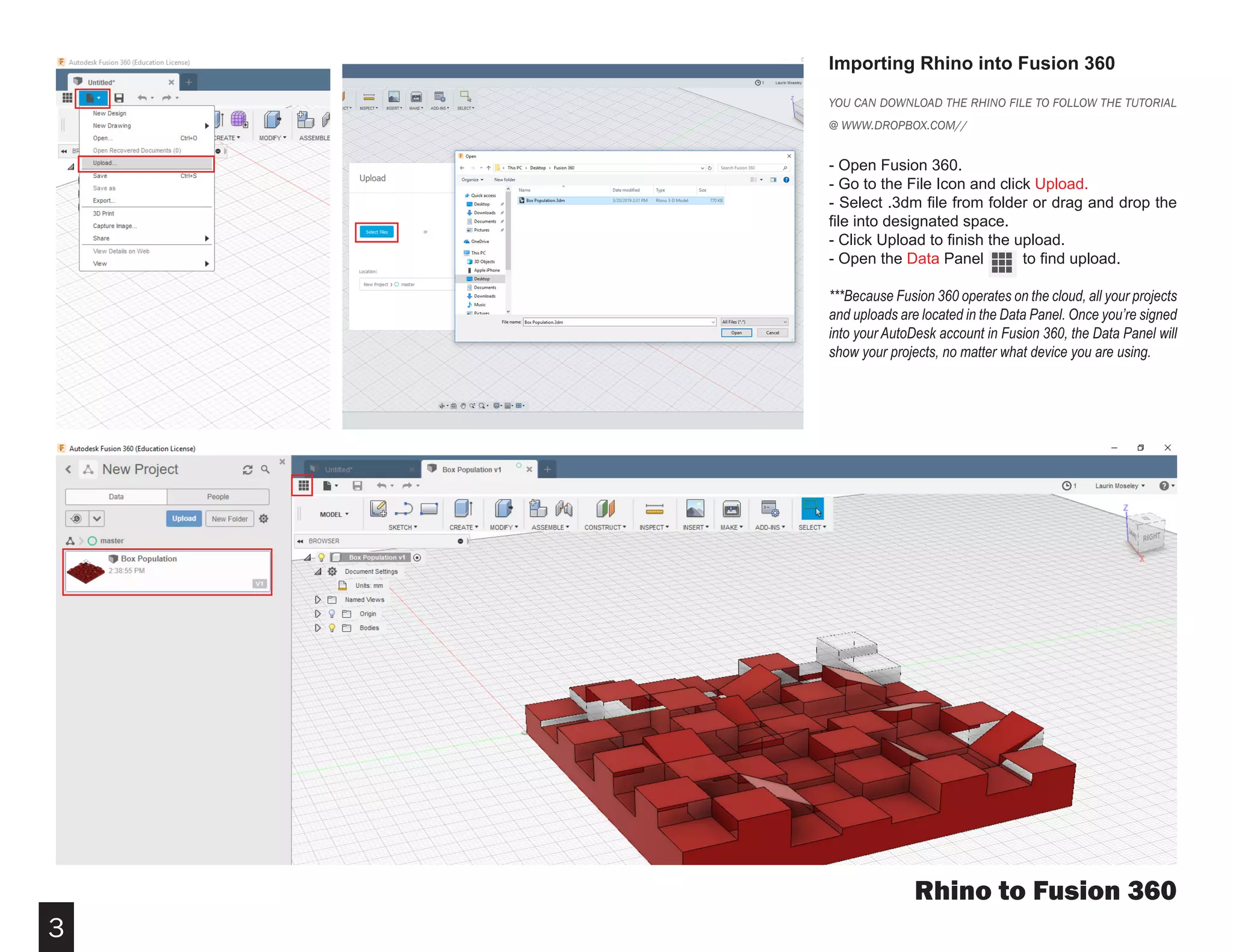
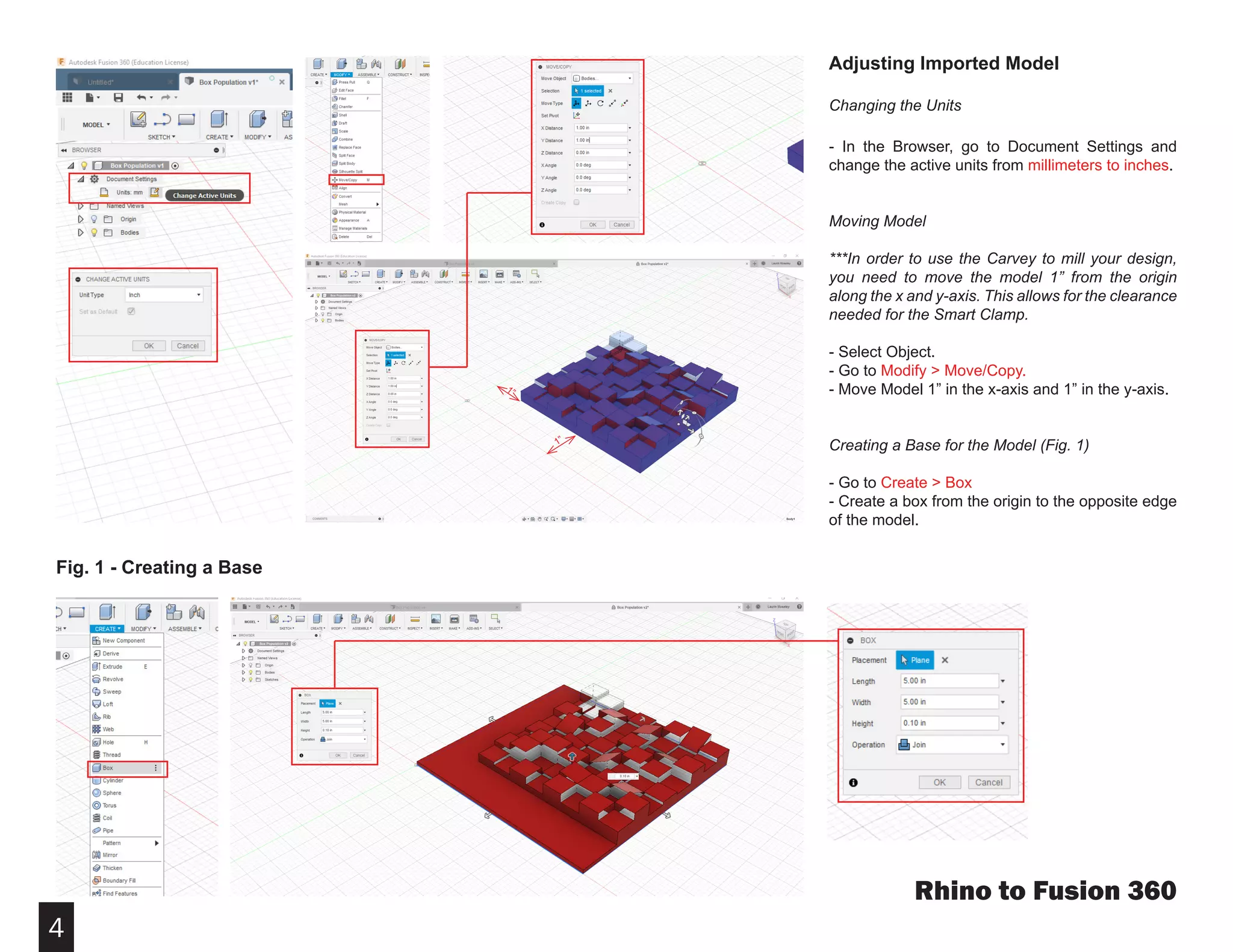
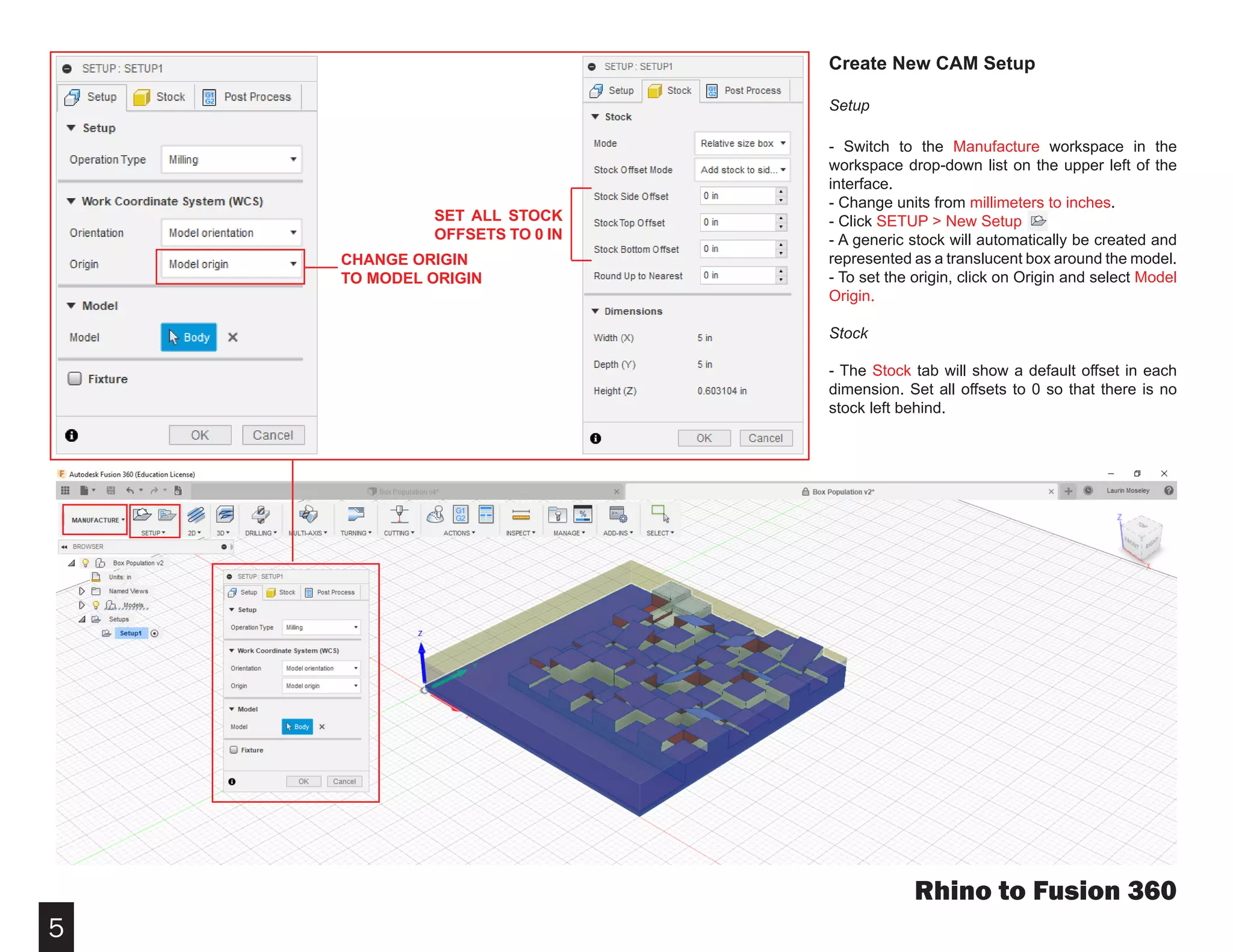
