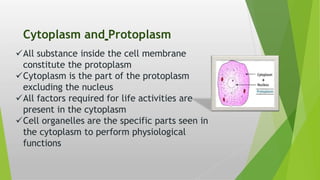
This document summarizes the structure and function of plant cells. It begins with an introduction stating that plant cells are the fundamental unit of life for plants and are eukaryotic. The document then lists and describes the major organelles of plant cells, including the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuoles, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. It explains the role and importance of each organelle. In conclusion, it emphasizes that the complex structure of plant cells allows them to perform vital functions and that chloroplasts play a key role in photosynthesis, which is essential for plant survival.







![Endoplasmic reticulum
The passage of the cell
Conduction of the materials inside the cell takes place
through this organelle
Also known as the cytoskeleton ,as it provides strength and
shape to the cell
Endoplasmic reticulum is in two types
1. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
[in which ribosome is attached]
2. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
[in which ribosome is not attached]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellbiologypdf-240124173157-cb6363f1/85/ASSIGNMENT-Cell-biology-9-320.jpg)


