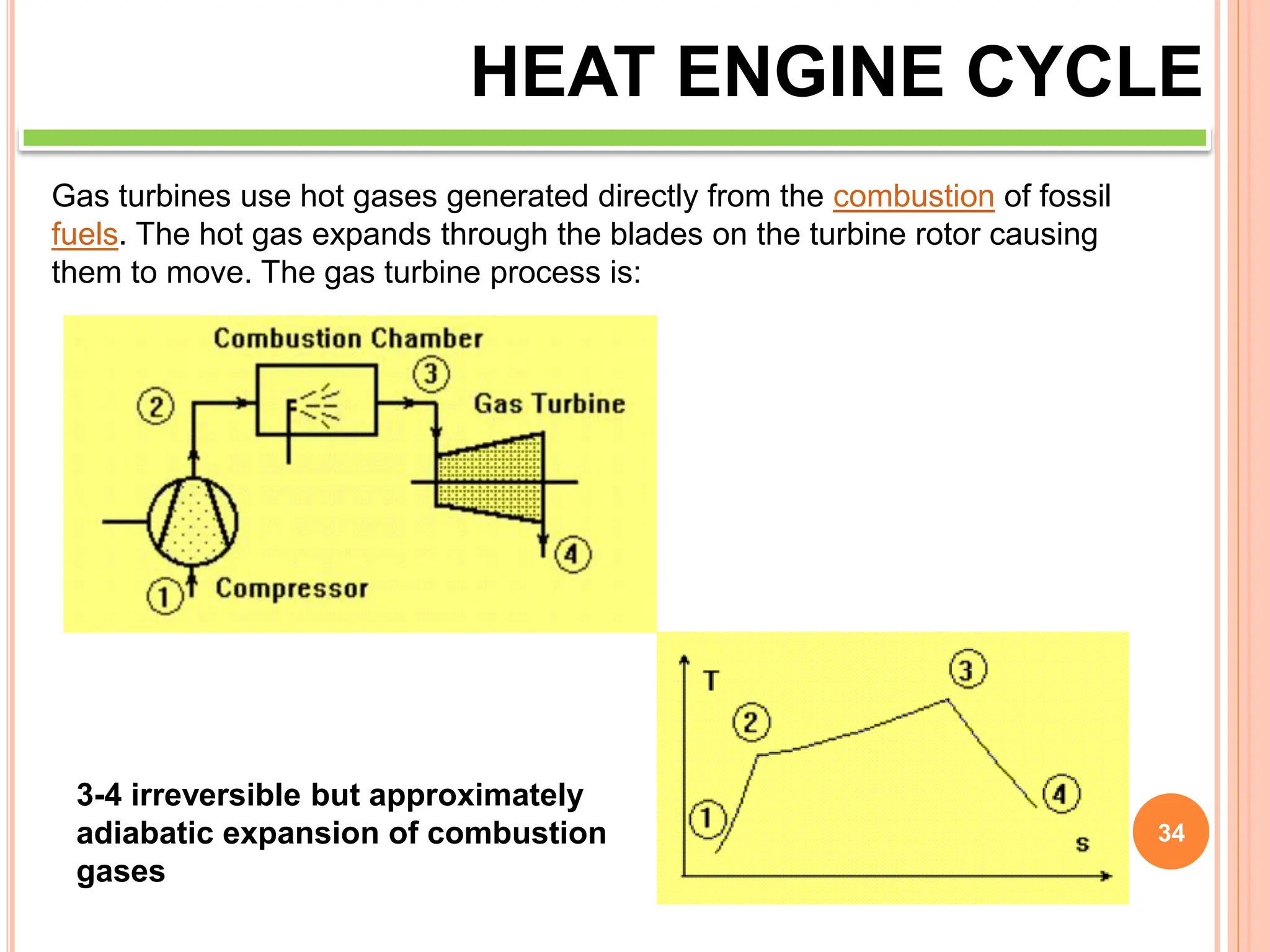
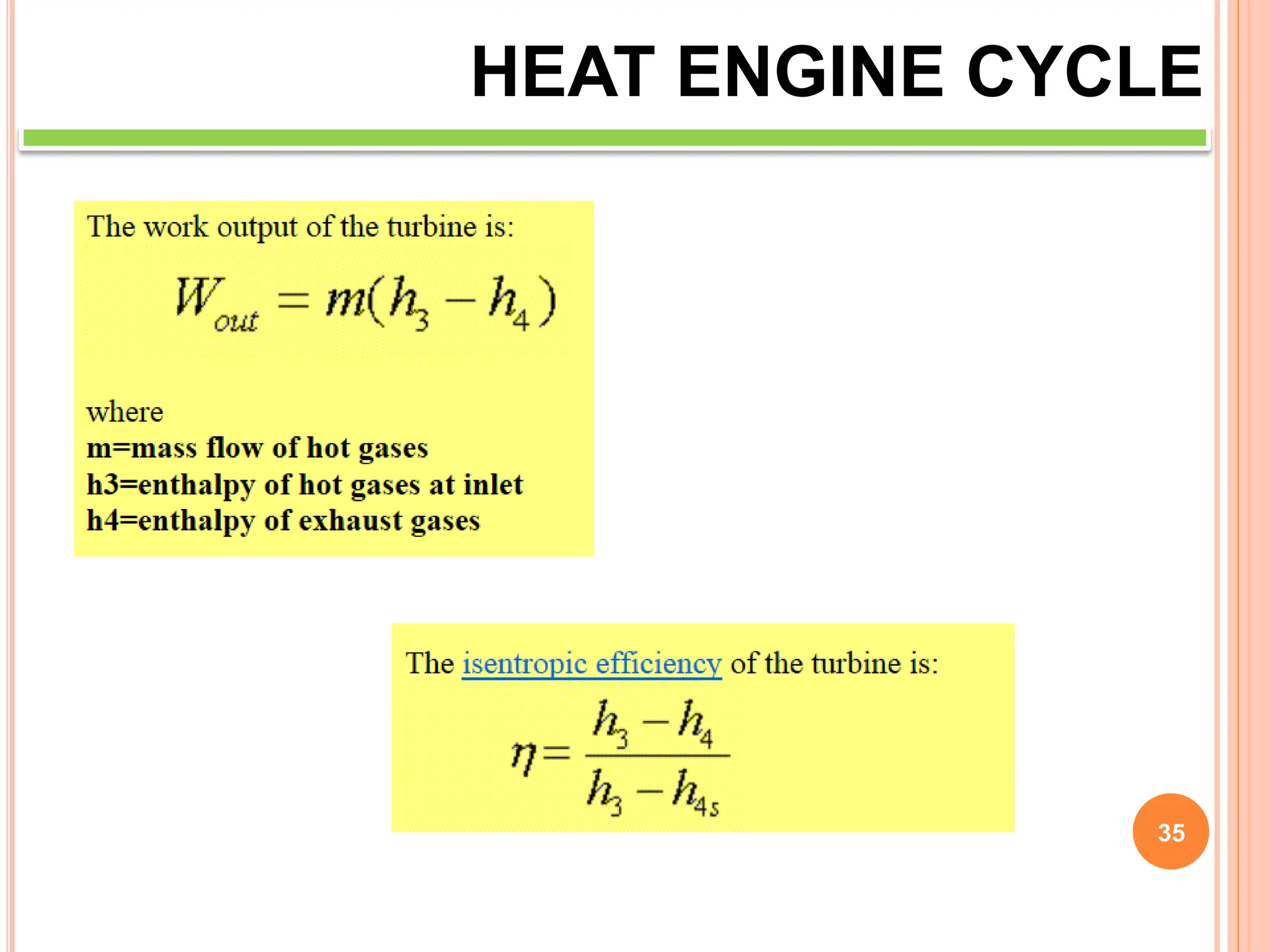
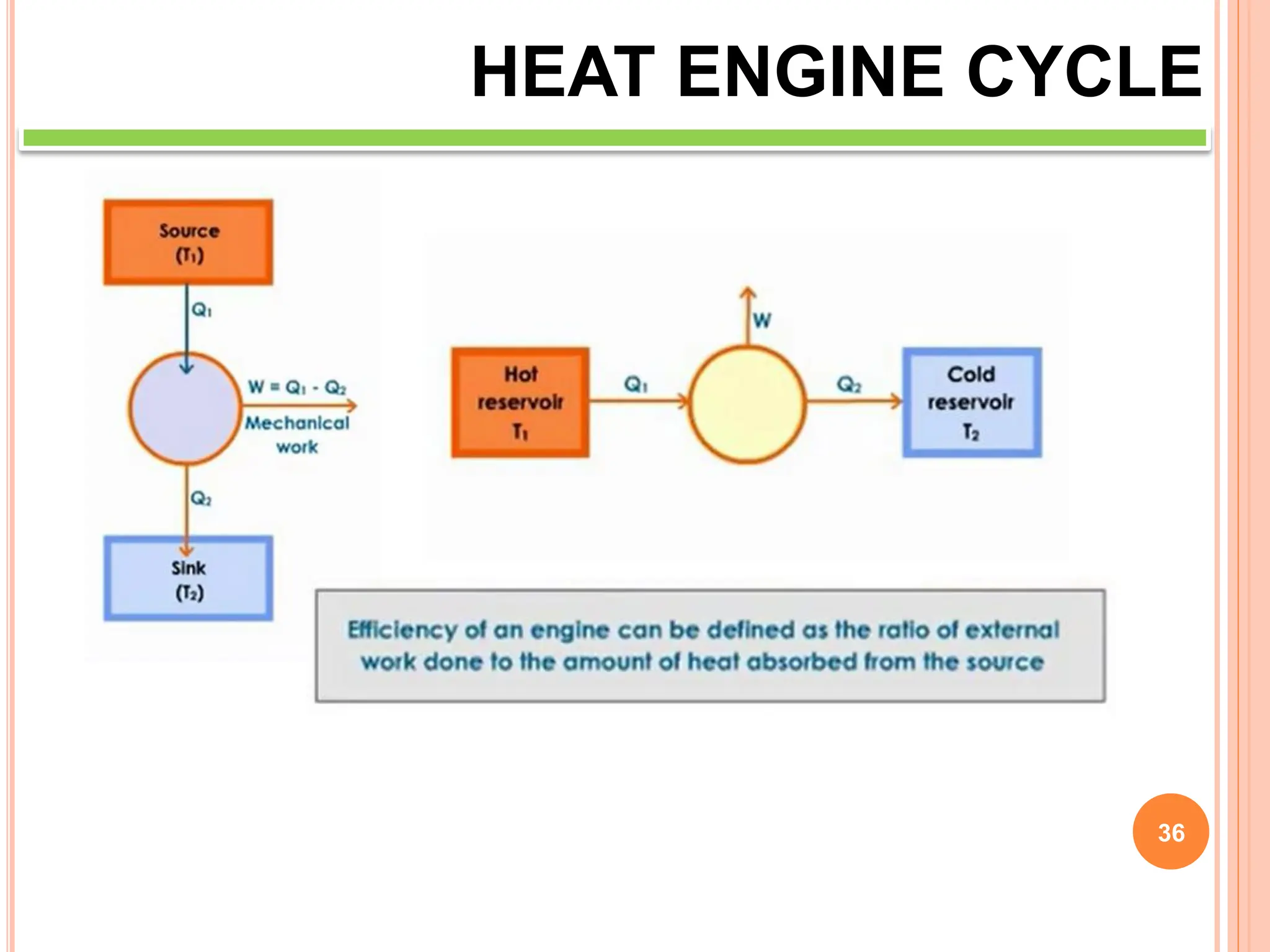
