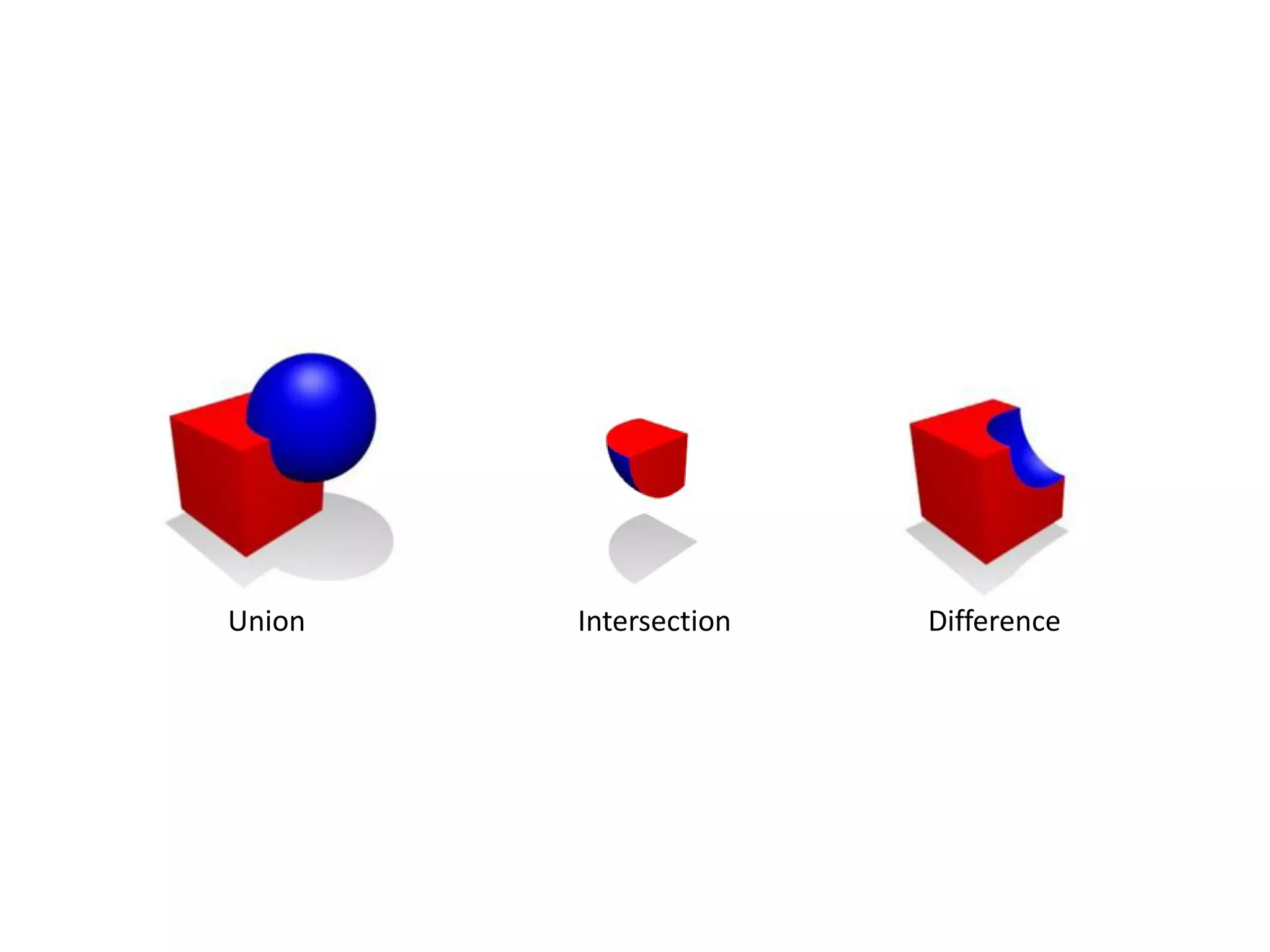
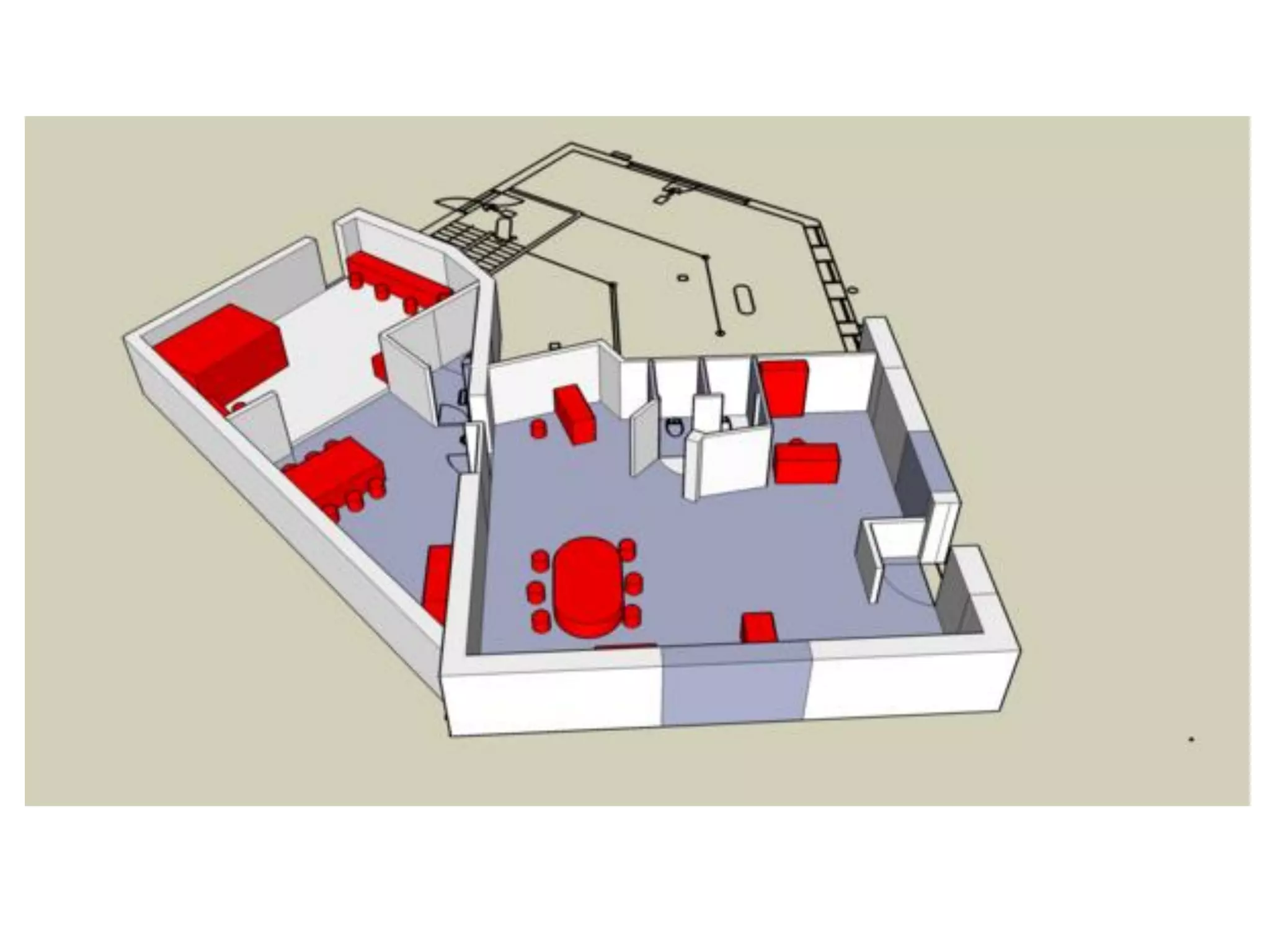
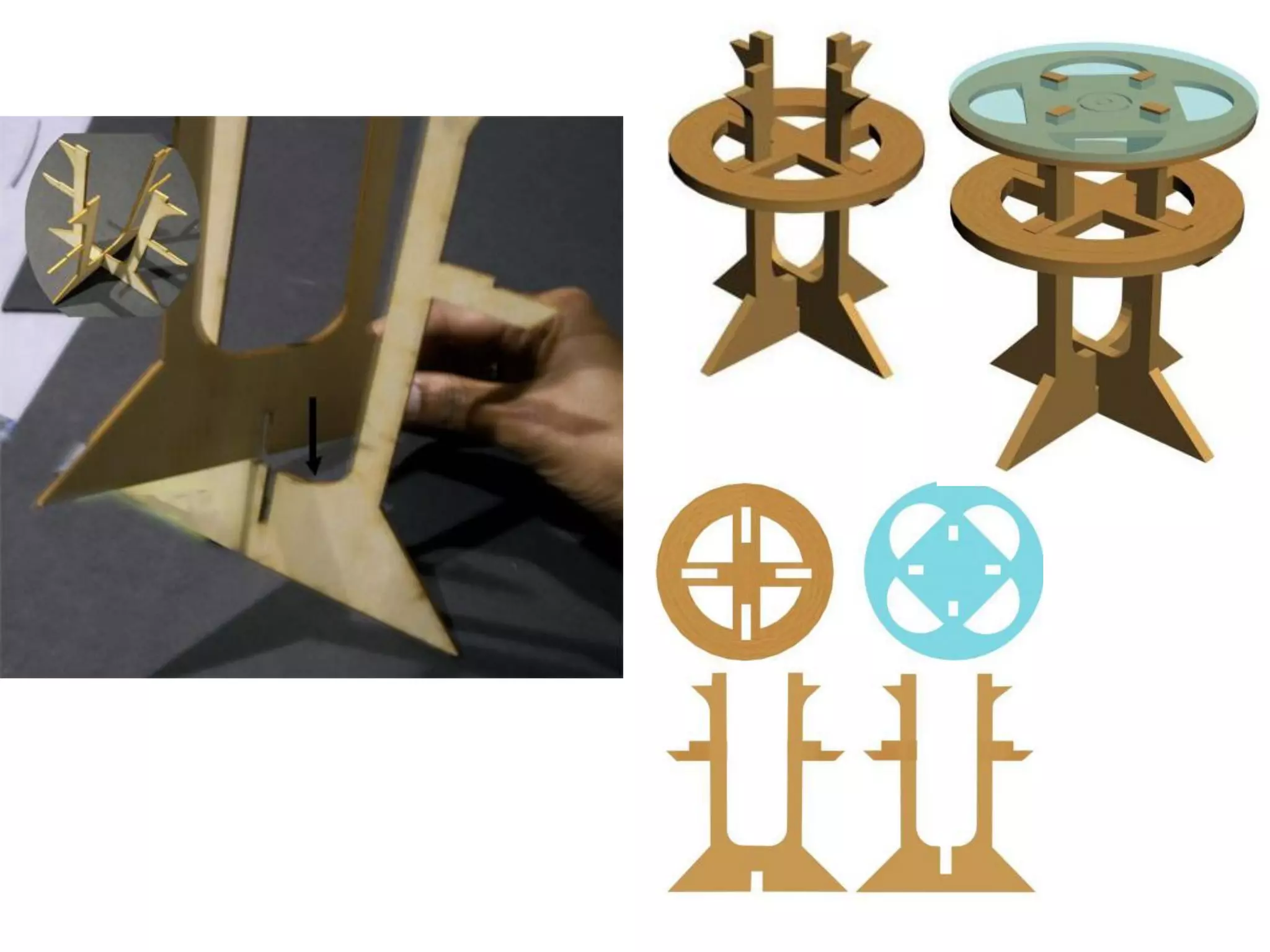
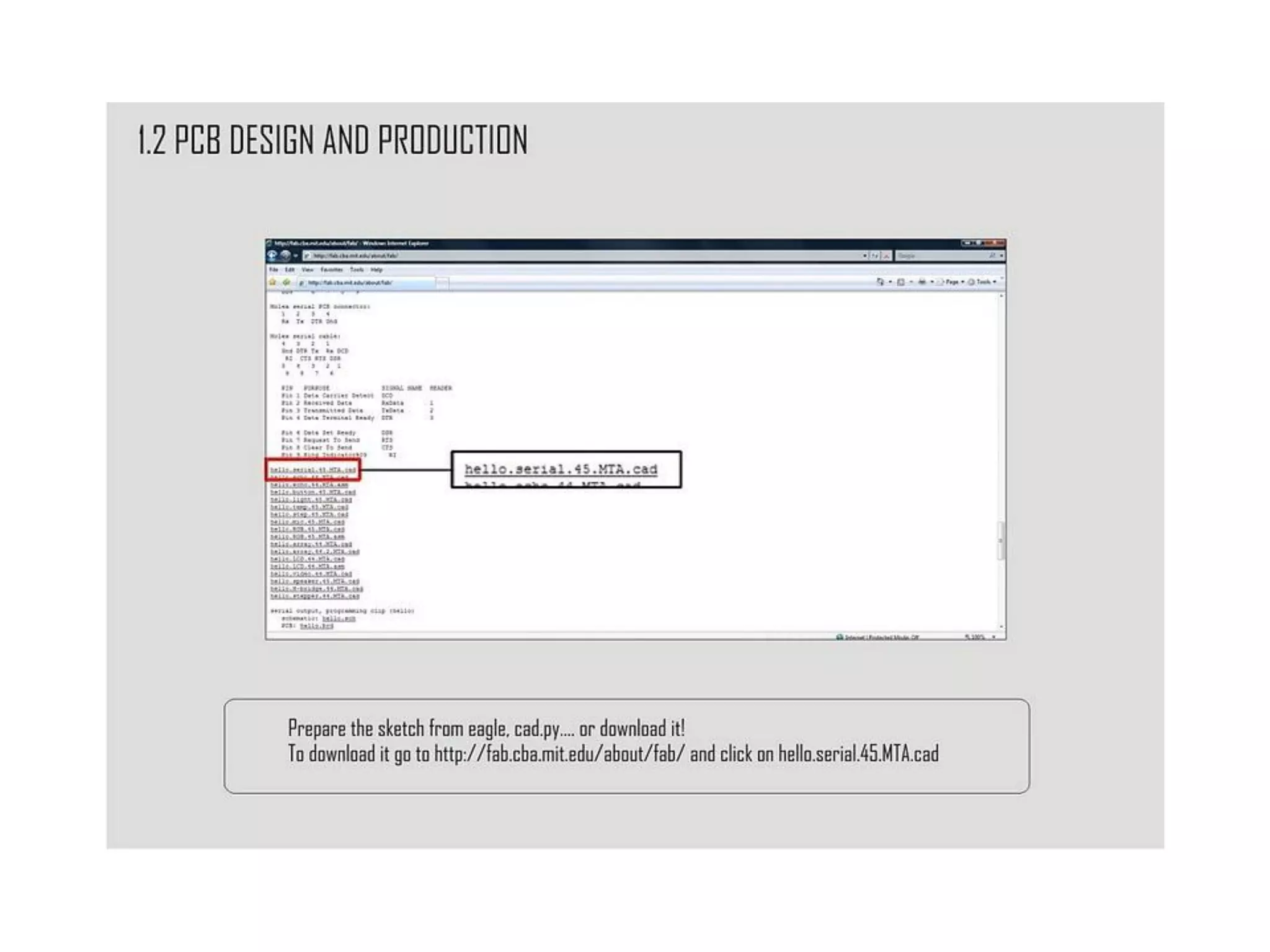
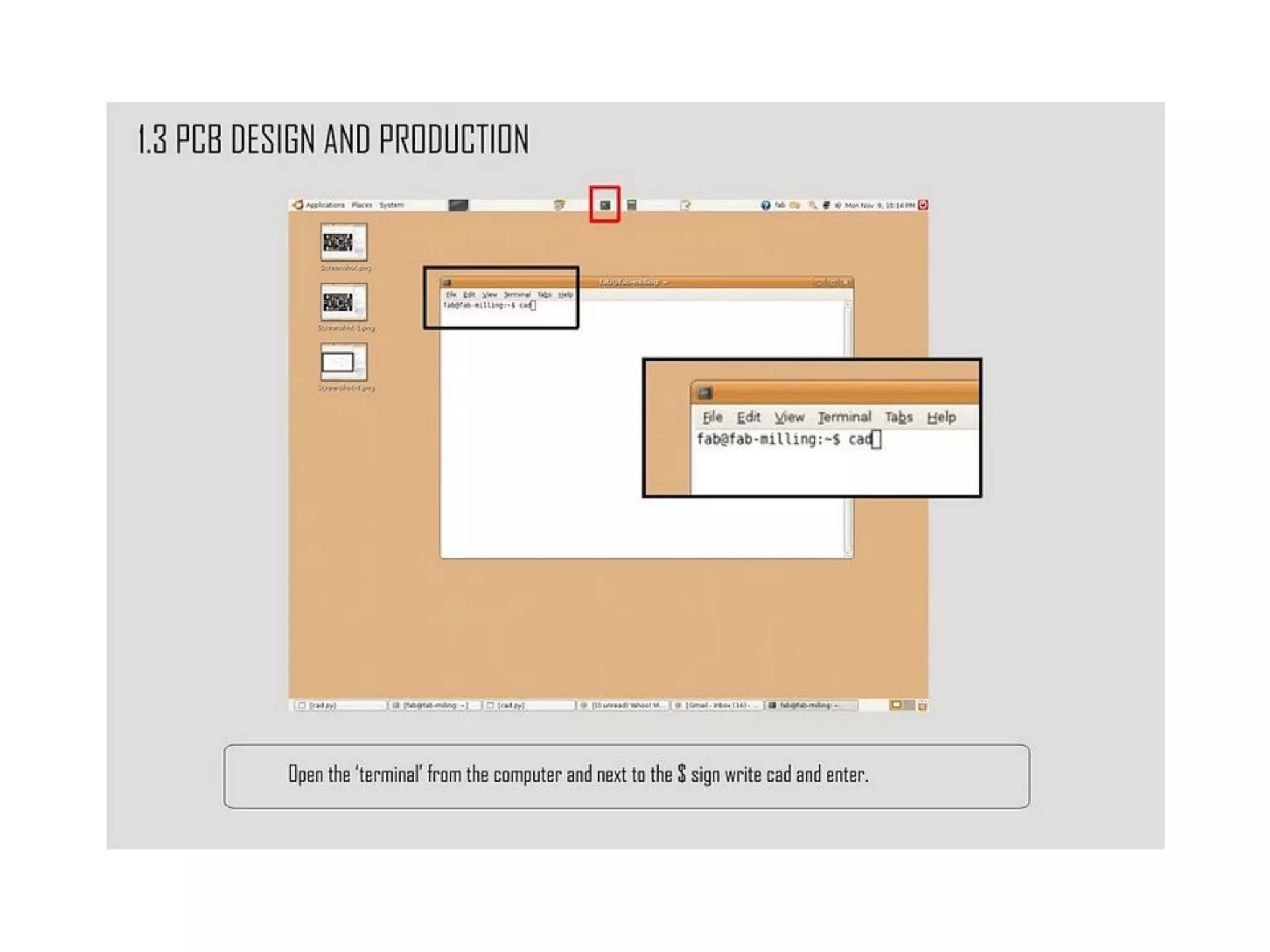