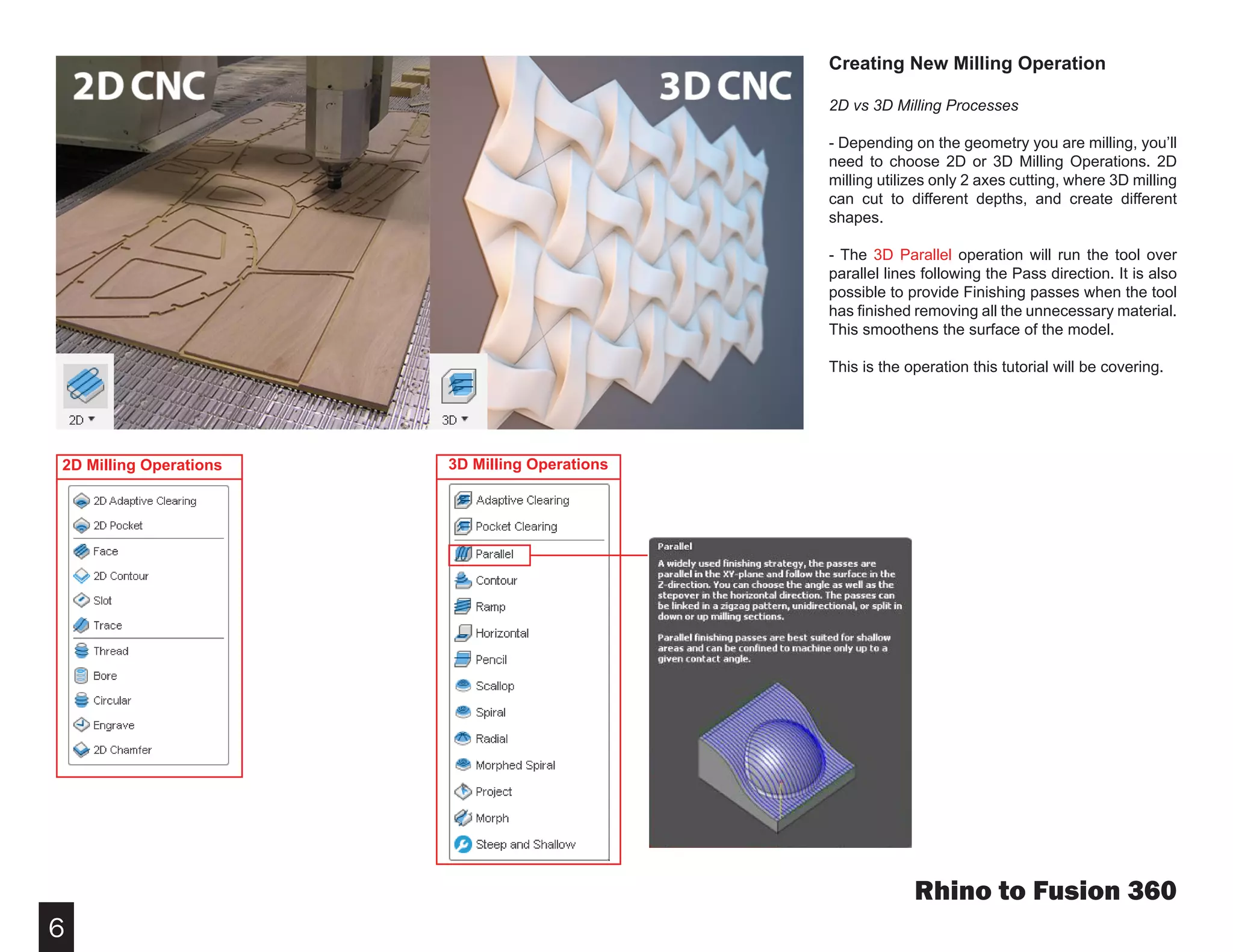
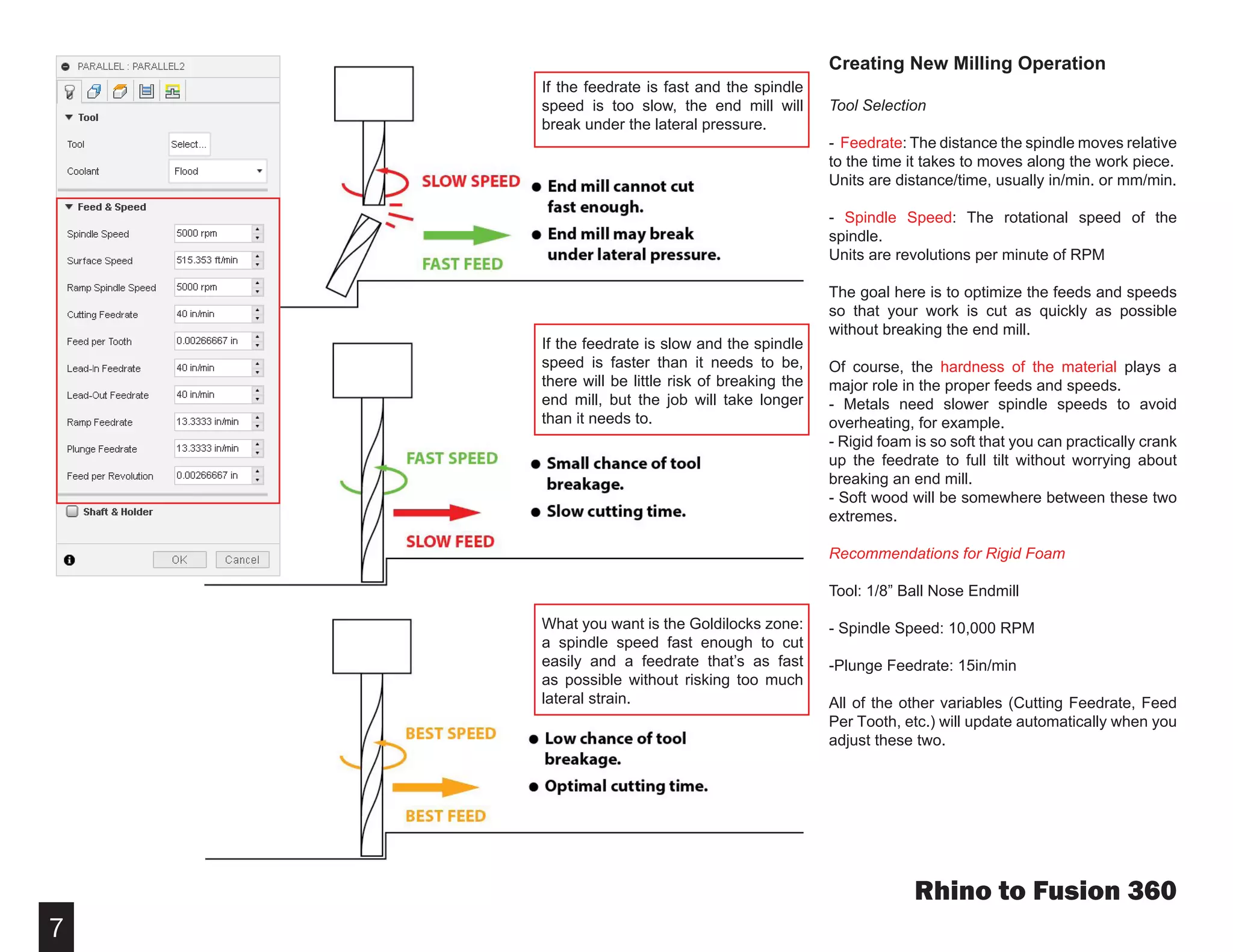
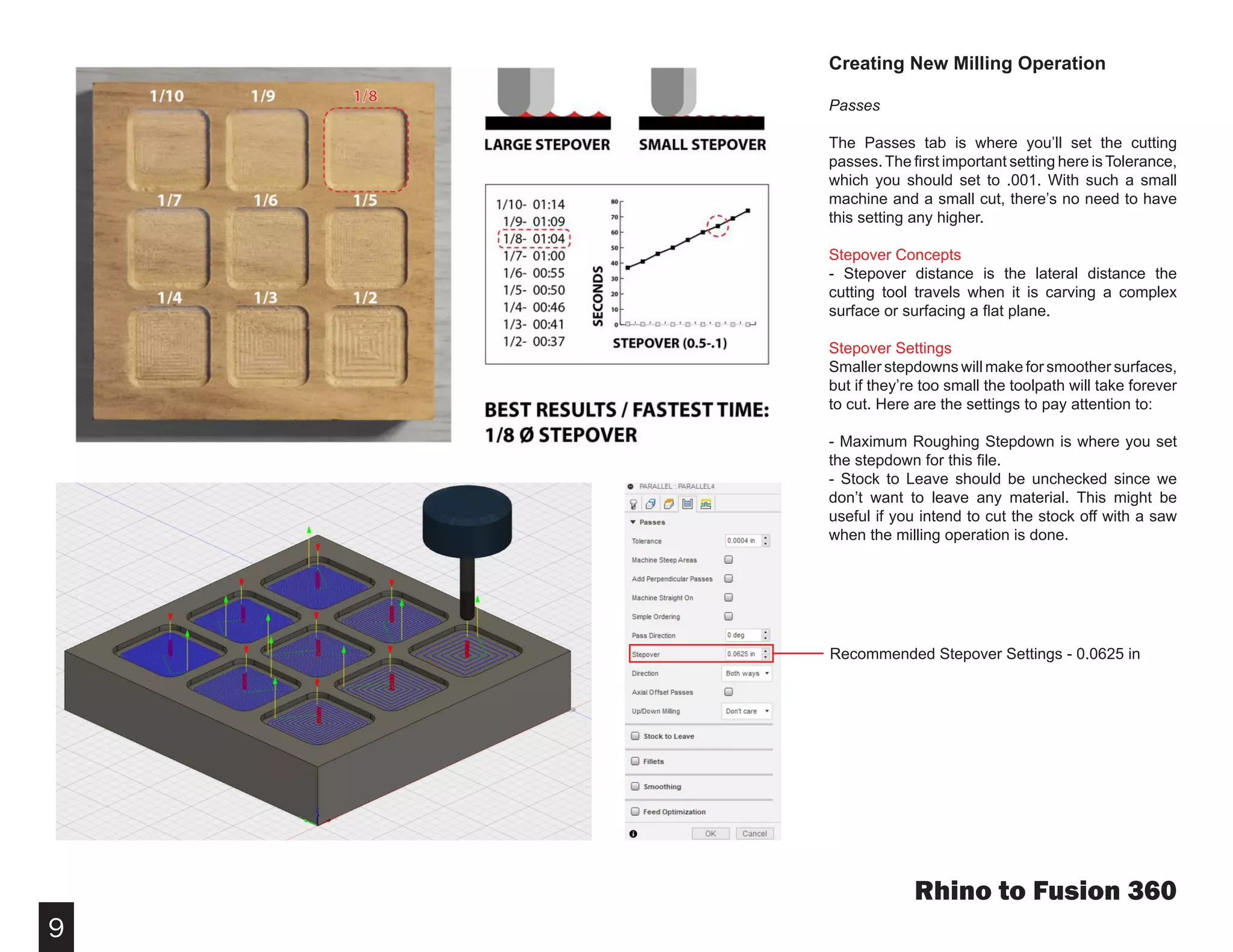
Fusion 360 is free 3D modeling software that students can use. It can import files from other 3D modeling programs like Rhino. This document provides steps to import a Rhino file into Fusion 360, make adjustments to the model like moving and resizing it, then set up toolpaths to CNC mill the model using Autodesk's CAM module. It describes how to select the tool, depths, stepover distances and other settings, then simulate and post-process the toolpath into G-code that can be run on a CNC machine like the Carvey.