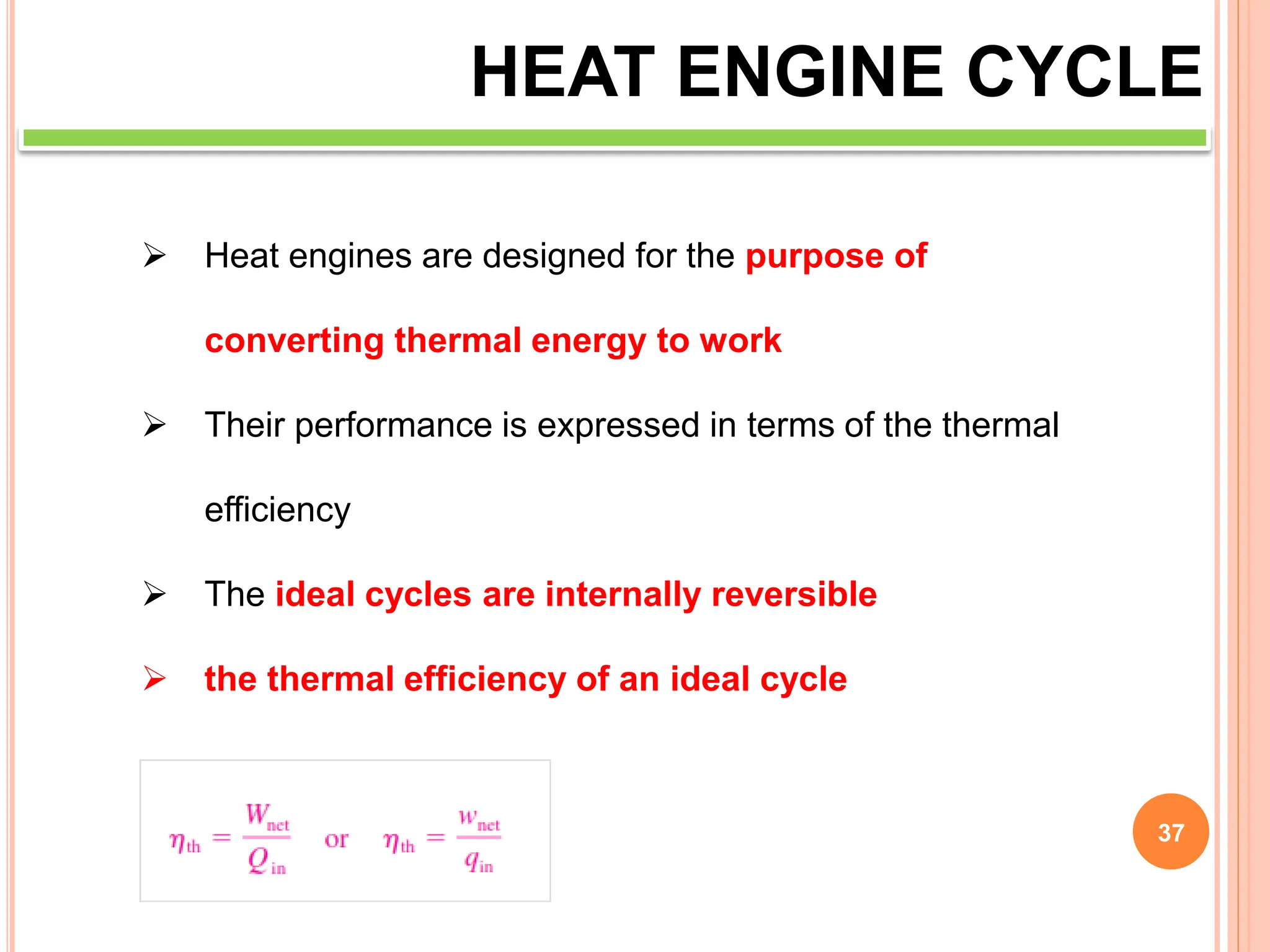
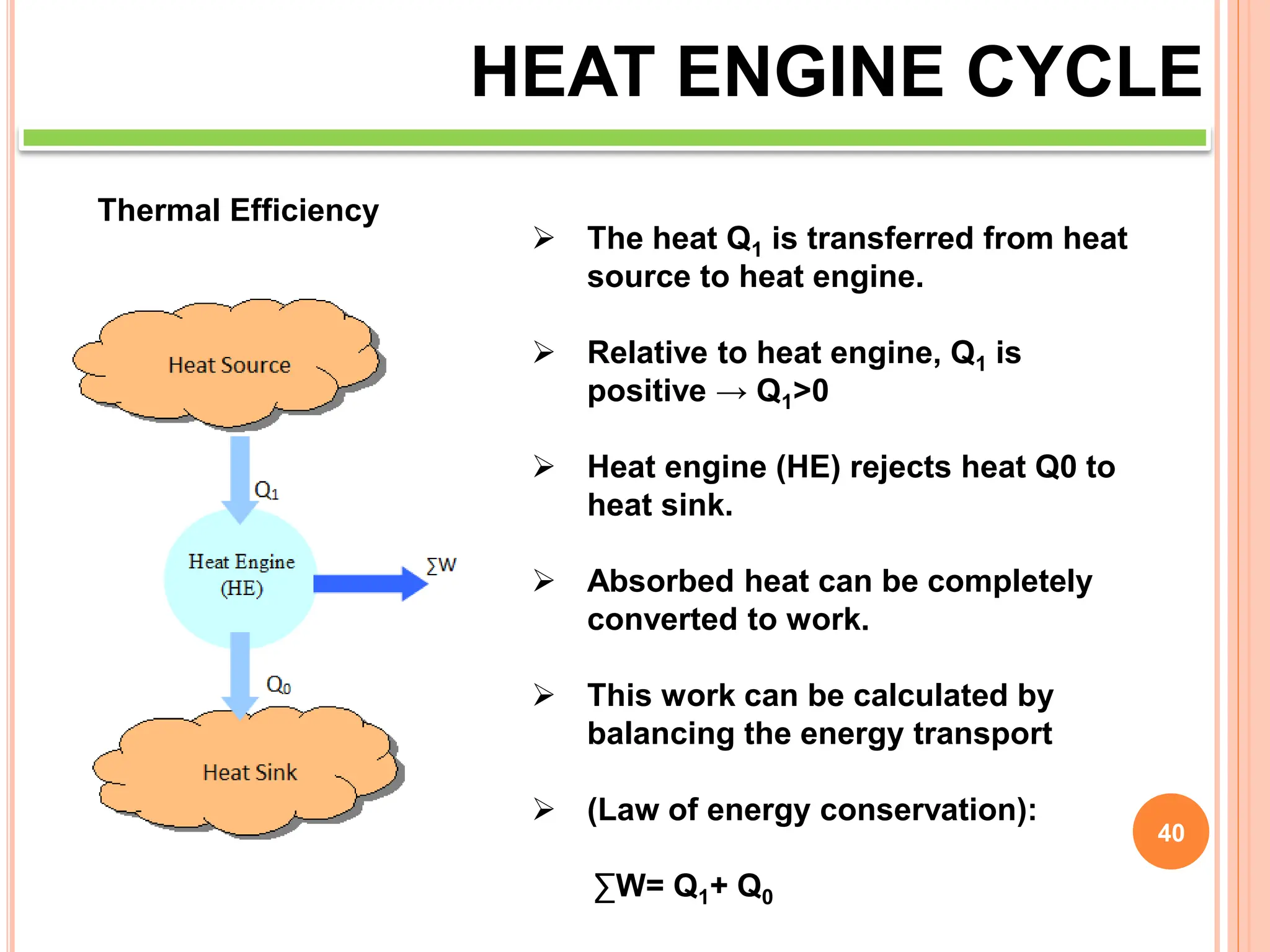
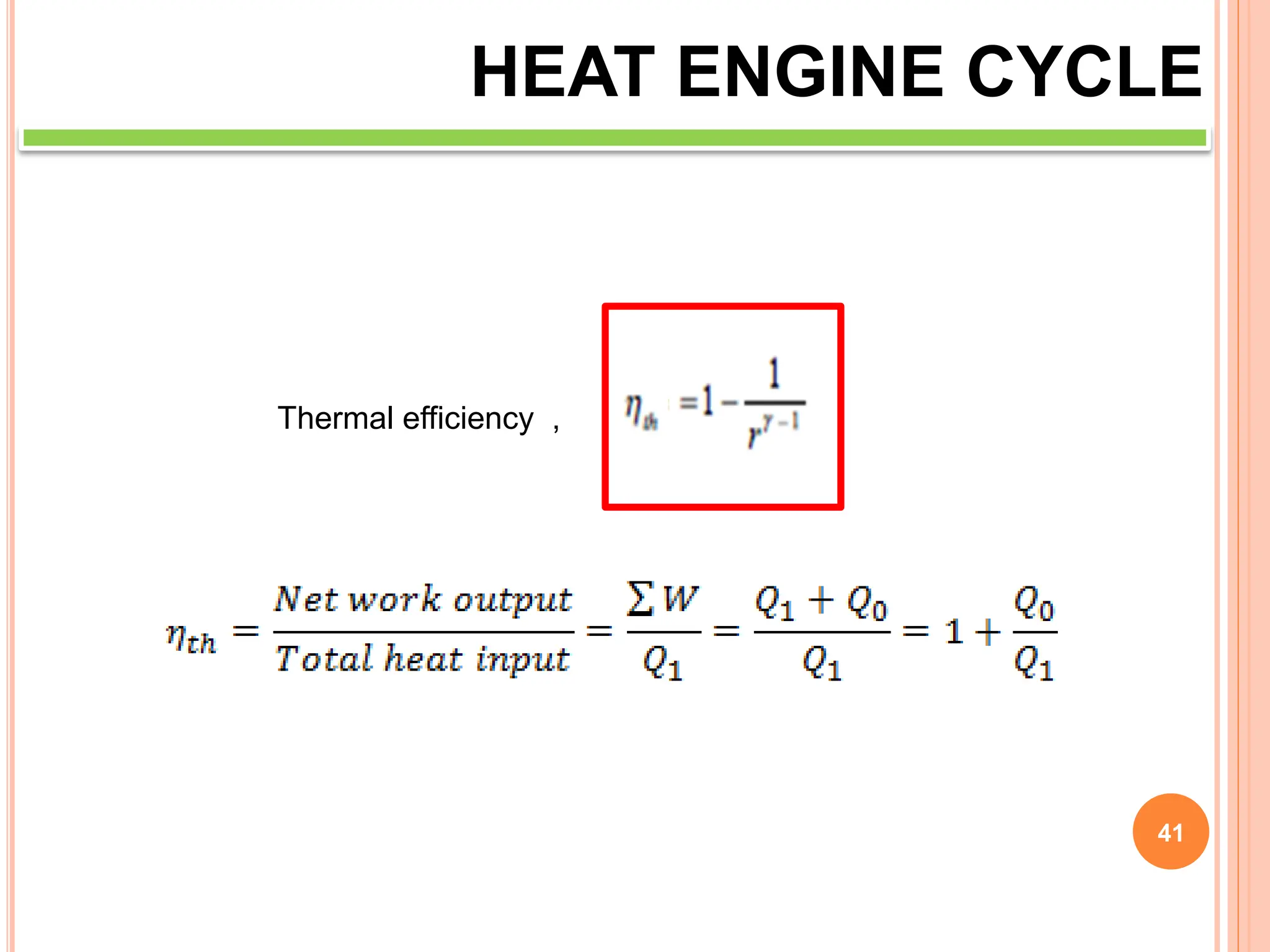
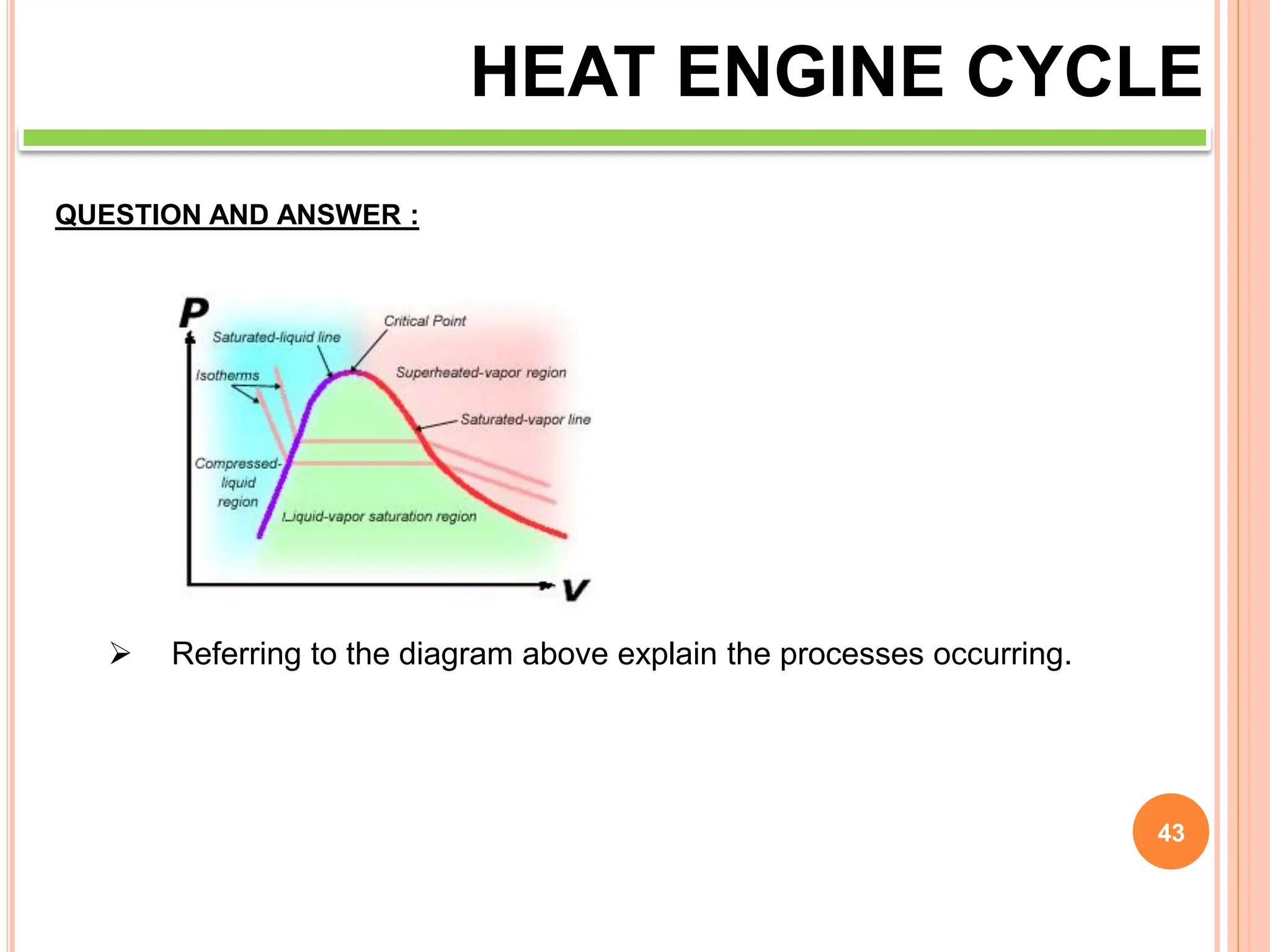
This document discusses heat engine cycles and concepts. It begins by defining a heat engine as a thermodynamic system that converts heat from a high temperature source into mechanical work. It describes how thermodynamics studies the relationships between heat, temperature, pressure, and volume during energy conversion processes. The document then discusses key concepts like the first and second laws of thermodynamics, heat engine efficiency, ideal cycles, and entropy changes. It provides examples of pressure-volume diagrams and equations for calculating work and thermal efficiency. In several sections, it poses and answers questions about heat engines and their operating principles.