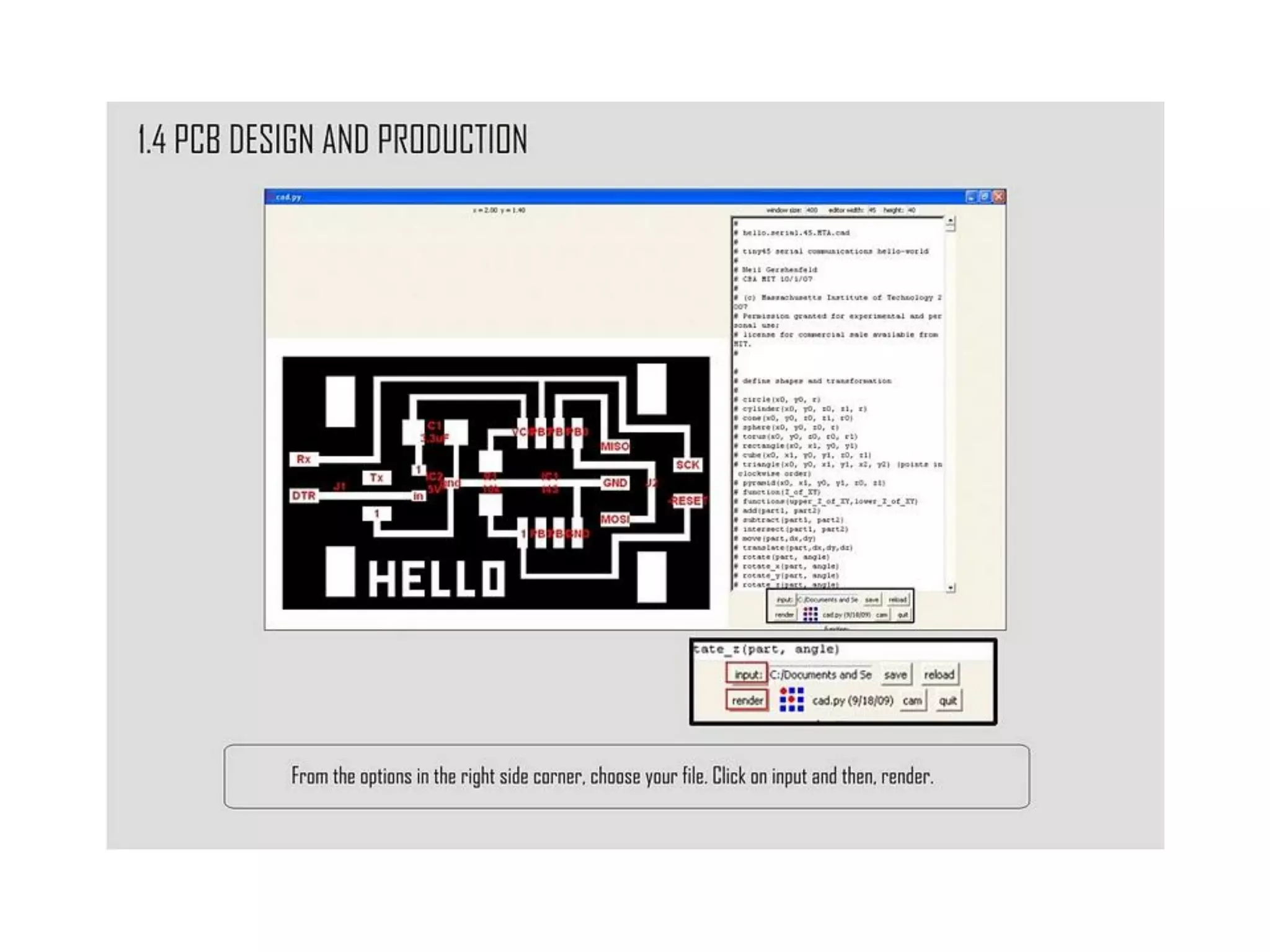
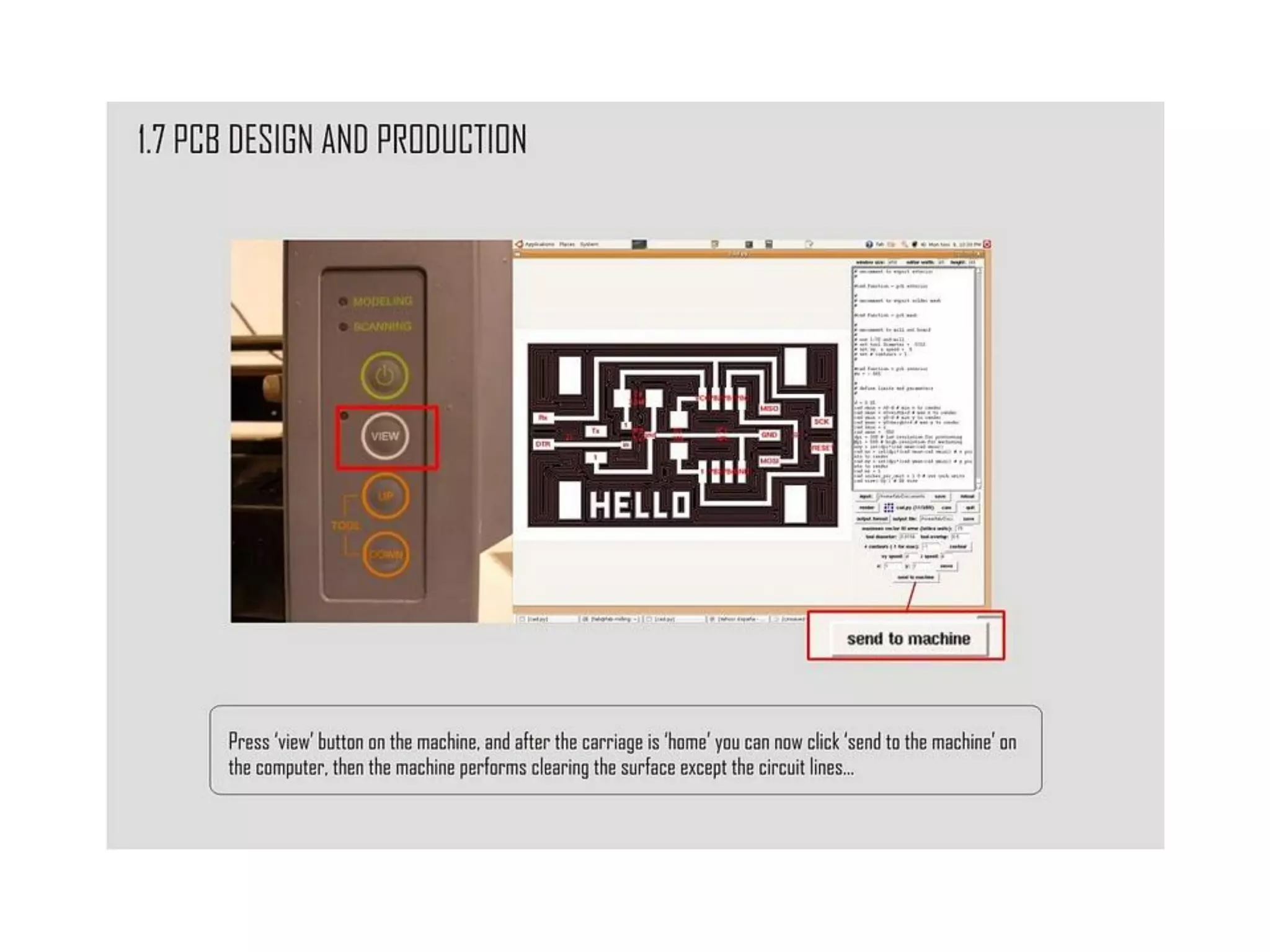
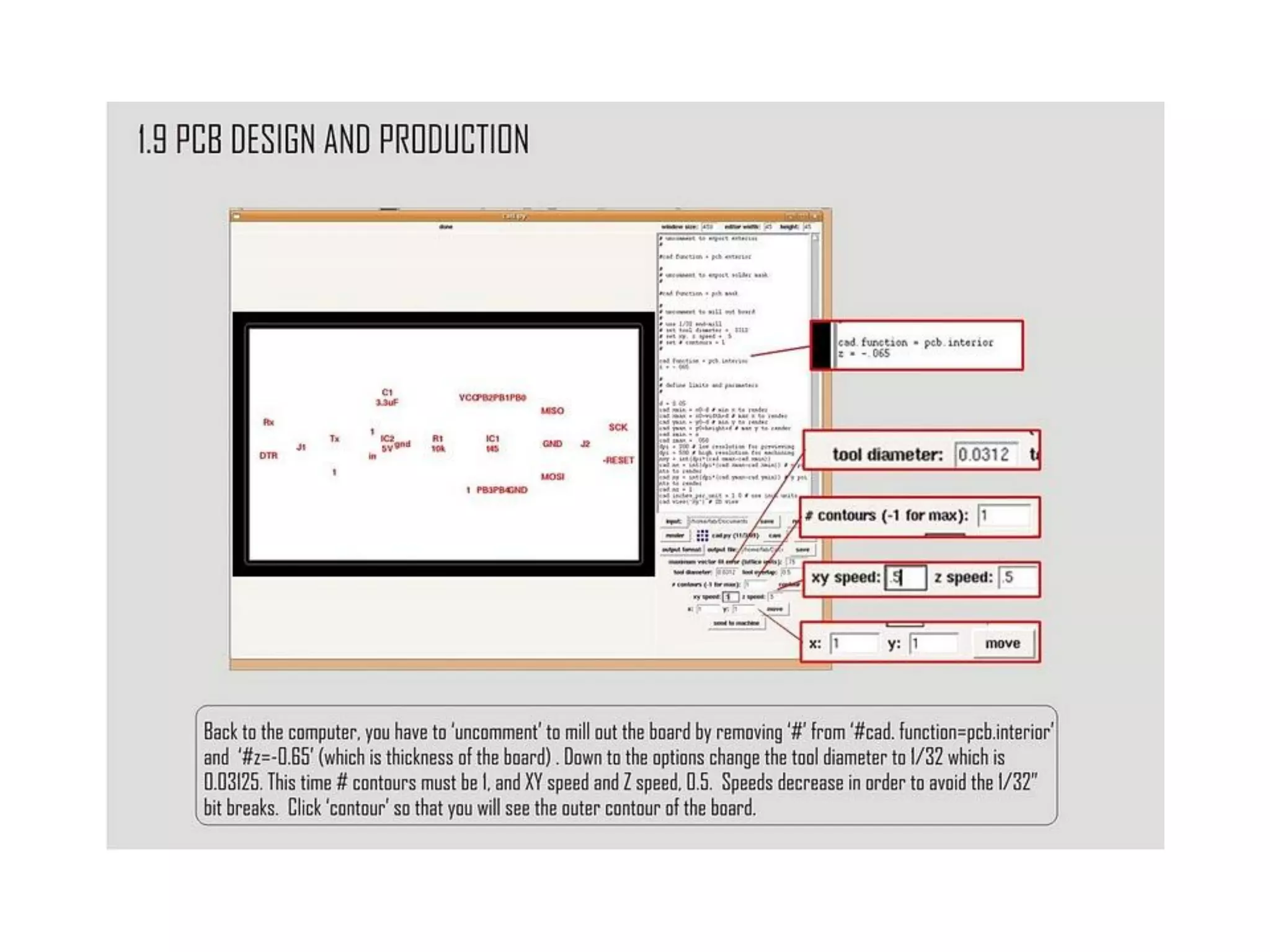
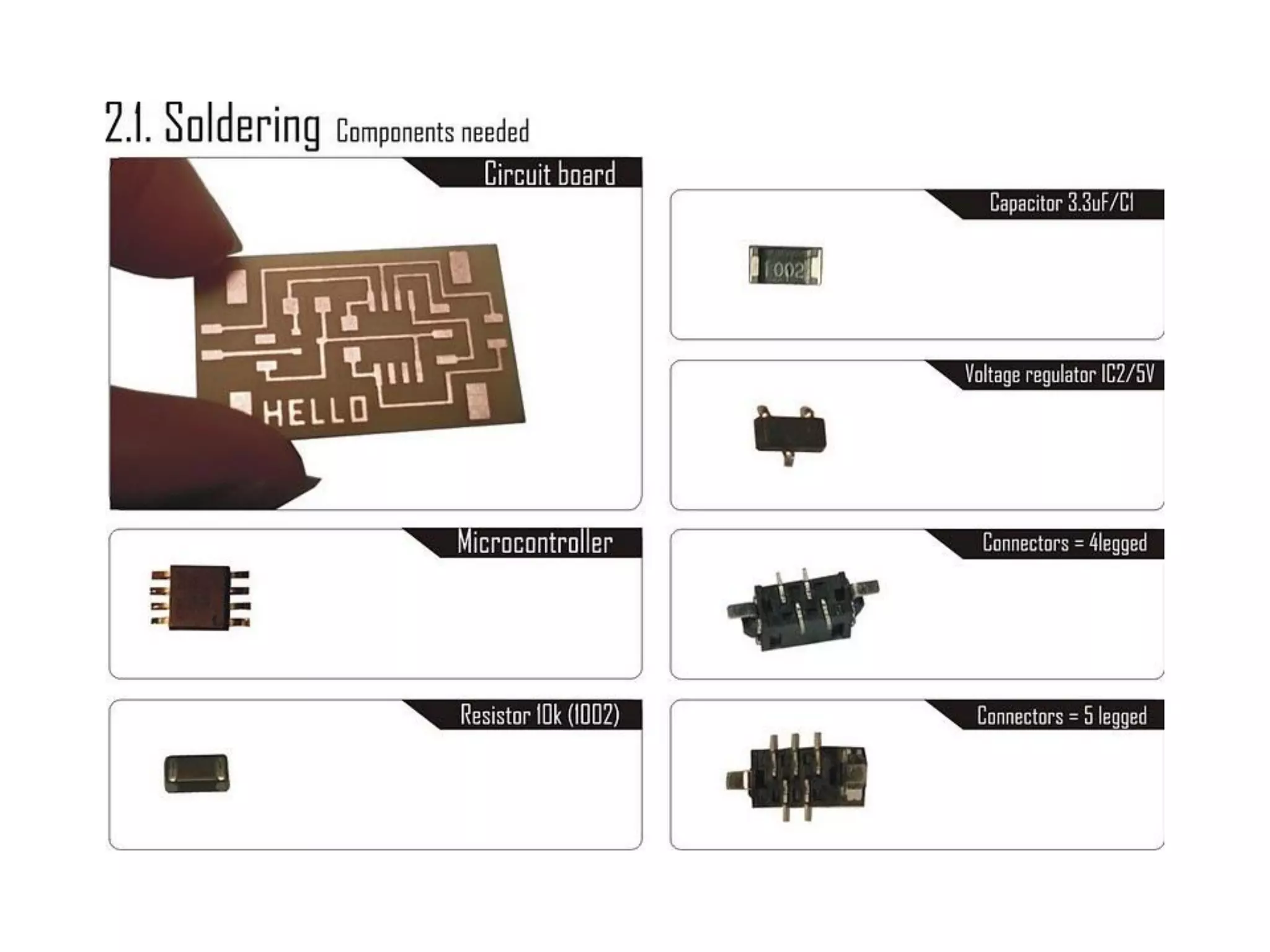
