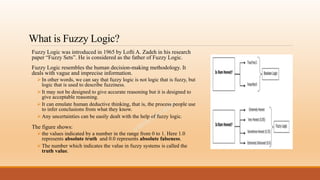
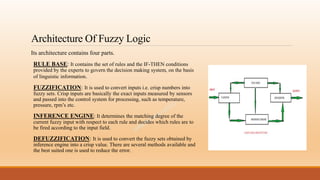
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic that allows intermediate values between conventional evaluations like true/false, yes/no, or black/white. It employs the concept of fuzzy sets, where elements have degrees of membership as opposed to full membership. Fuzzy logic has applications in areas like control systems, pattern recognition, and decision making where precise probabilities or crisp boundaries are not easily determined.


![Introduction To Fuzzy Logic And Fuzzy Systems
The word fuzzy refers to things which are not clear or are vague. Any event, process or function that is changing
continuously cannot always be defined as either true or false, which means that we need to define such activities
in a fuzzy manner.
Fuzzy logic is derived from fuzzy set theory dealing with reasoning that is approximate rather than precisely
deduced from classical predicate logic.
What is fuzzy set theory?
Fuzzy set theory is an extension of classical set theory where elements have varying degrees of membership.
A logic based on the two truth values, True and False, is sometimes inadequate when describing human reasoning.
Fuzzy logic uses the whole interval between 0 (false) and 1(true)to describe human reasoning.
A Fuzzy Set is any set that allows its members to have different degree of membership, called membership function, in the
interval [0, 1].
Fuzzy set theory defines Fuzzy Operators on Fuzzy Sets.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonfuzzylogicandfuzzysets-200711071303/85/Presentation-on-fuzzy-logic-and-fuzzy-systems-3-320.jpg)