Embed presentation
Download to read offline


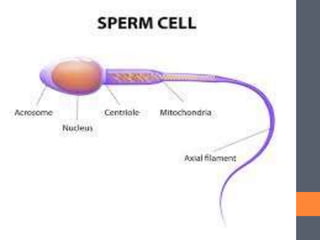

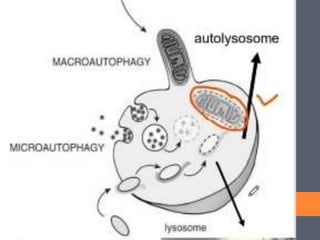

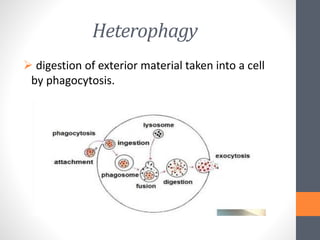
Lysosomes perform several functions including intracellular digestion, extracellular digestion, autophagy, autolysis, and heterophagy. Intracellular digestion occurs entirely within cells and breaks down food, while extracellular digestion happens outside cells such as when sperm fuse with eggs. Autophagy is when lysosomes digest cellular organelles or food reserves, and autolysis is self-destruction of cells by their own lysosomal enzymes, such as during aging. Heterophagy is digestion of exterior material phagocytosed by cells.