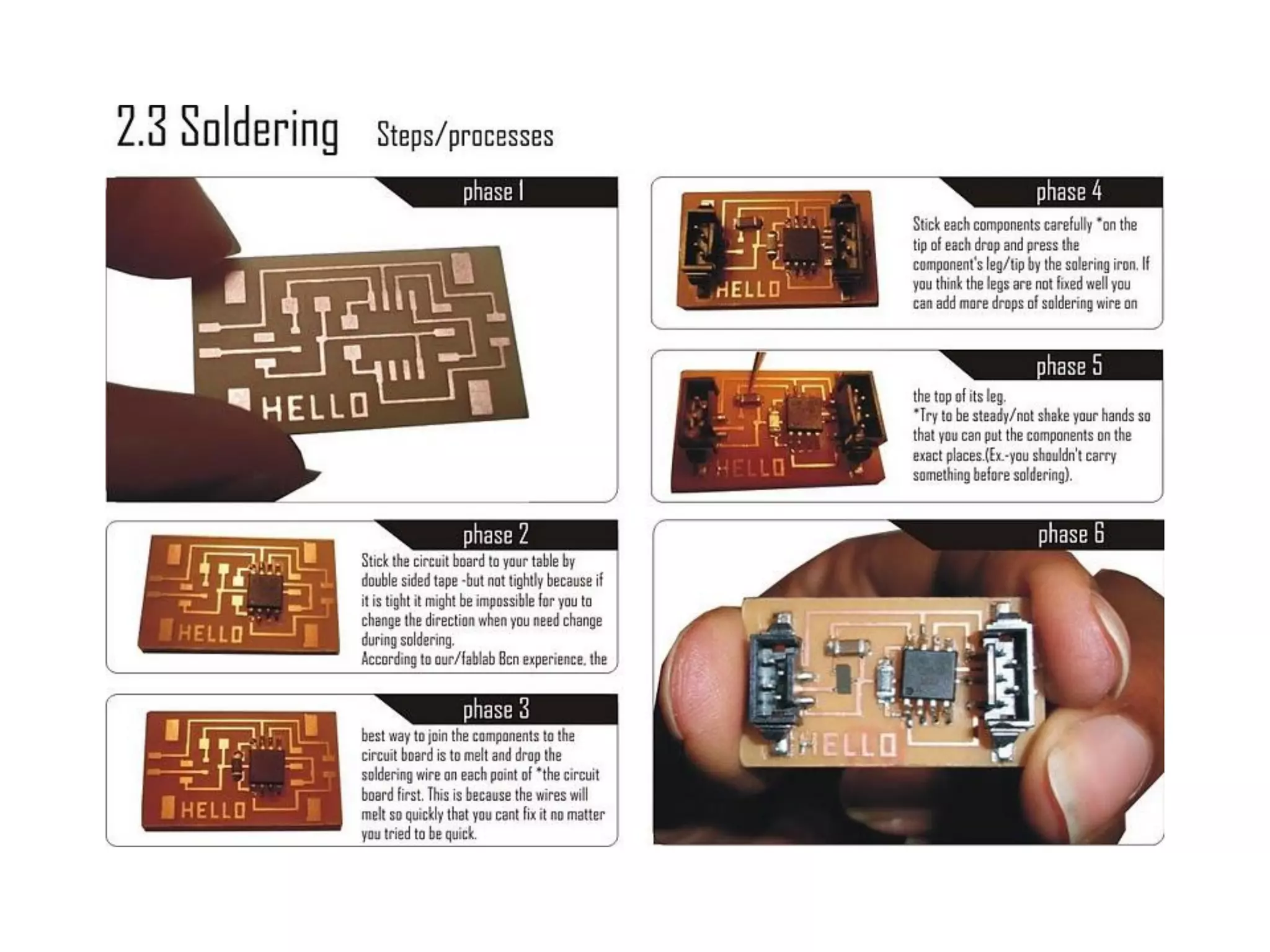
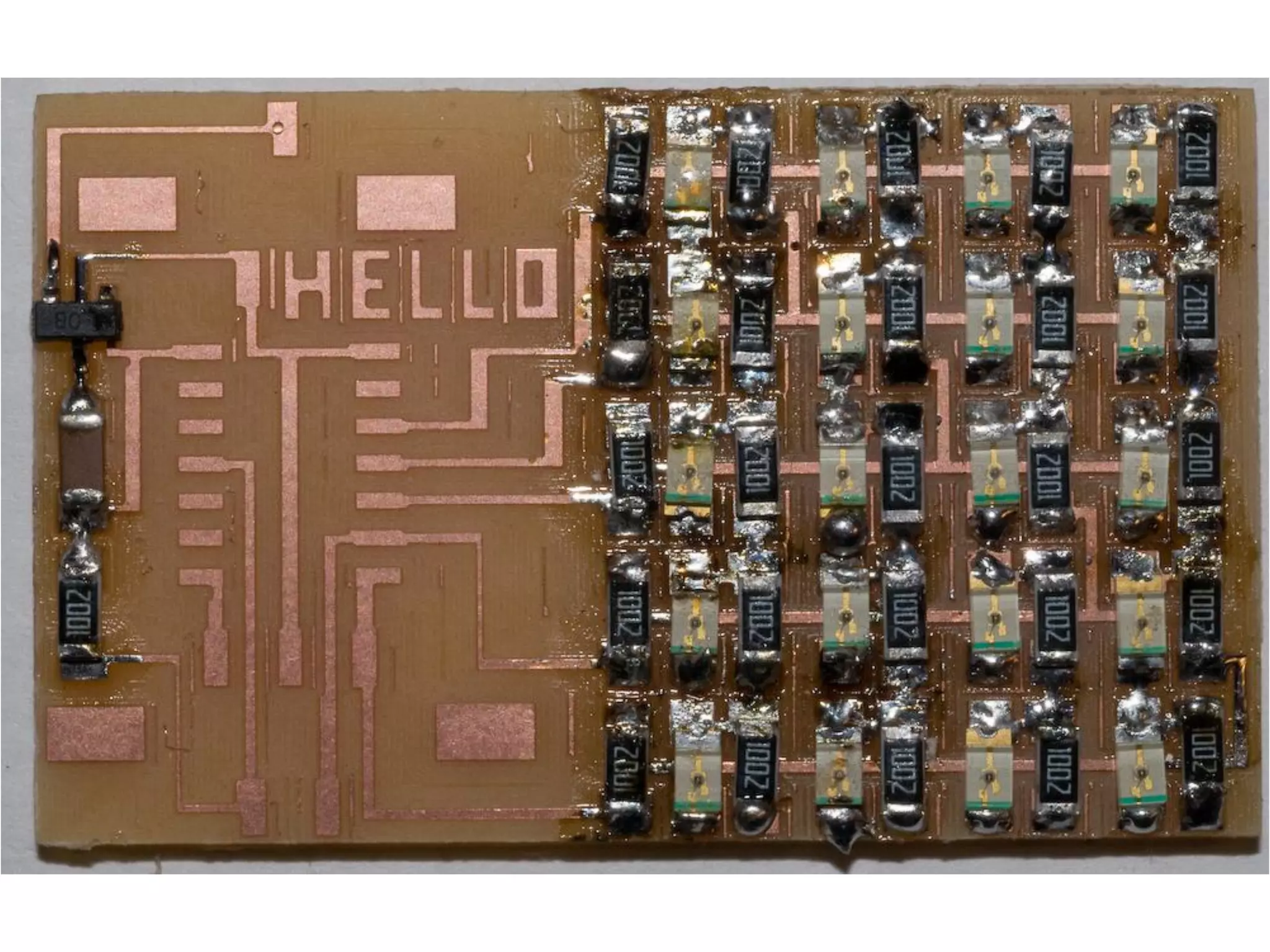
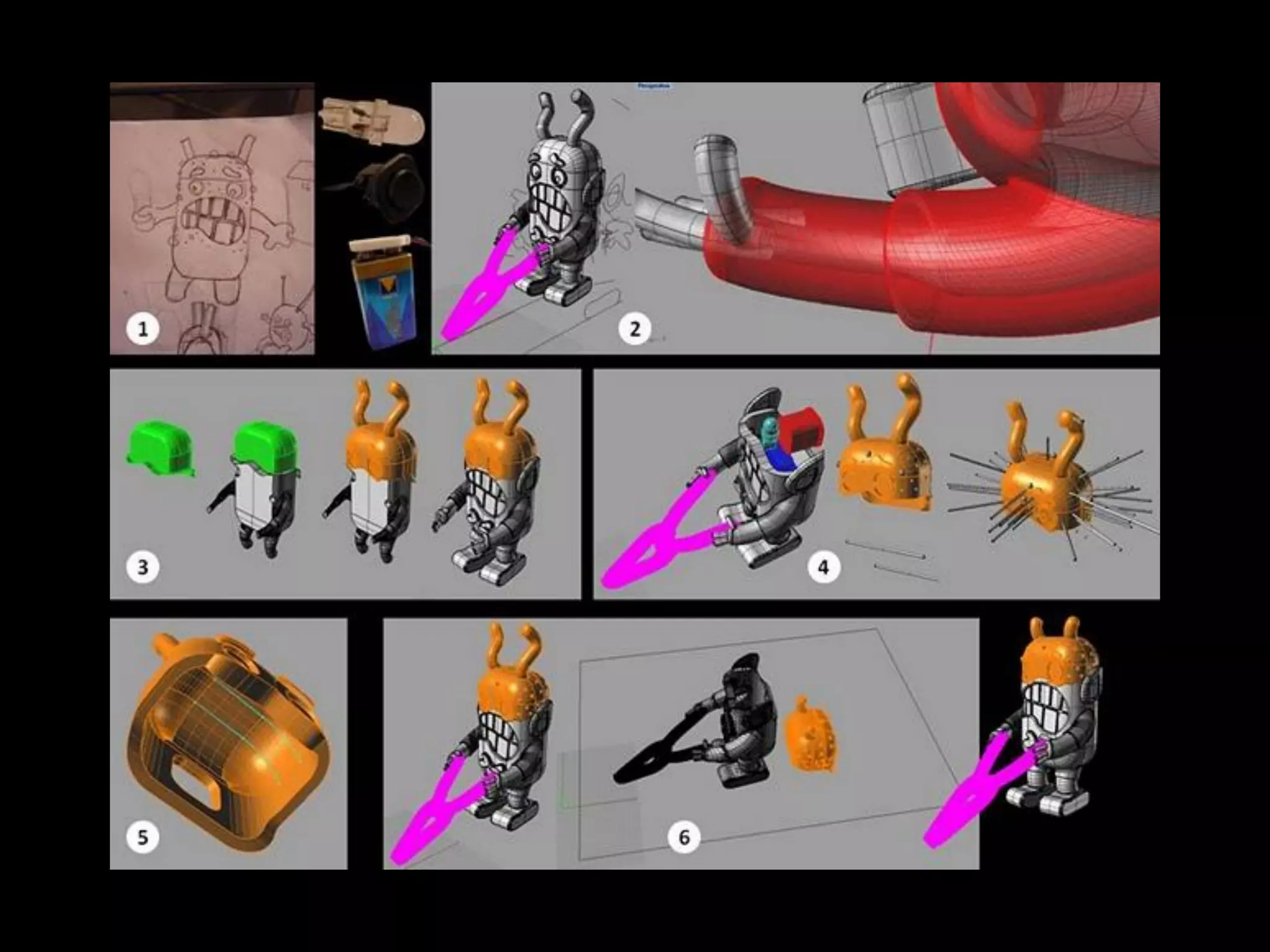
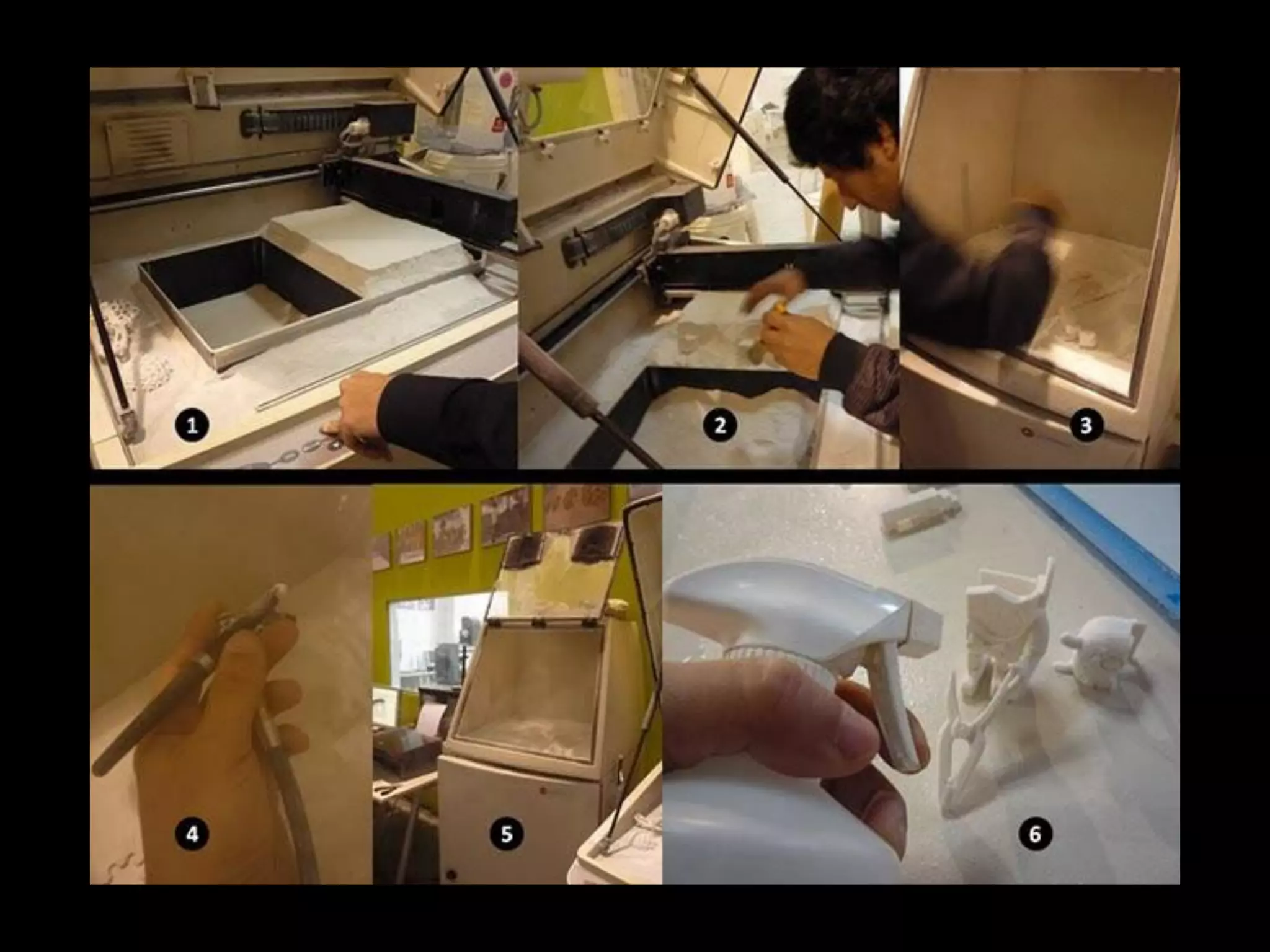
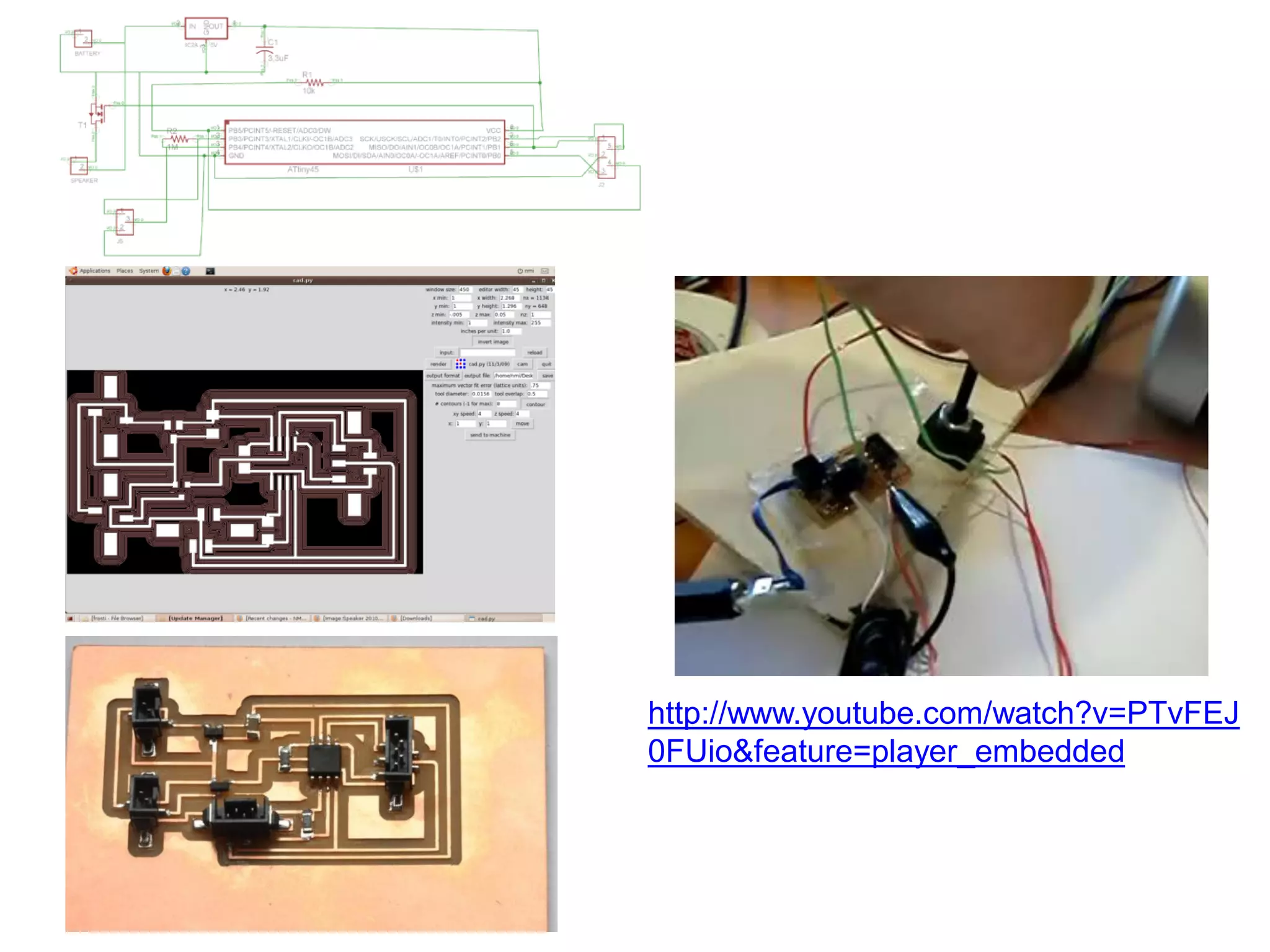
