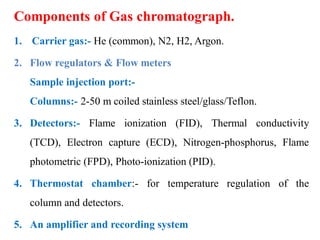
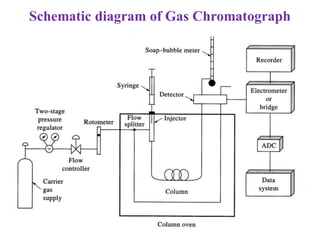
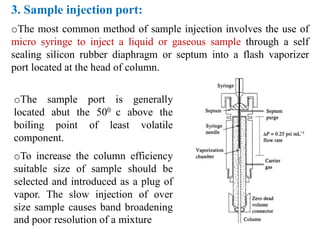
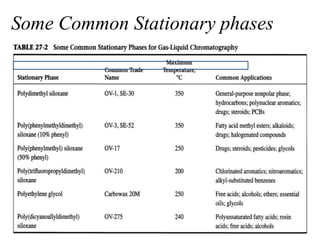
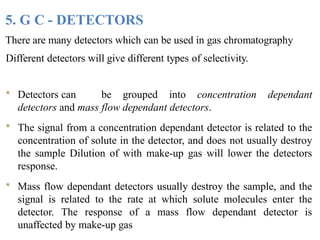
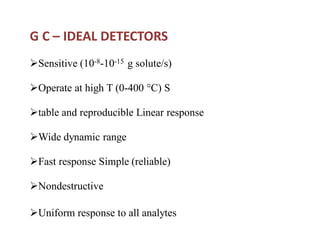
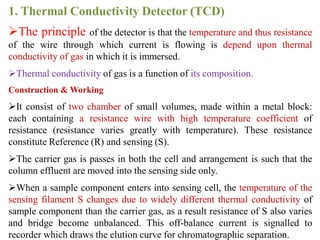
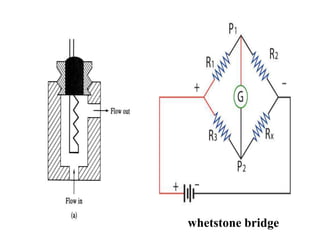
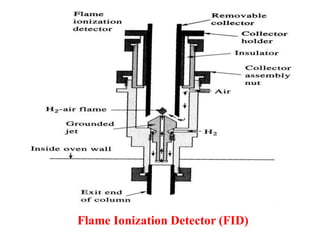
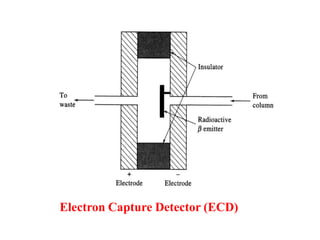
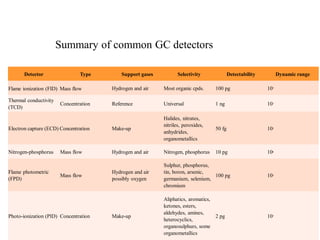
Gas chromatography is a technique used to separate components in a mixture using an inert gas as the mobile phase and a stationary phase in the column. Key aspects of gas chromatography include the carrier gas, sample injection, columns with solid or liquid stationary phases, temperature programming, and detectors like FID, TCD, ECD that measure separated components. Gas chromatography provides sensitive, precise, and accurate analysis of mixtures like drugs, foods, pollutants, and more within a short time.