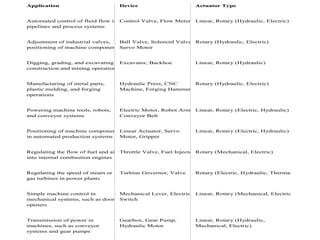
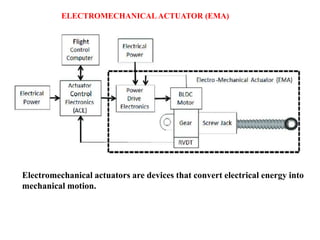
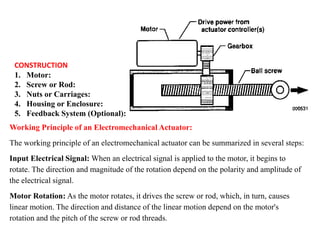
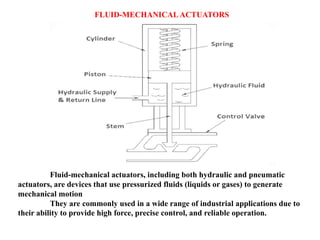
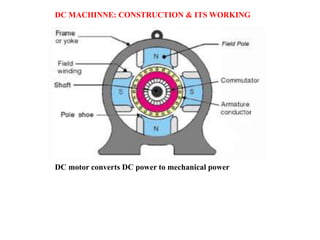
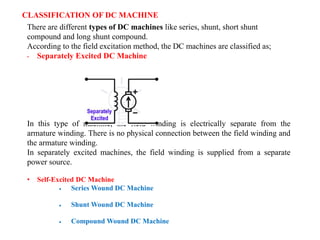
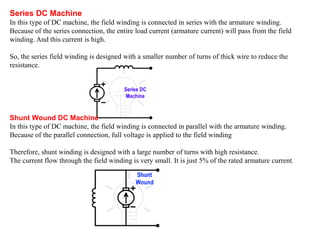
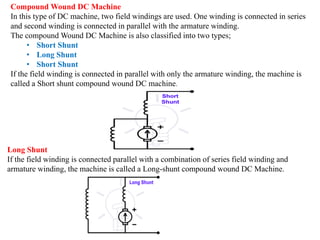
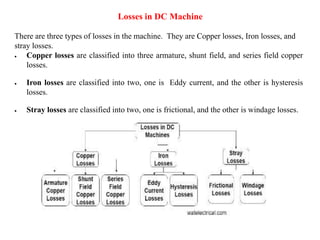
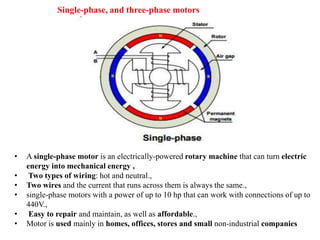
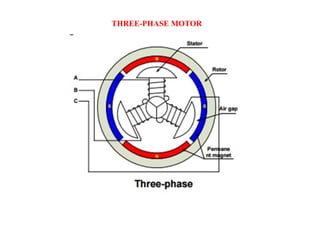
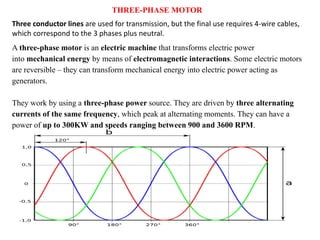
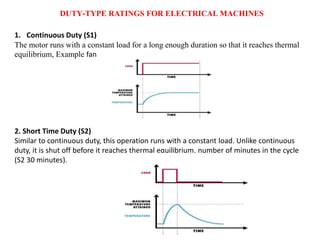
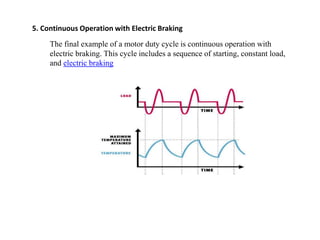
Sensors convert physical parameters like temperature, pressure, speed, and position into electrical signals. Common automotive sensors include temperature, pressure, speed, and position sensors. Actuators convert electrical signals into mechanical action. Common automotive actuators include fuel injectors, ignition coils, throttle actuators, and brake actuators. Electronic control units process sensor data and send control signals to actuators using complex algorithms to optimize vehicle performance, safety, and fuel efficiency. Actuators and sensors in engine control modules manage functions like fuel injection and ignition timing. Actuators also control transmission shifting and anti-lock braking systems.