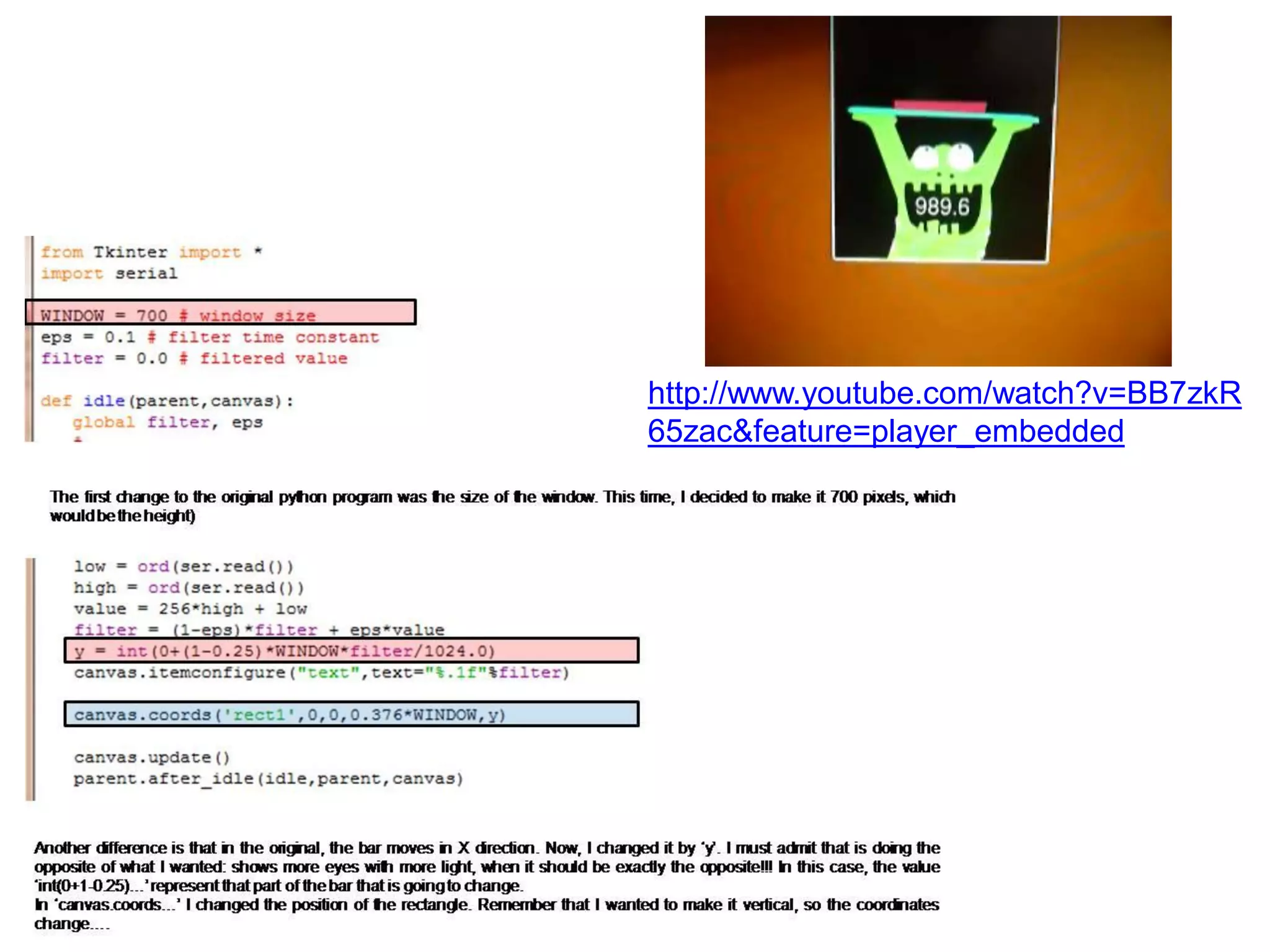
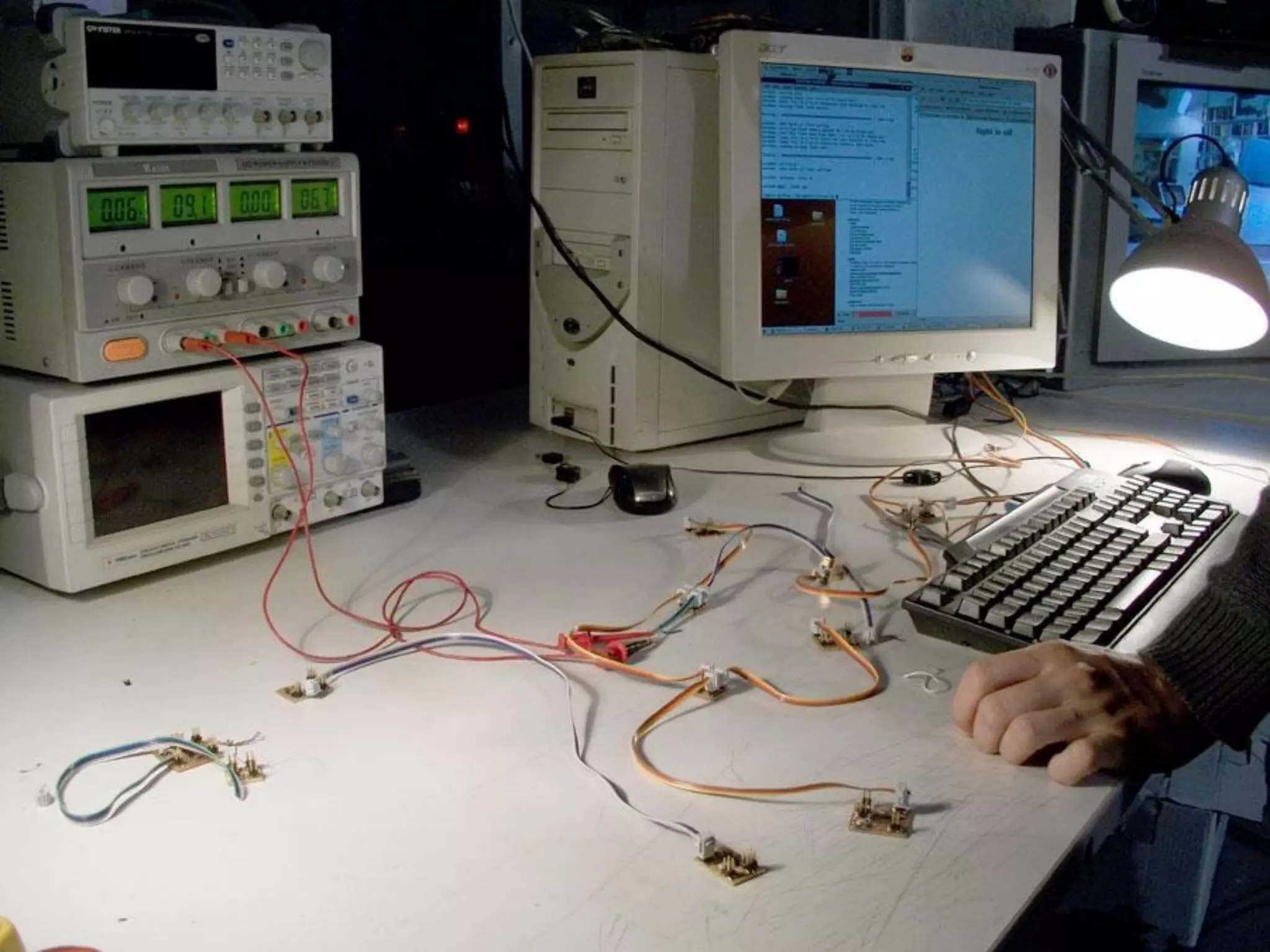
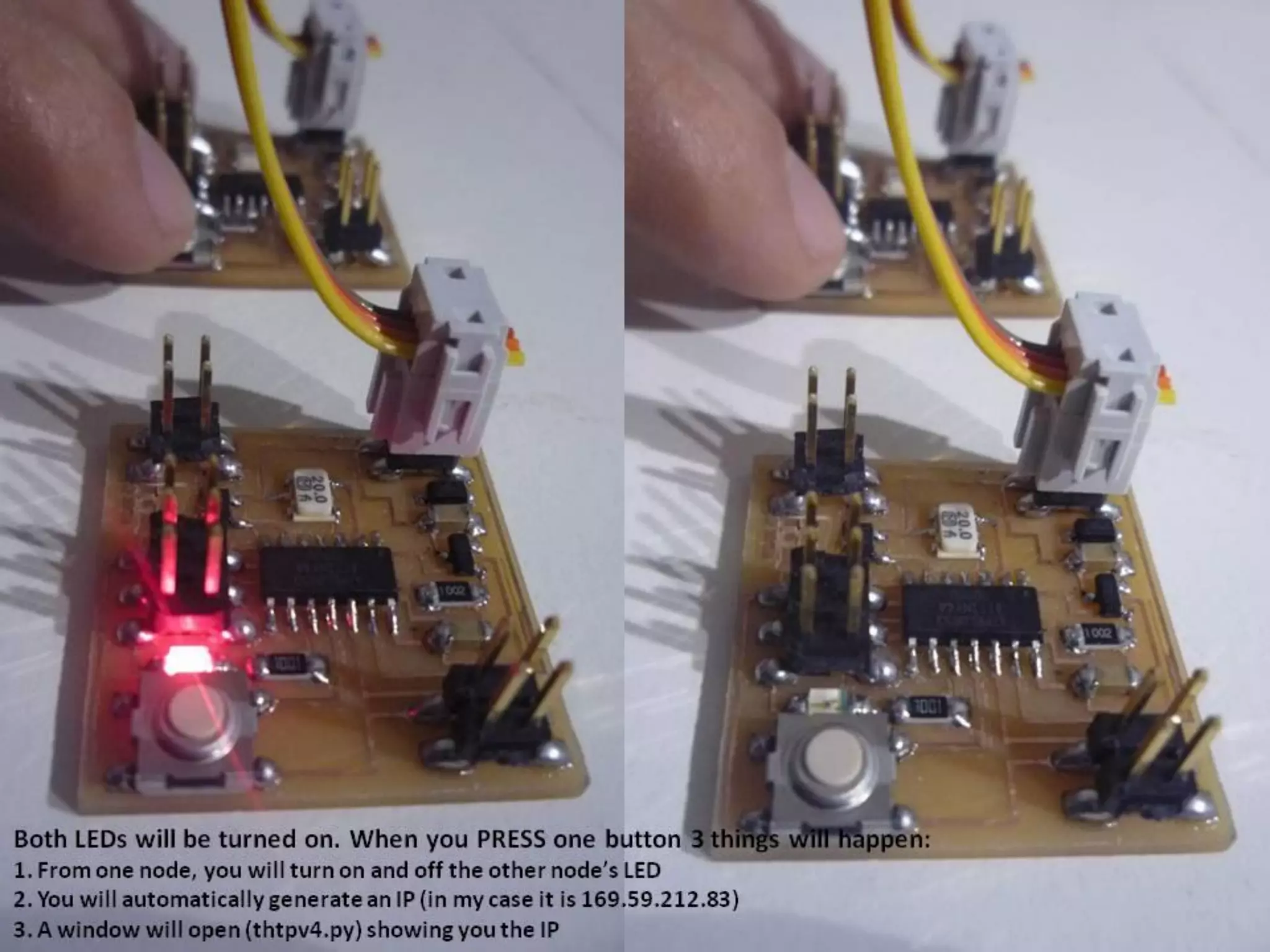
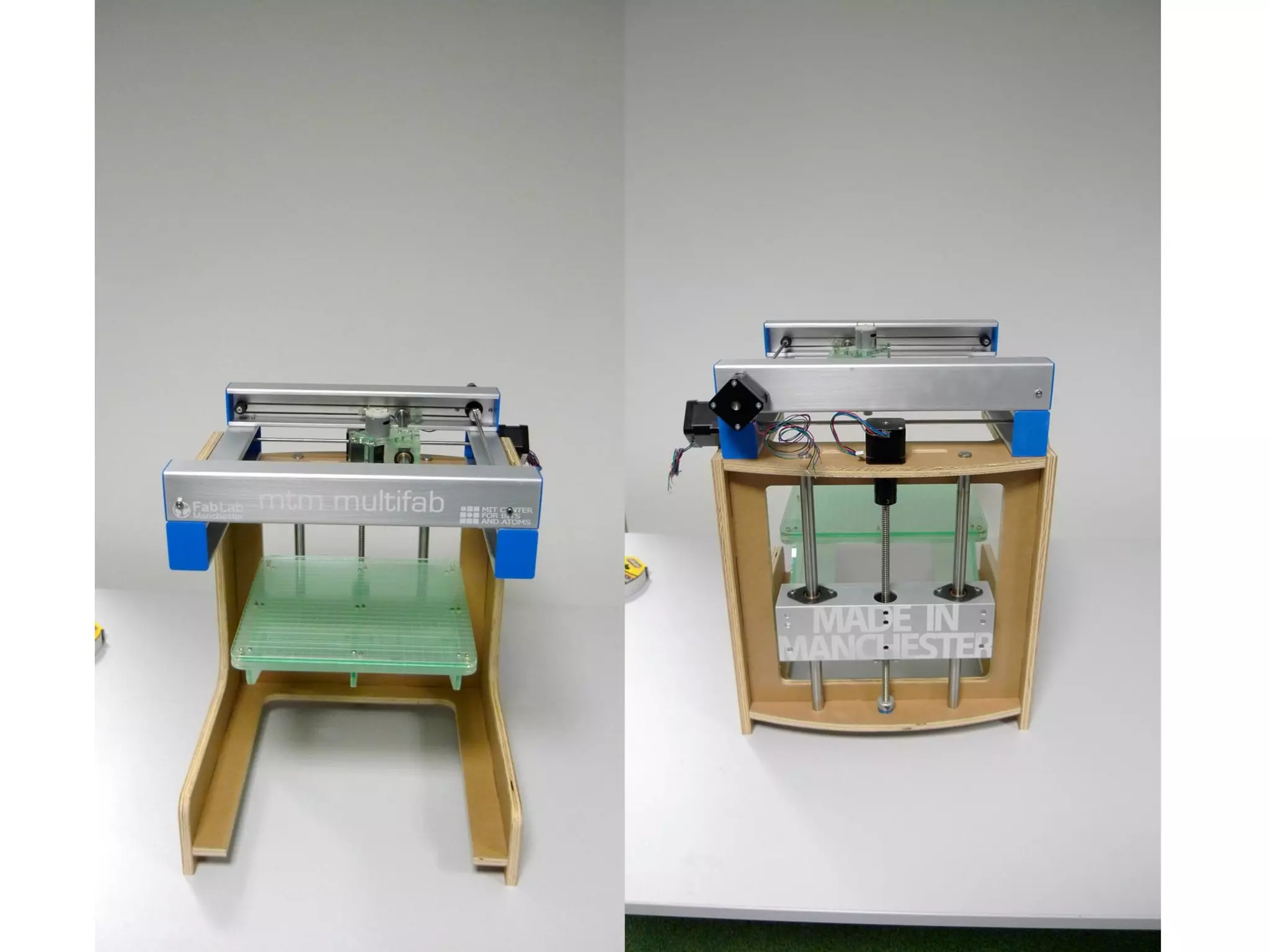
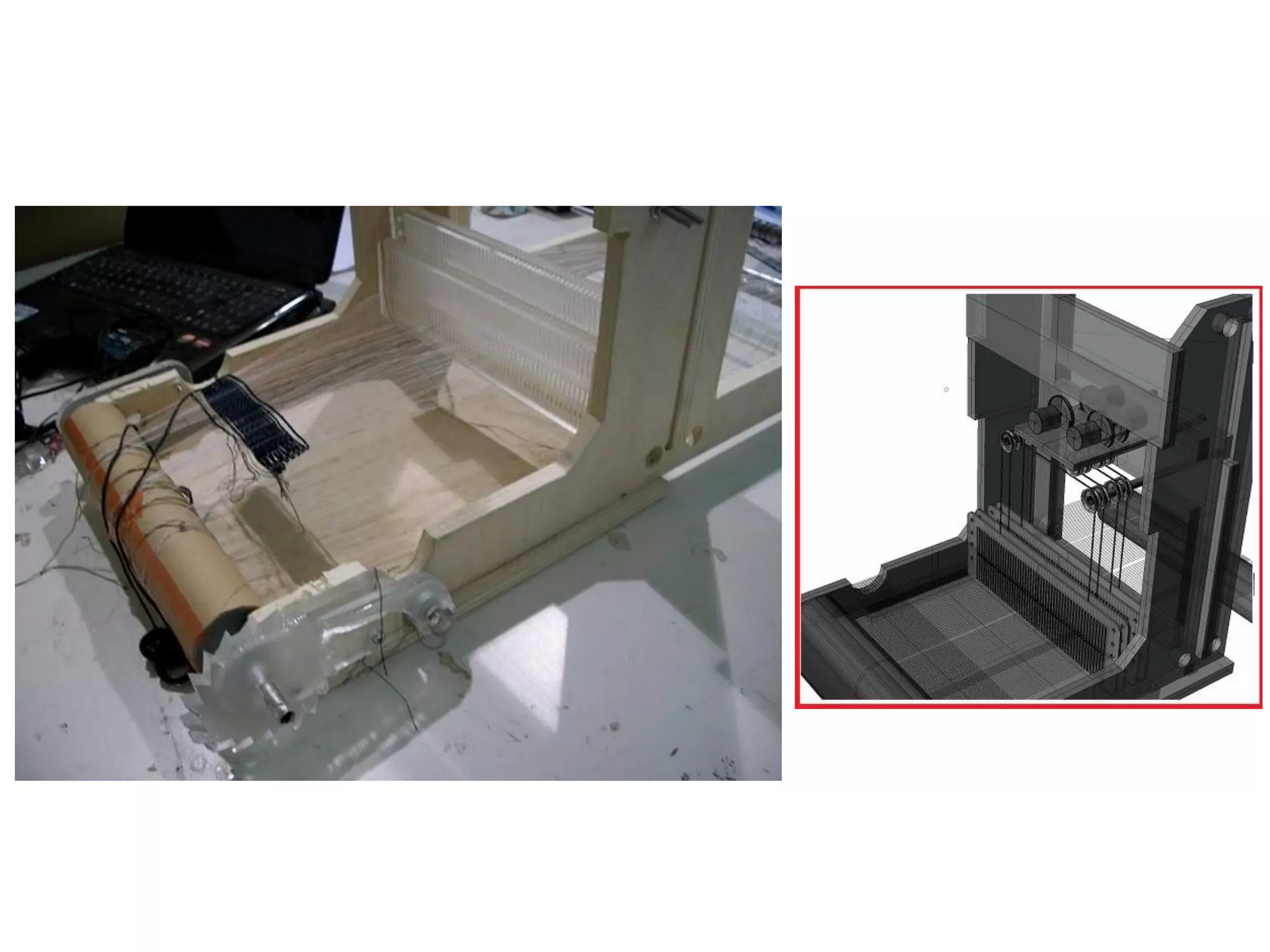
