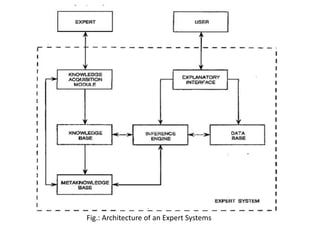
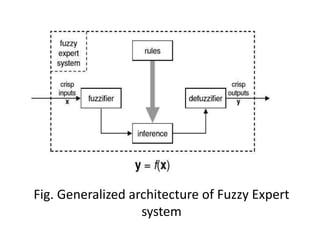
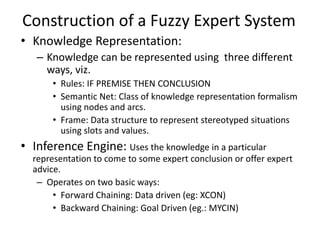
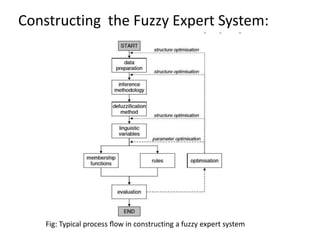
This document presents a presentation on fuzzy expert systems. It introduces expert systems and how they combine human expertise with computational capabilities. It then discusses the evolution of fuzzy expert systems to handle imprecision and uncertainty. The key components of a fuzzy expert system are described, including the knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface. Steps for constructing a fuzzy expert system are outlined, from knowledge representation to testing rules. Pros and cons as well as applications in various domains like agriculture, education, and medicine are also summarized.