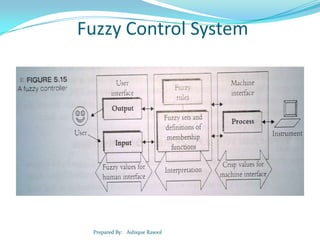
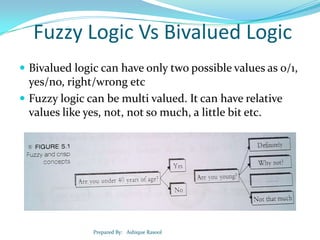
Fuzzy logic is a flexible machine learning technique that mimics human thought by allowing intermediate values between true and false. It provides a mechanism for interpreting and executing commands based on approximate or uncertain reasoning. Unlike binary logic which can only have true or false values, fuzzy logic uses linguistic variables and degrees of membership to represent concepts that may have a partial truth. Fuzzy systems find applications in automatic control, prediction, diagnosis and user interfaces.


![Fuzzy Set
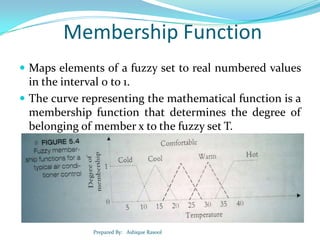
Let X be a non empty set, A fuzzy set A in X is
characterized by its membership function μA: X ->
[0,1], where μA(x) is the degree of membership of
element x in fuzzy set A for each x ∈ X
Prepared By: Ashique Rasool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-131016035408-phpapp01/85/Chapter-5-Fuzzy-Logic-5-320.jpg)



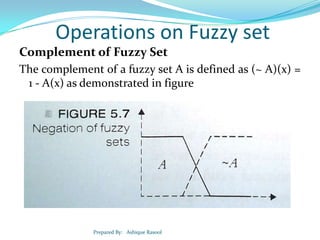

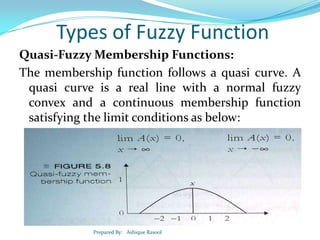
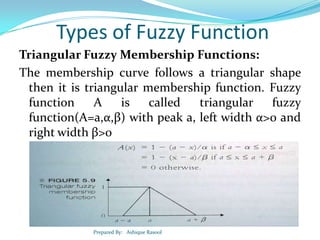
![Types of Fuzzy Function
Trapezoidal Fuzzy Membership Functions:
The membership curve follows a trapezoidal shape.
Fuzzy function A is called triangular fuzzy
function(A=a,α,β) with tolerance interval [a, b],
left width α and right width β
Prepared By: Ashique Rasool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-131016035408-phpapp01/85/Chapter-5-Fuzzy-Logic-15-320.jpg)