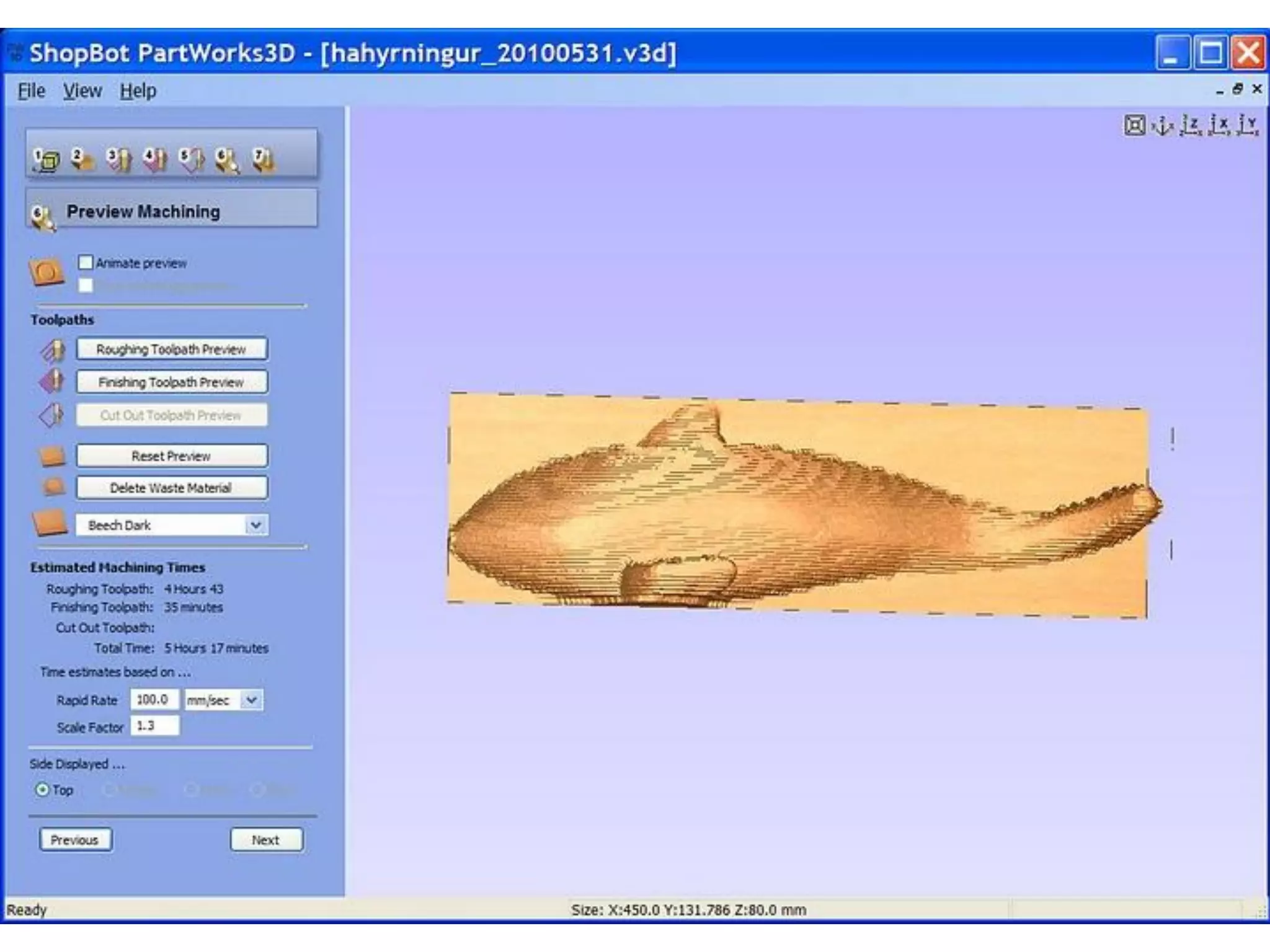
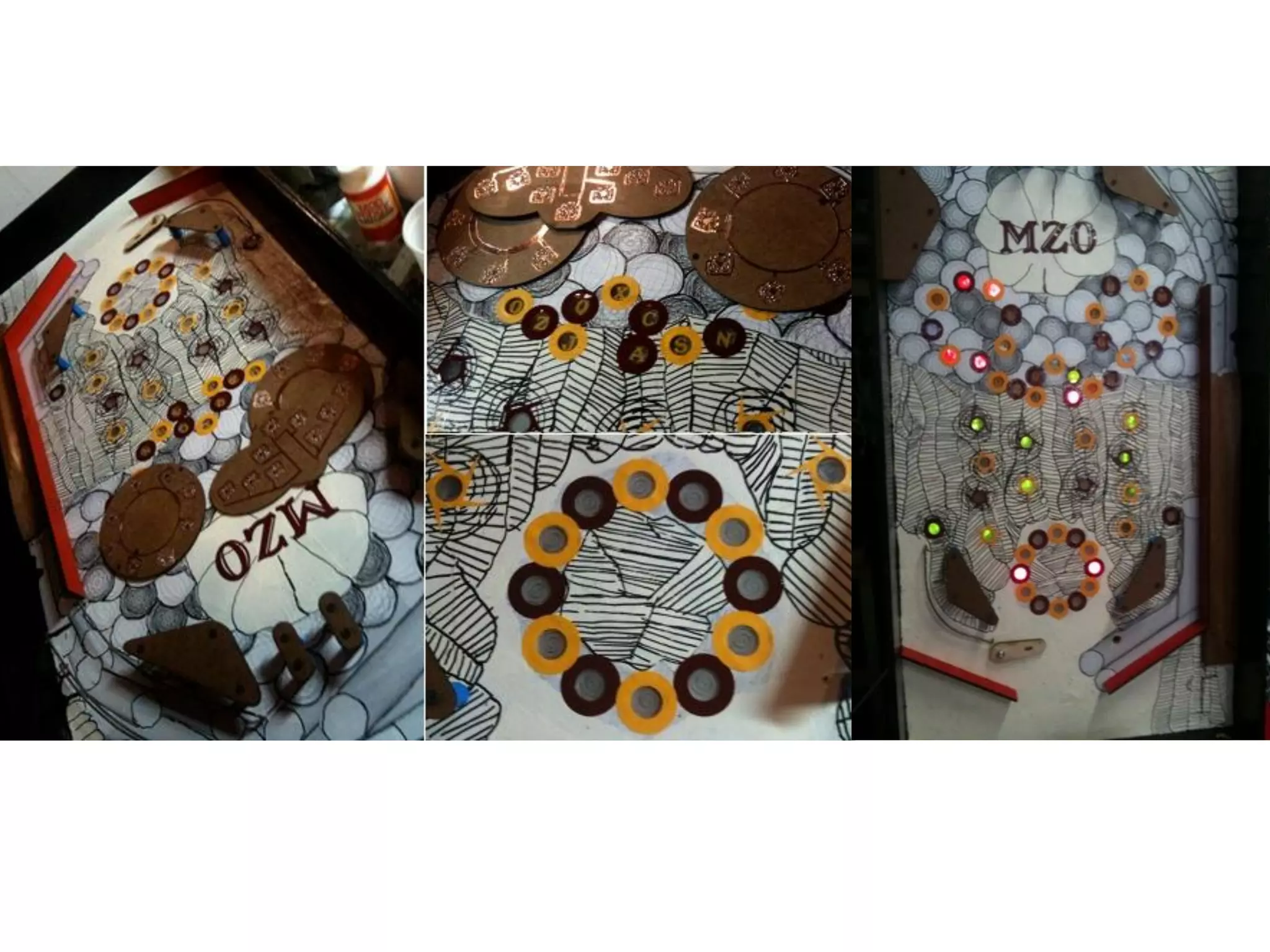This document provides an overview of digital fabrication principles and practices including:
