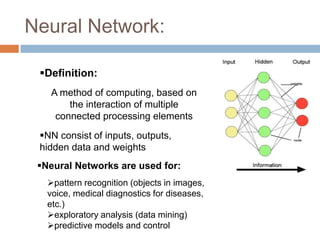
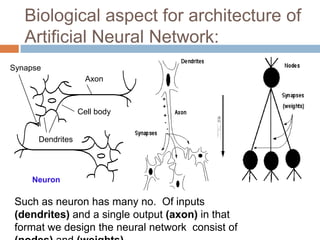
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence using fuzzy logic and neural networks. It discusses key concepts such as fuzzy logic, which allows for partial set membership rather than binary logic, and neural networks, which are modeled off the human brain. The document also introduces fuzzy-neural hybrid networks, which combine fuzzy logic and neural networks to leverage the strengths of both approaches. Examples of applications include pattern recognition, data mining, and control systems.

![Traditional Logic v/s Fuzzy
Logic:
Slow Fast
Speed = 0 Speed = 1
Fastest
Slow
Fast
[ 0.0 – 0.25 ]
[ 0.25 – 0.50 ]
[ 0.50 – 0.75 ]
[ 0.75 – 1.00 ]
Slowest
(a) Boolean Logic. (b) Multi-valued Logic.
0 1 10 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 100 1 10
Traditional logic Fuzzy logic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptamravati-130717063449-phpapp02/85/Ppt-on-artifishail-intelligence-6-320.jpg)


![• Transfer function g is linear
• If wk=0 then wk AND xk=0 while if wk=1 then wk
AND xk= xk independent of xk
y=OR(x1 AND w1, x2 AND w2 … xn AND wn)
OR:[0,1]x[0,1]n->[0,1]
OR Fuzzy-Neural:
y=AND(x1 OR w1, x2 OR w2 … xn OR wn)
AND:[0,1]x[0,1]n->[0,1]
And Fuzzy-Neural:
y = g(w.x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptamravati-130717063449-phpapp02/85/Ppt-on-artifishail-intelligence-11-320.jpg)
