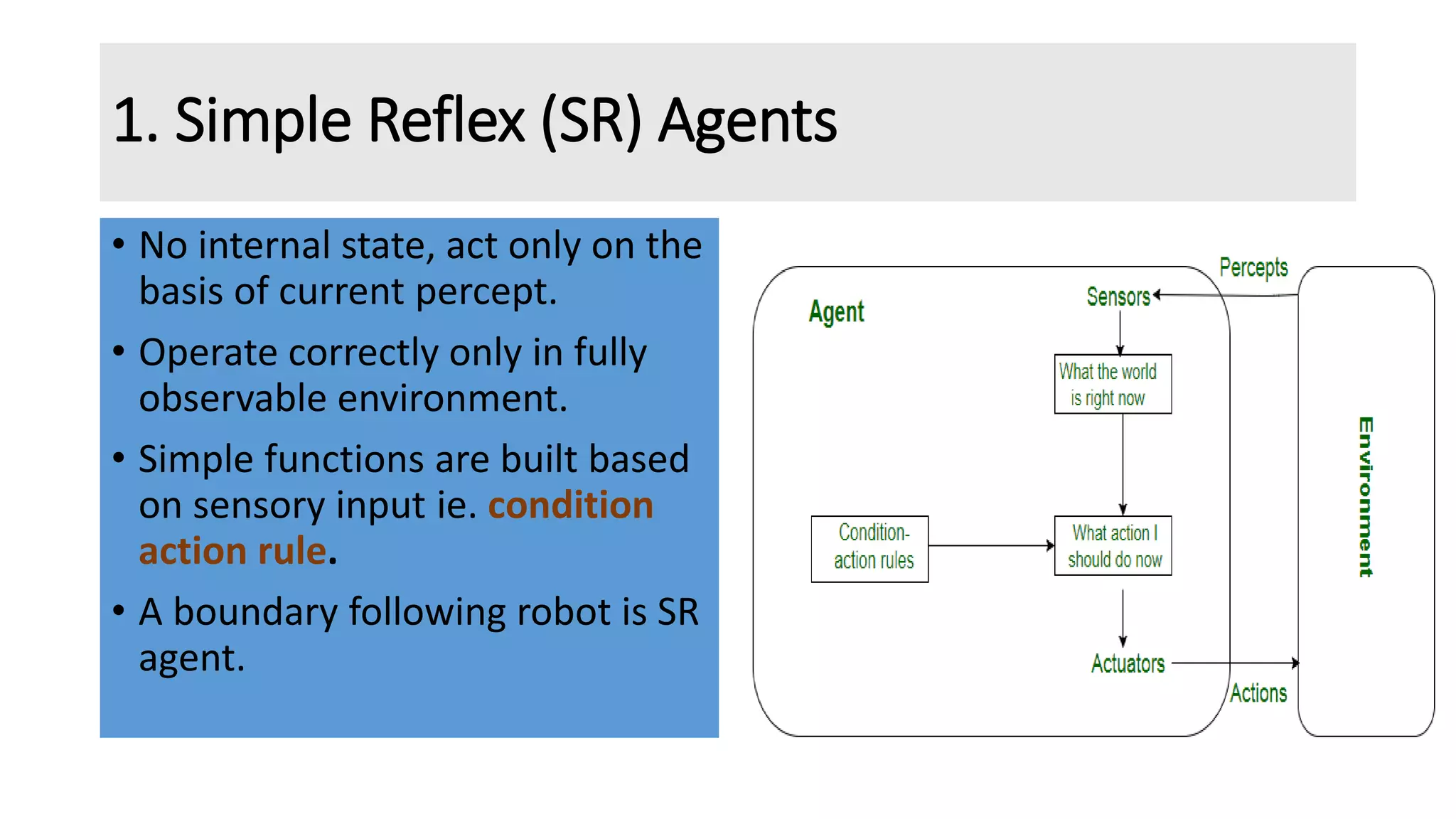
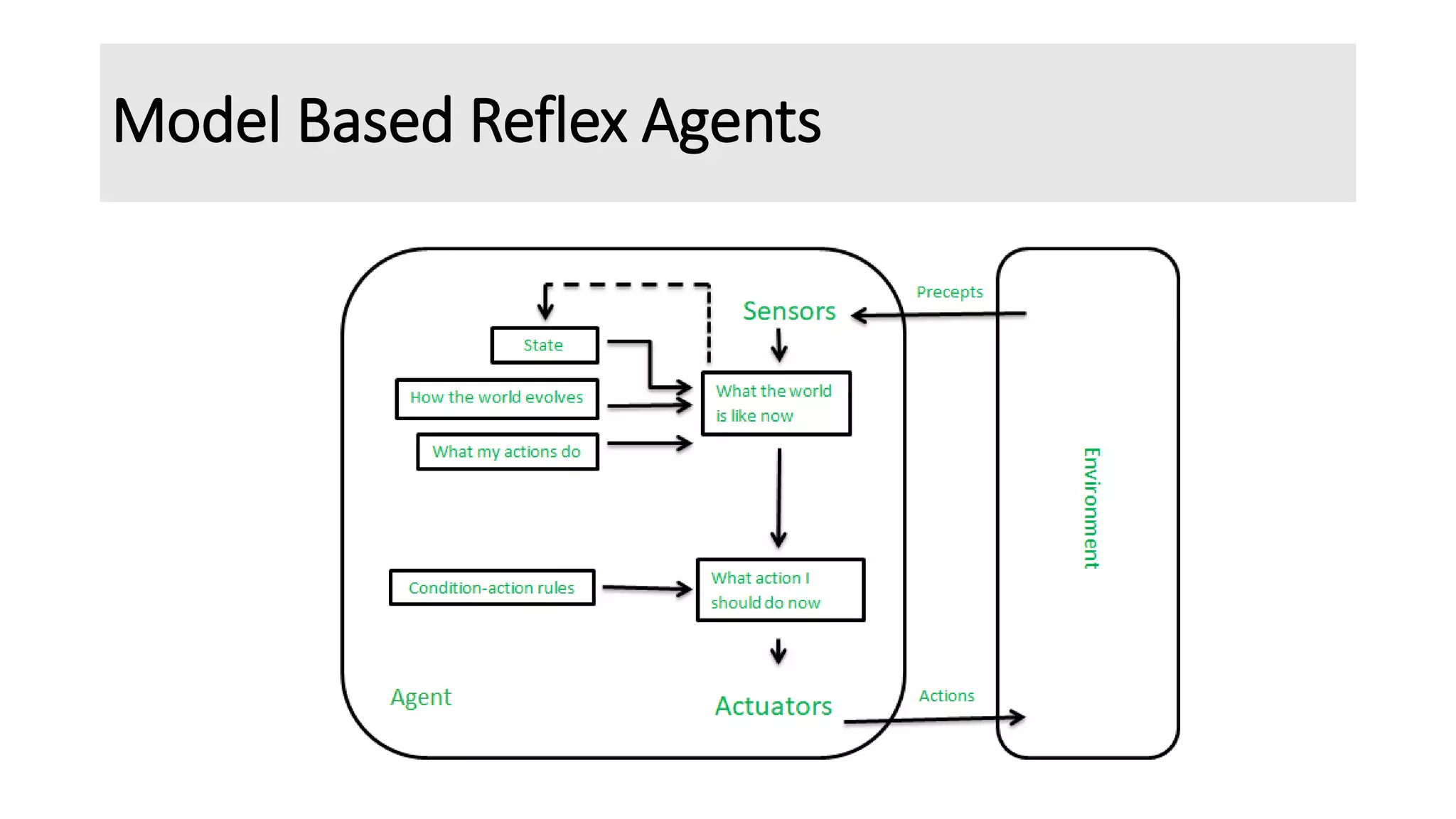
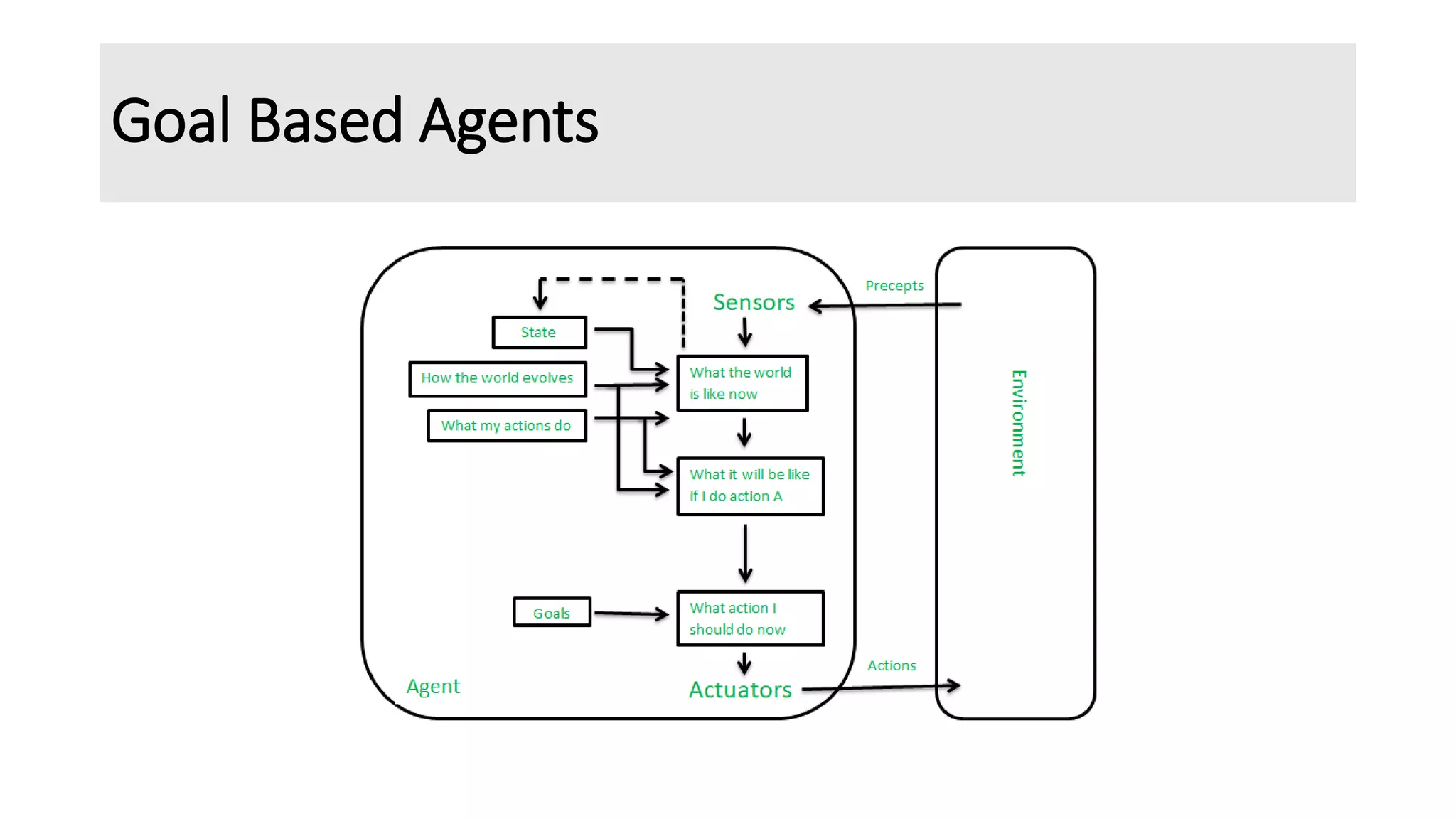