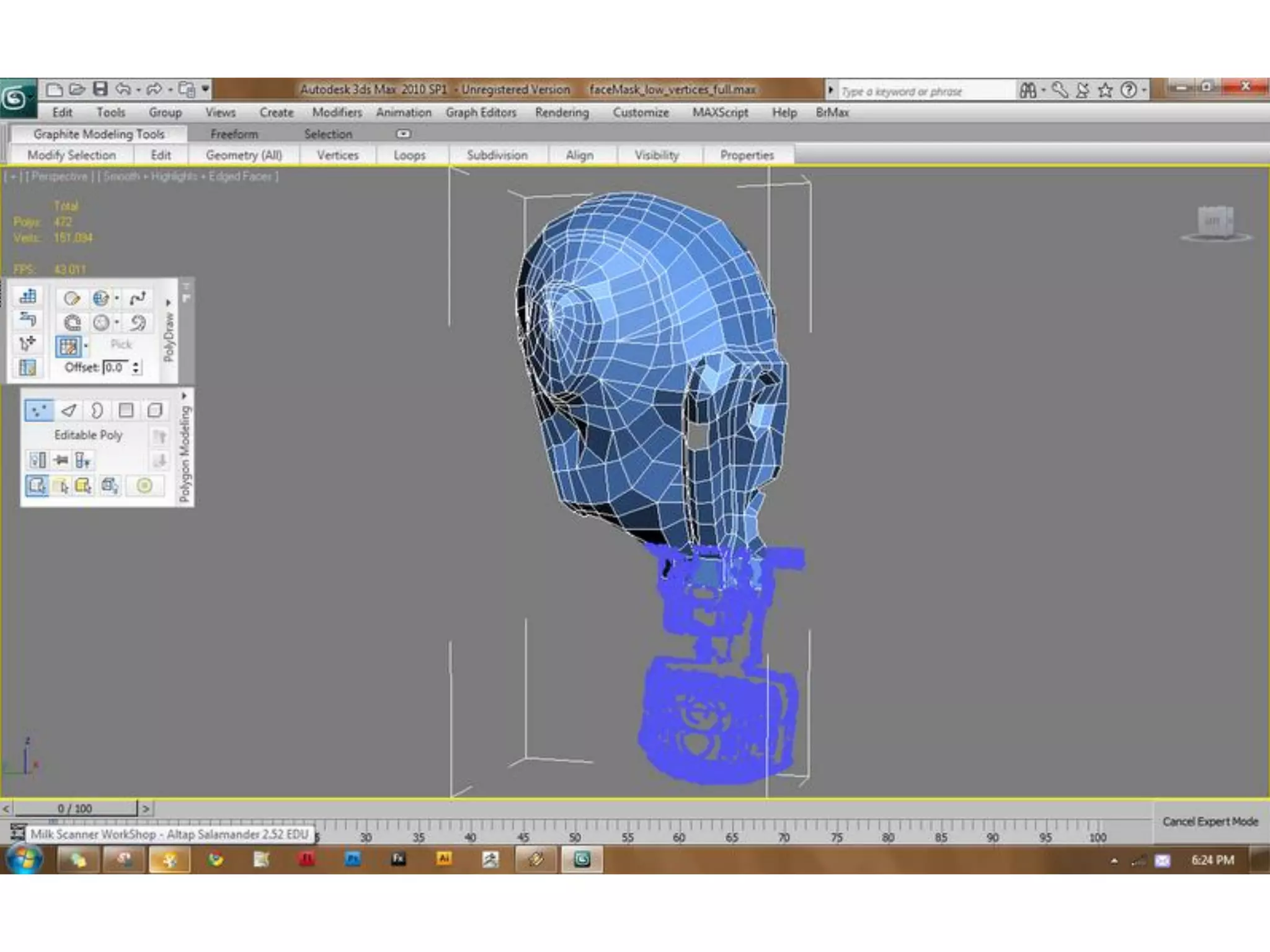
1. Computer aided design, manufacturing, and modeling techniques for 2D and 3D design.
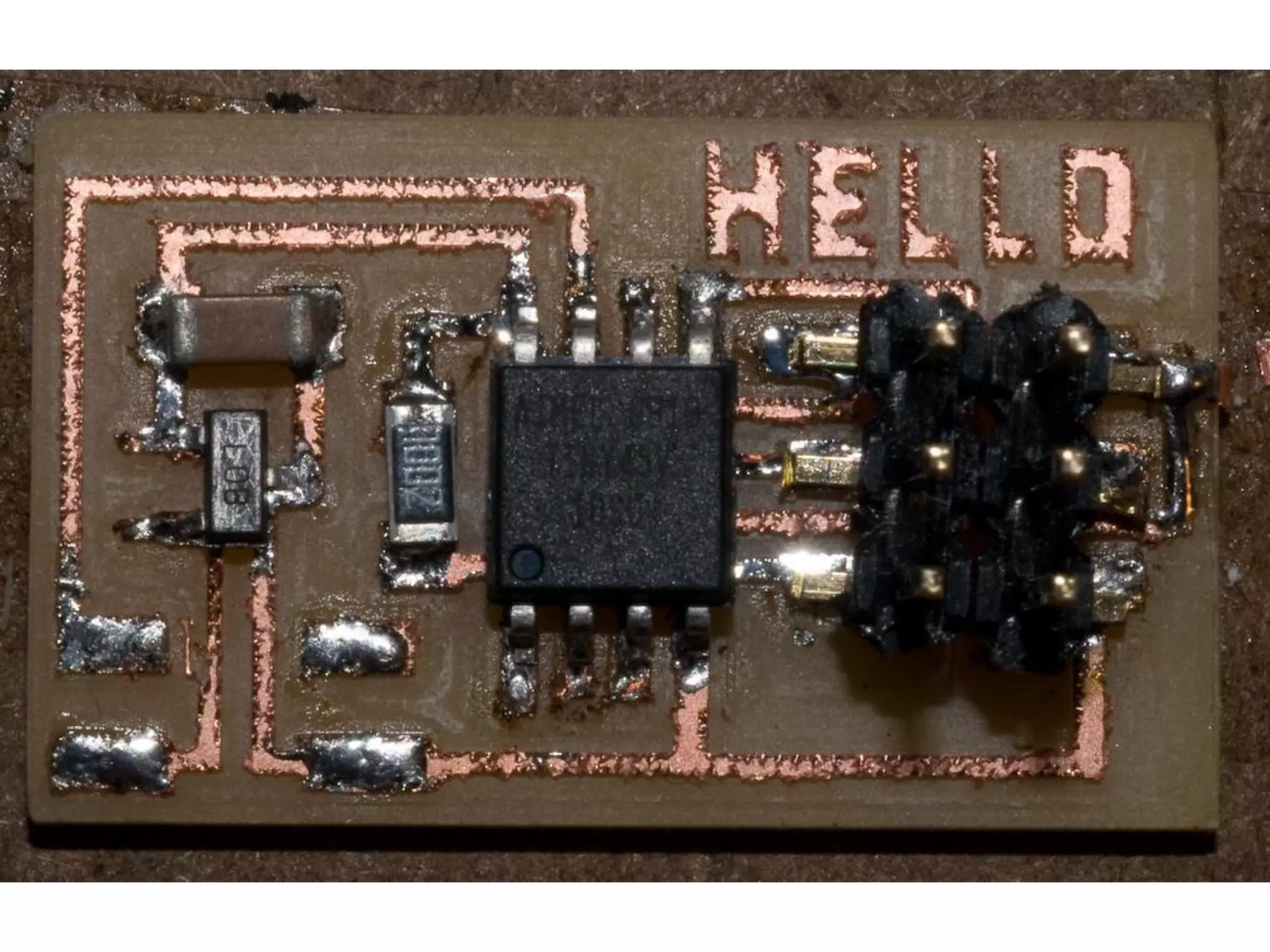
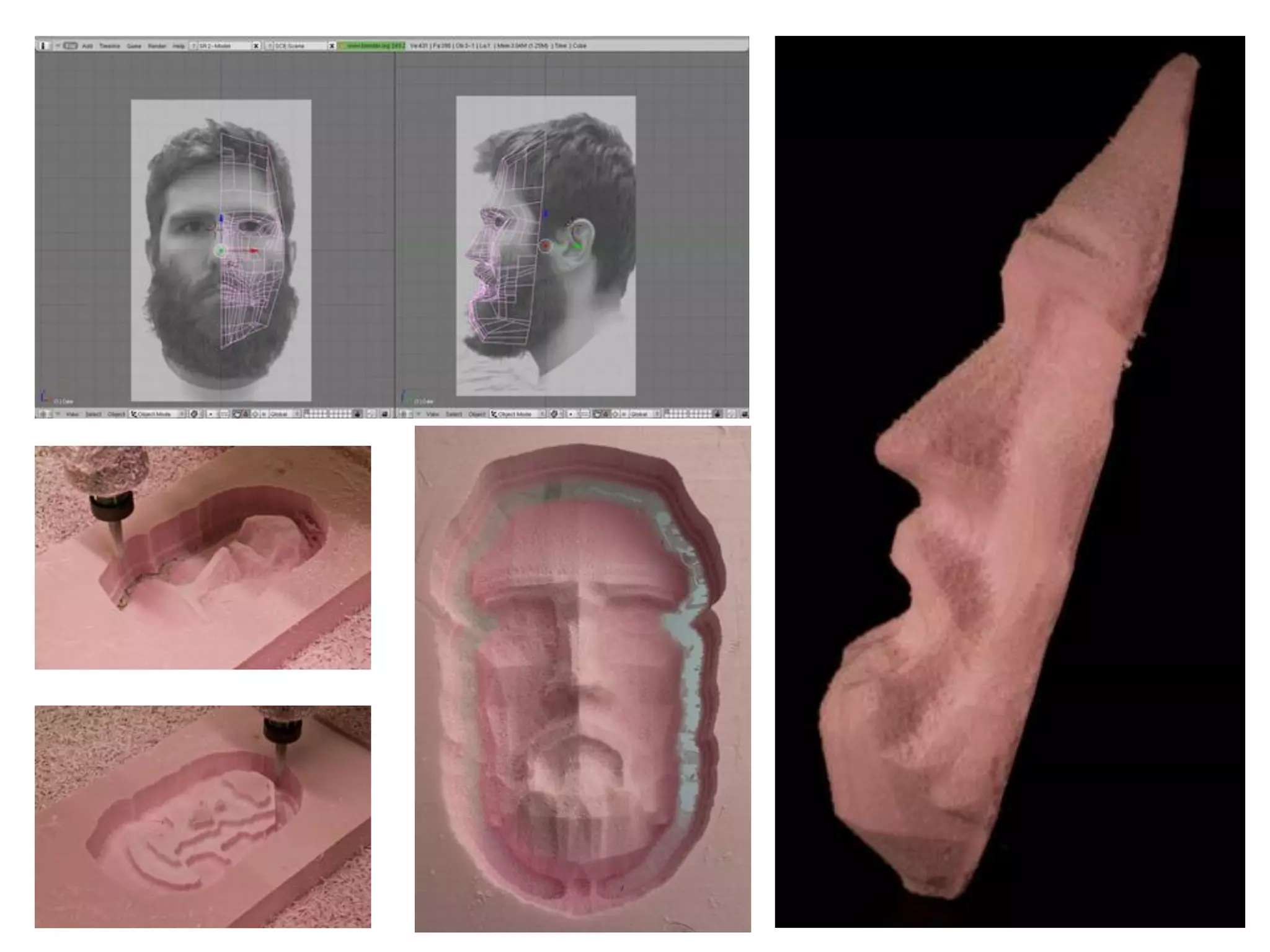
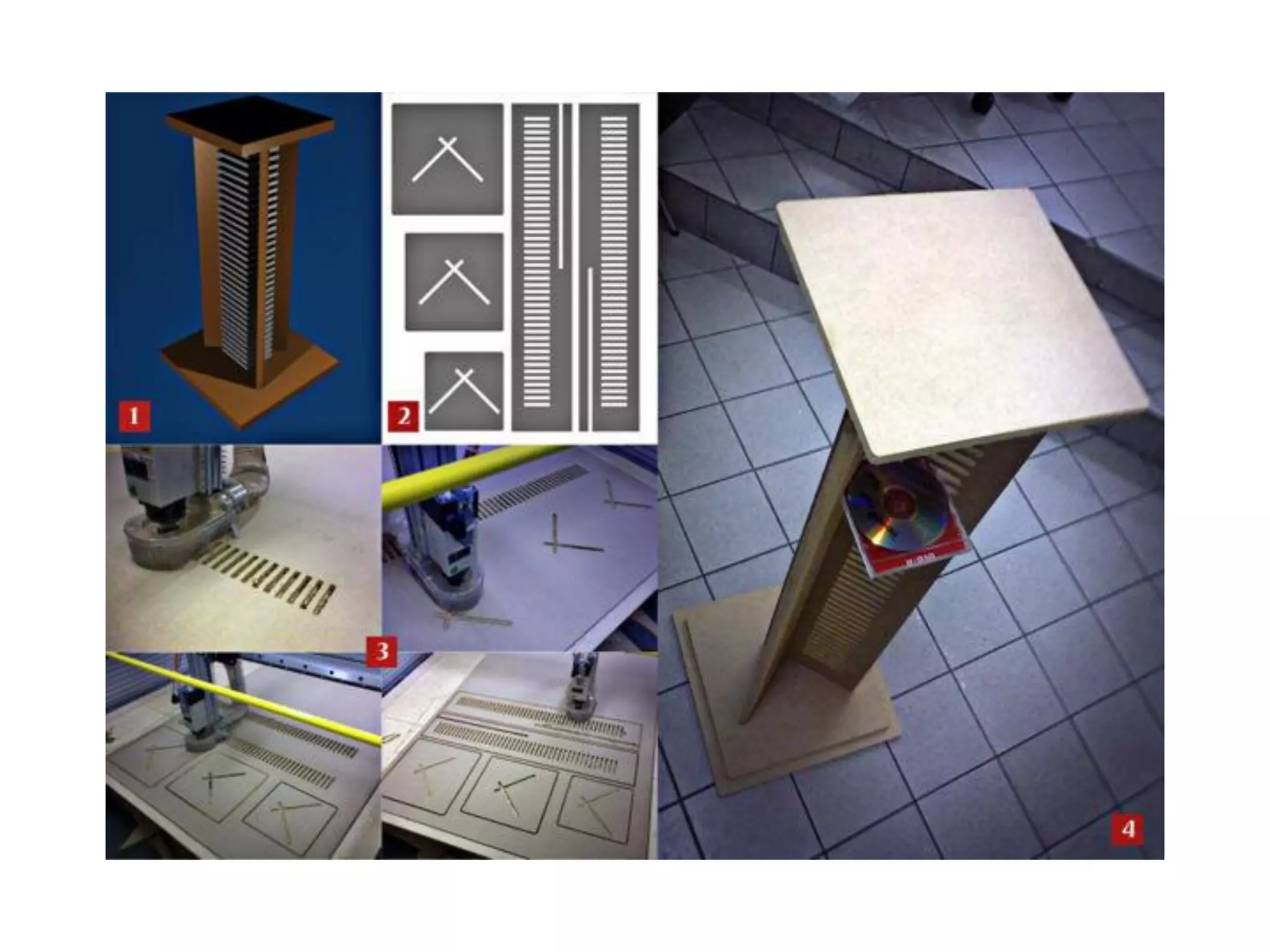
