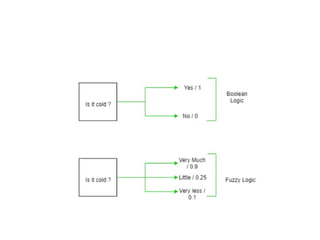
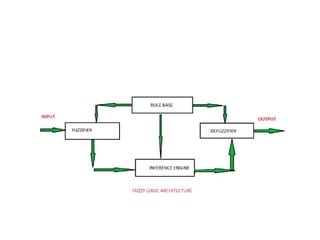
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic that allows for reasoning with imprecise or uncertain information, utilizing truth values between 0 and 1. It employs membership functions and fuzzy rules to model vagueness in decision-making across various applications, including control systems and artificial intelligence. The architecture of fuzzy logic systems consists of components such as rule bases, fuzzification, inference engines, and defuzzification to process input data and generate outputs.