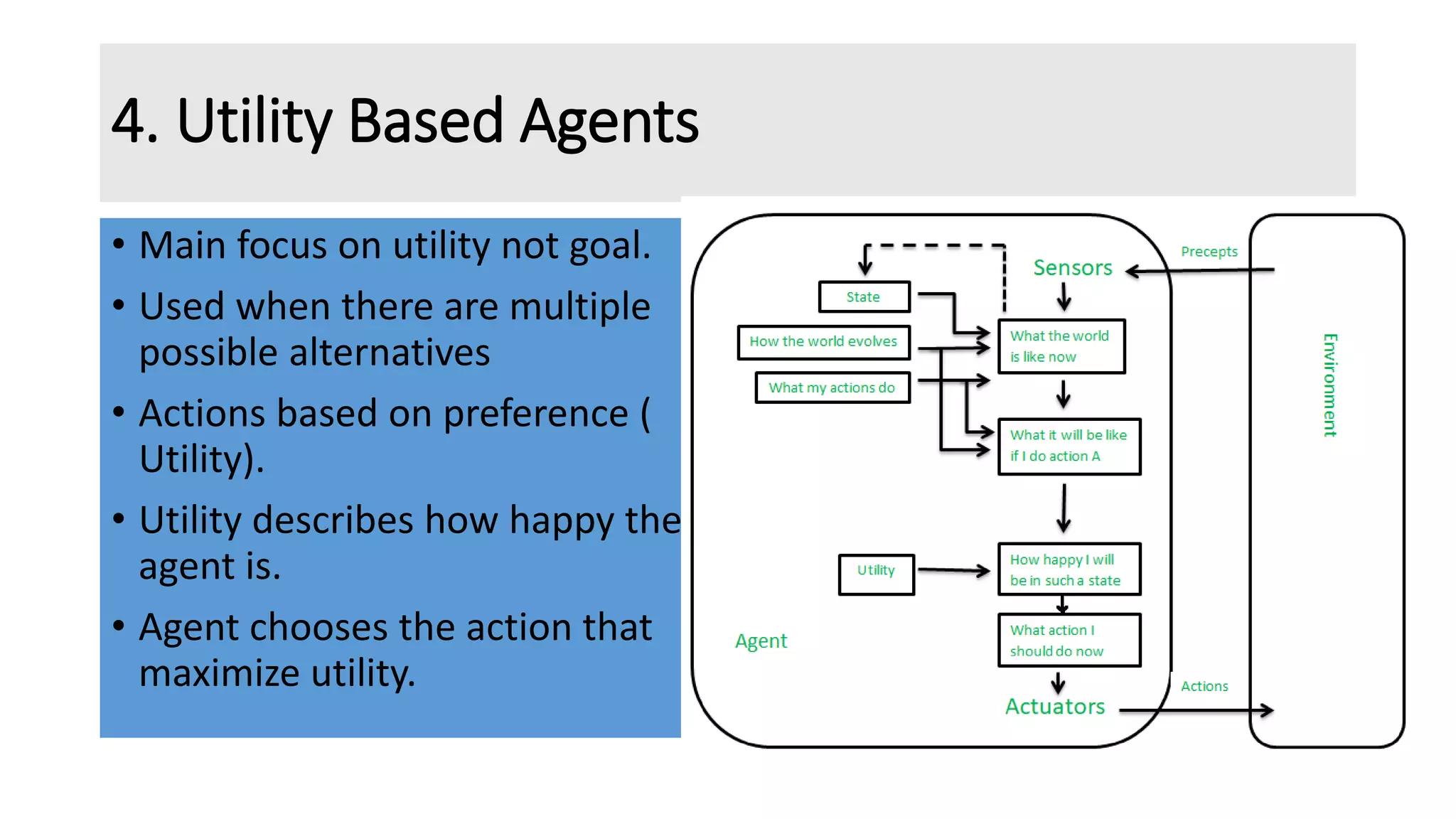
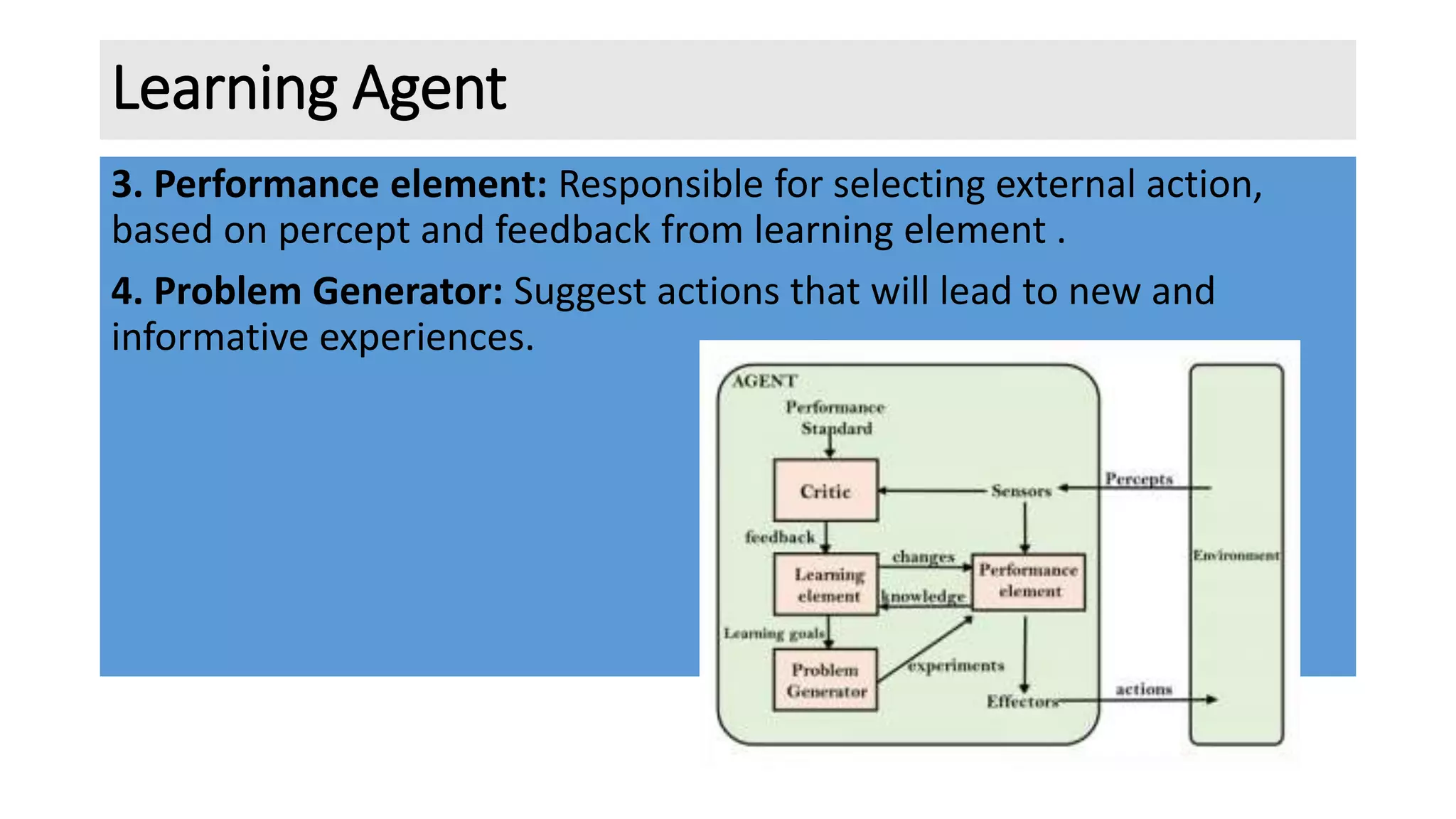
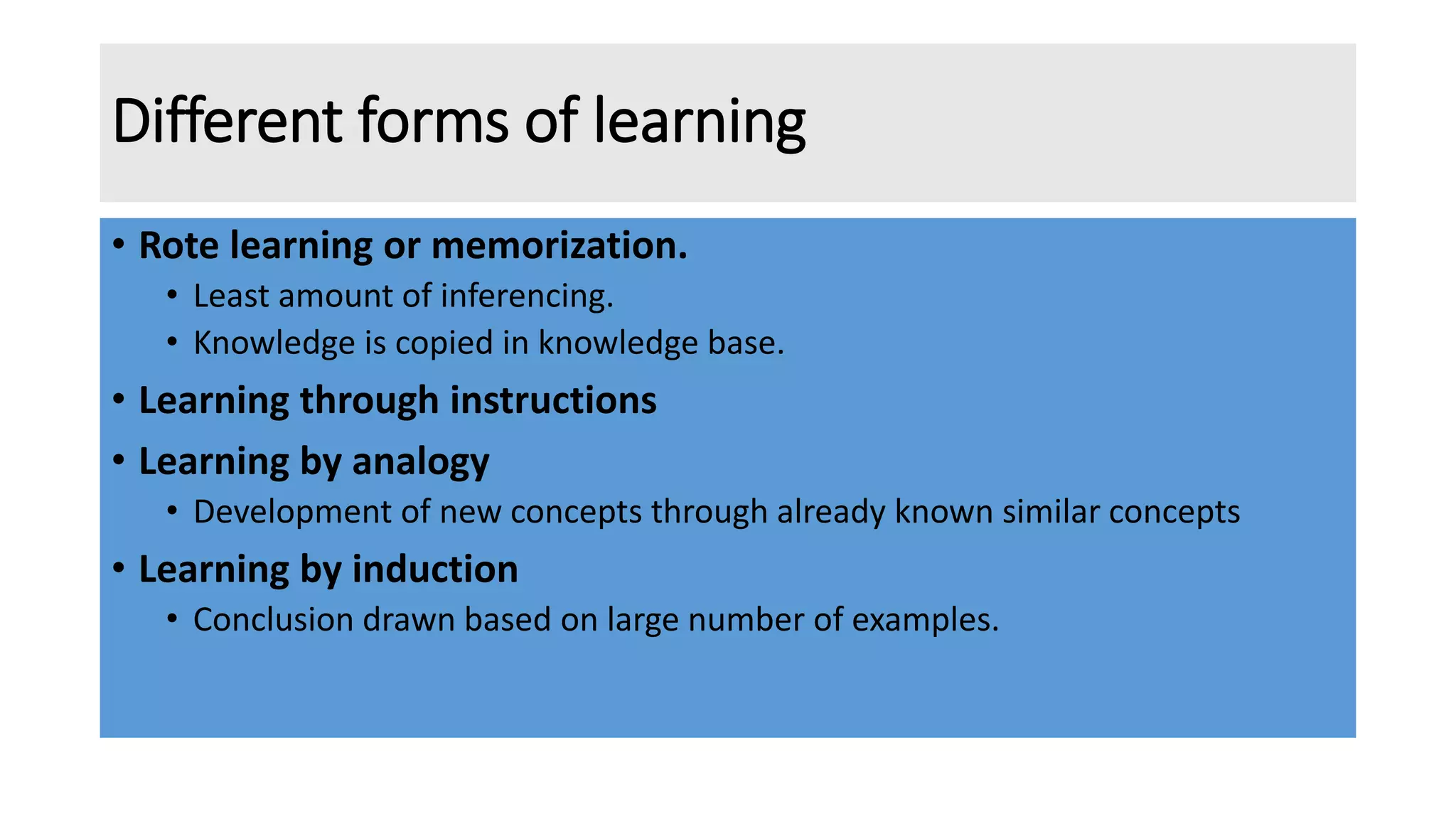
The document discusses different types of intelligent agents based on their architecture and programs. It describes five classes of agents: 1) Simple Reflex agents which react solely based on current percepts; 2) Model-based agents which use an internal model of the world; 3) Goal-based agents which take actions to reduce distance to a goal; 4) Utility-based agents which choose actions to maximize utility; and 5) Learning agents which are able to learn from experiences. The document also outlines different forms of learning like rote learning, learning from instruction, and reinforcement learning.