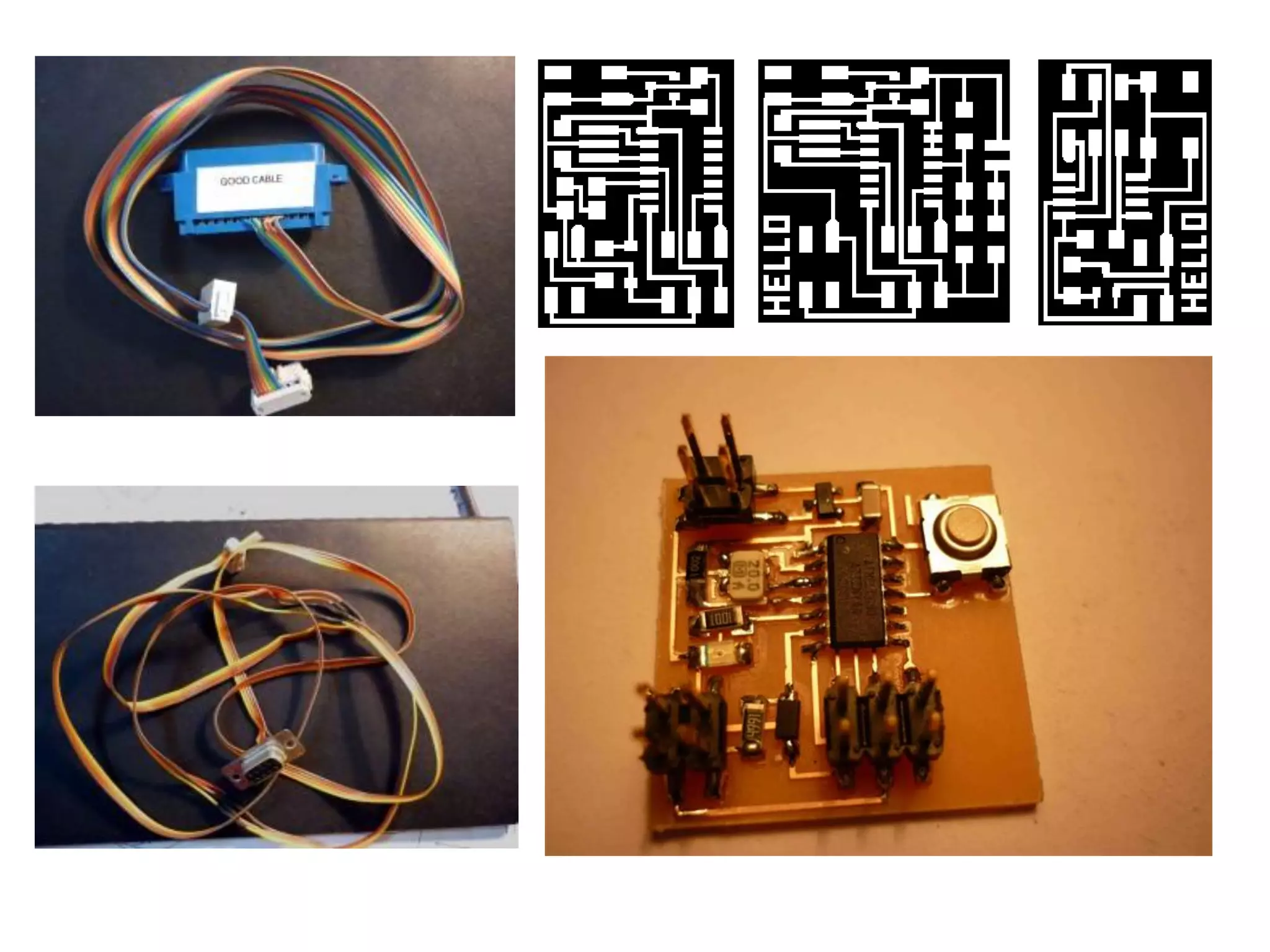
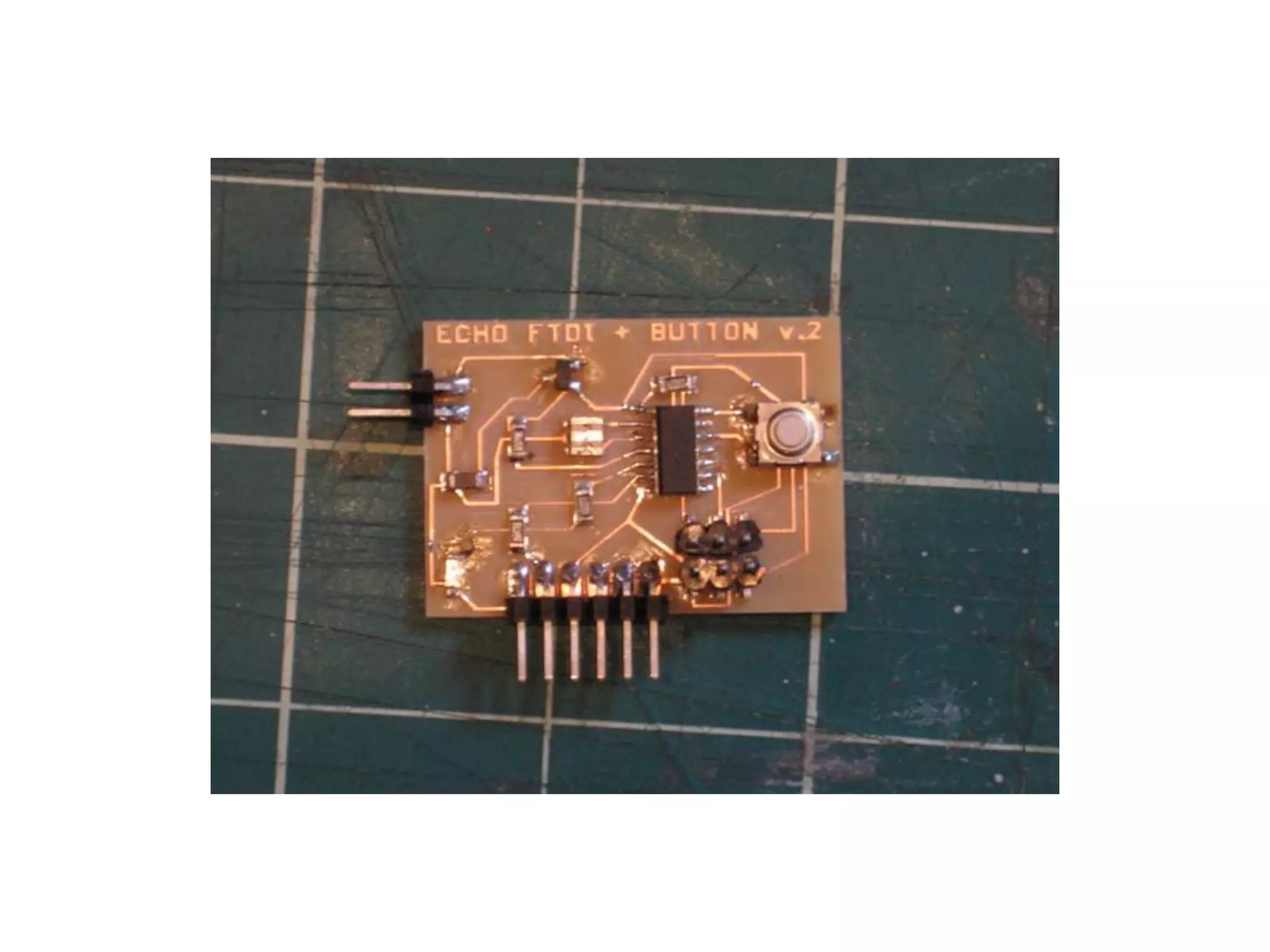
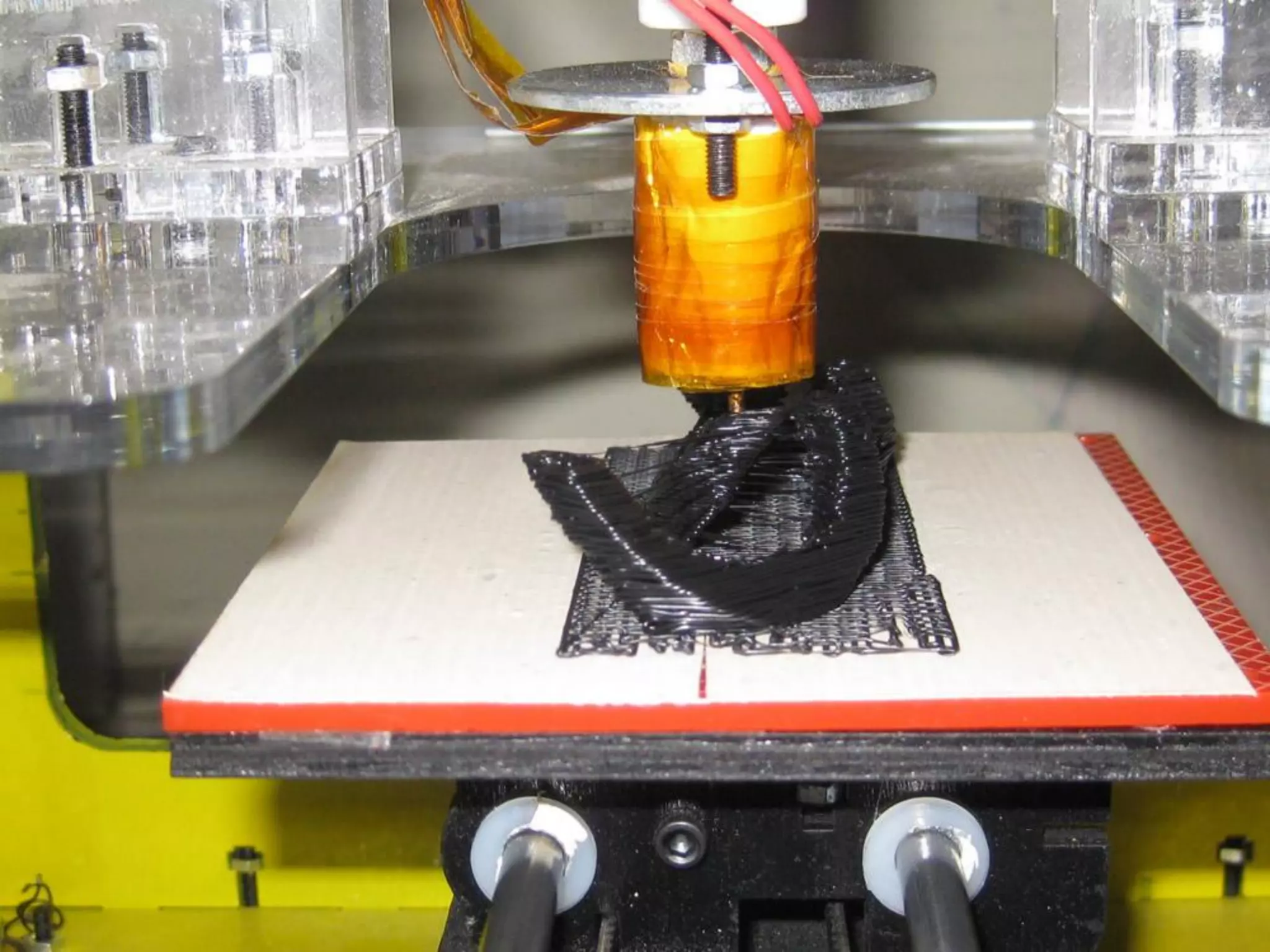
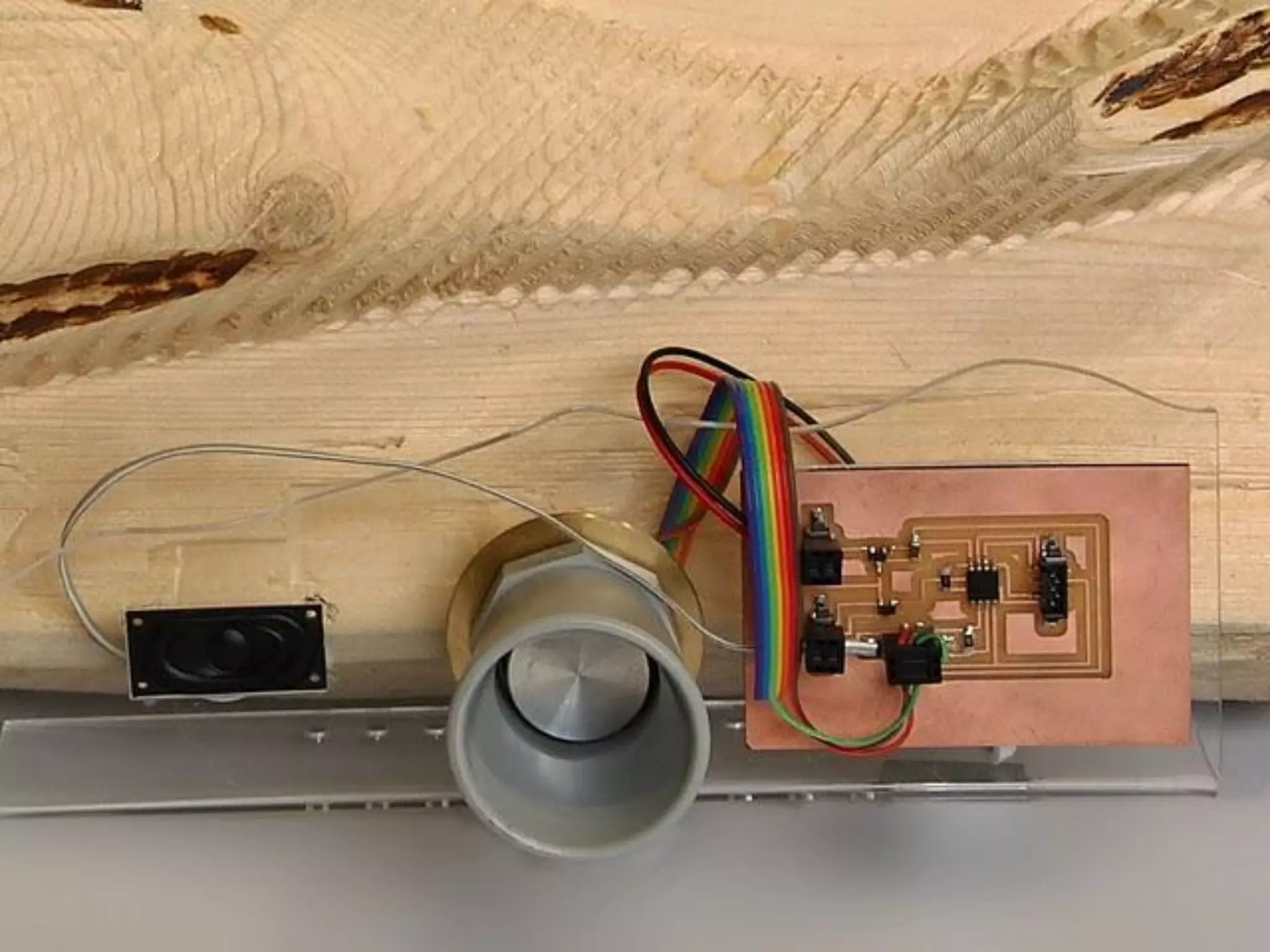
2. Computer controlled cutting, milling, and machining tools for electronics, wood, and metalworking.
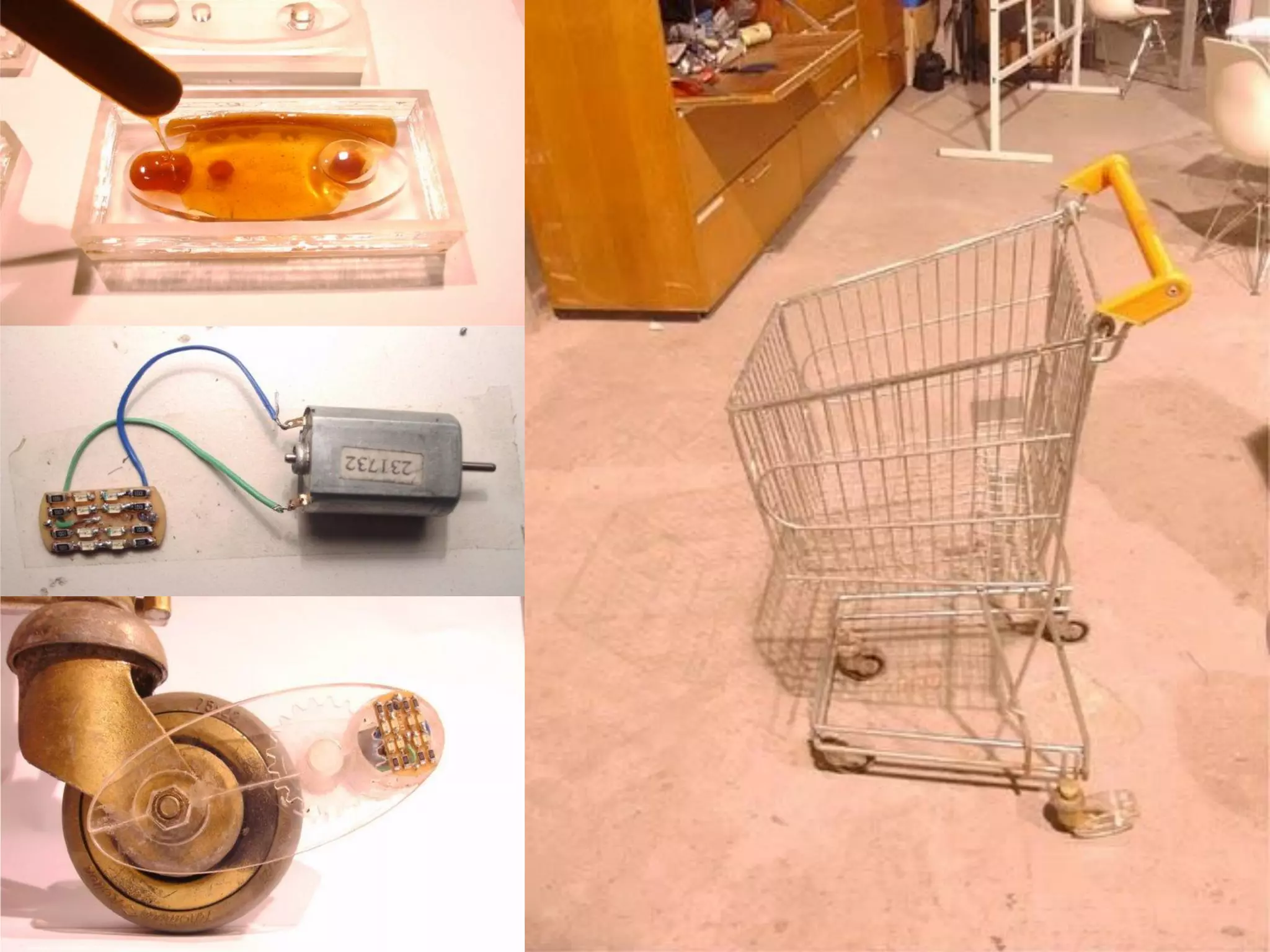
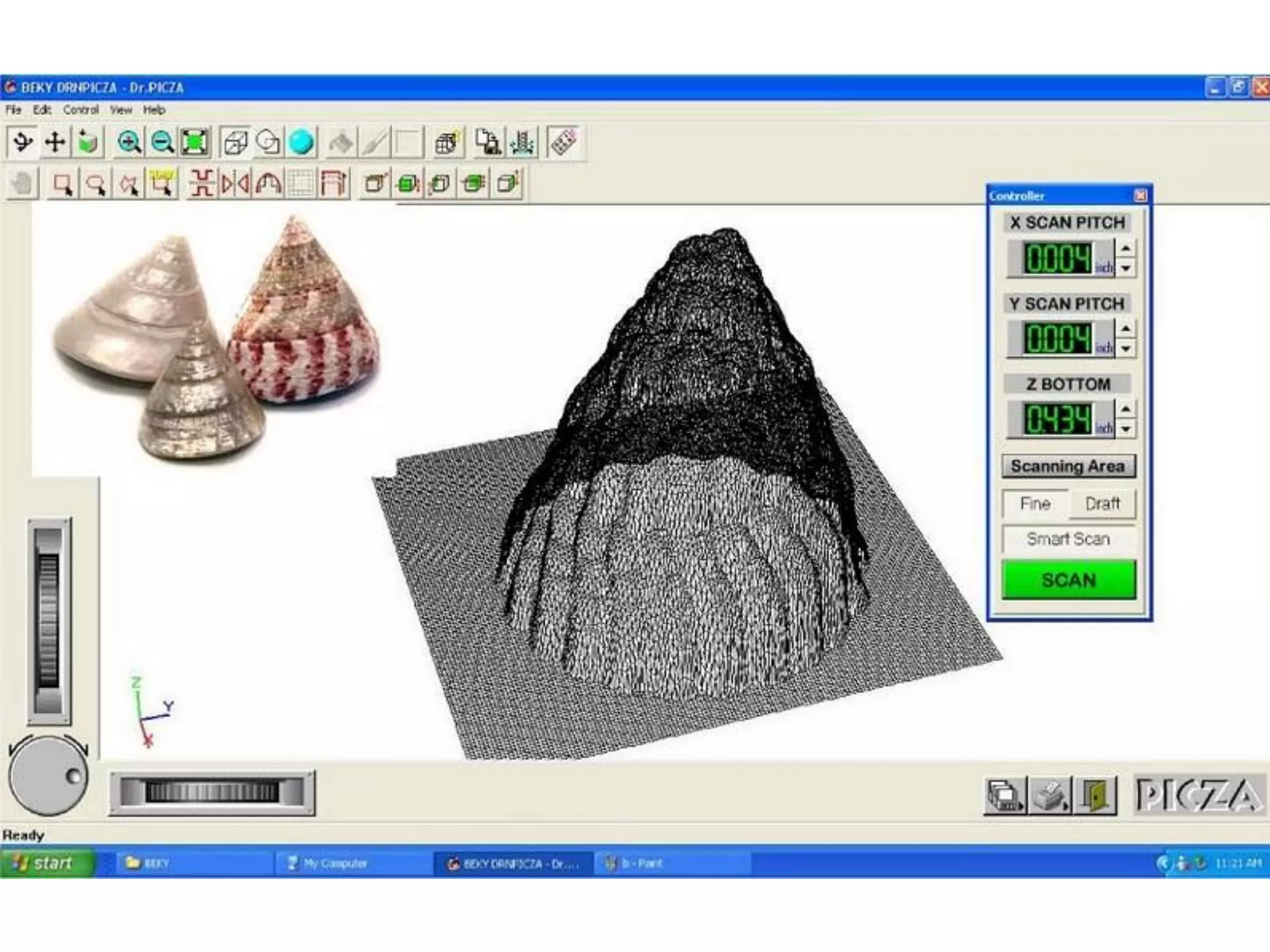
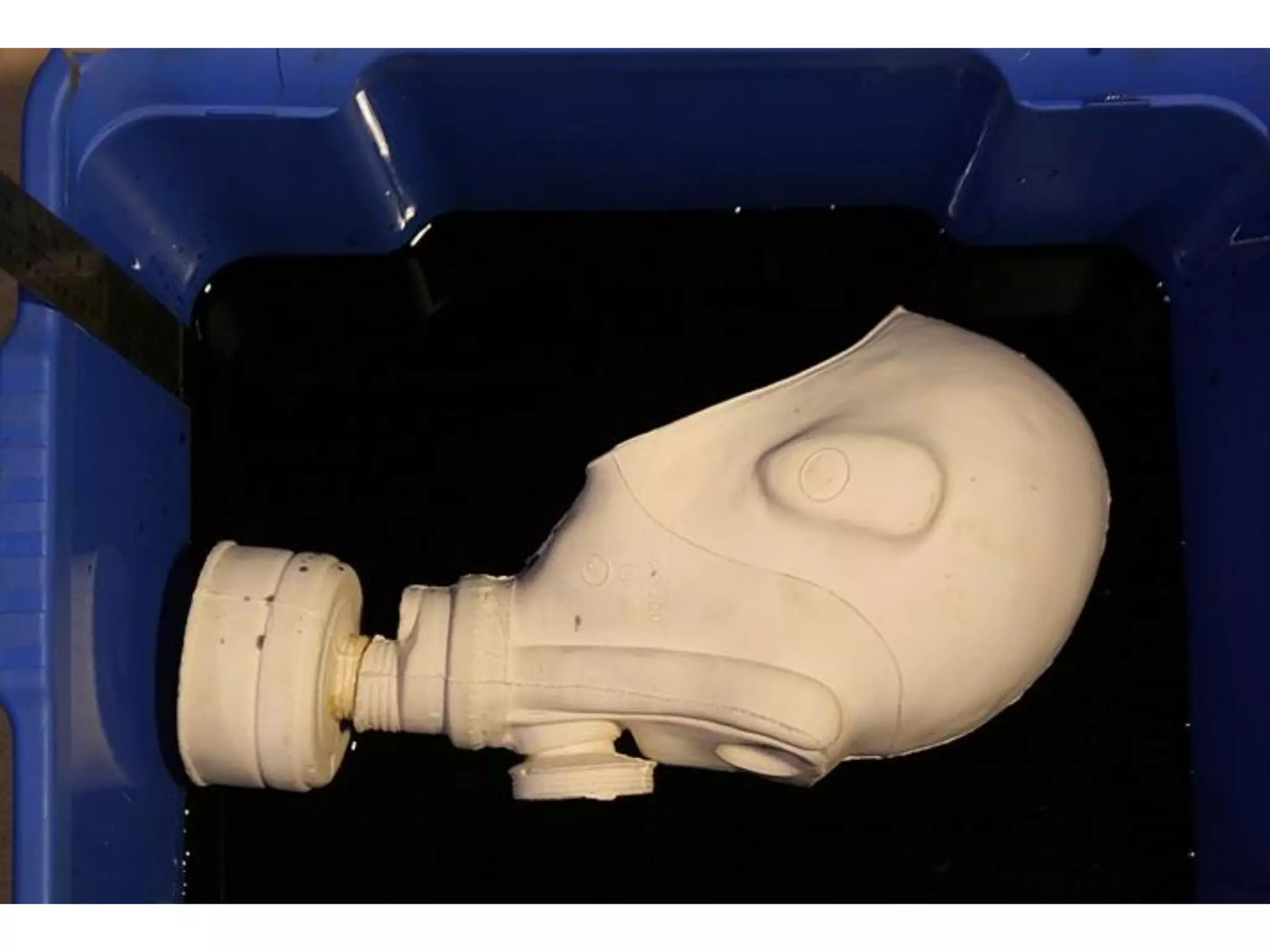
3. 3D scanning, printing, molding, and casting processes.