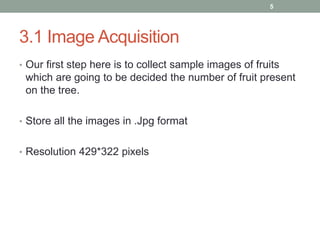
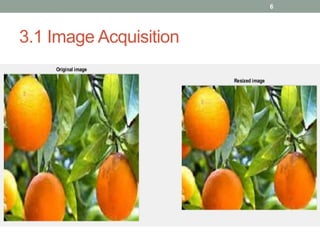
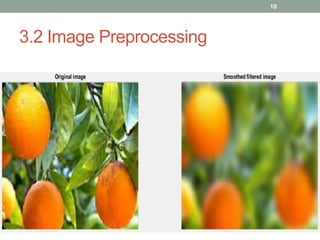
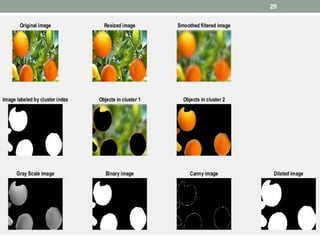
This document describes a fruit detection technique using morphological image processing. It outlines image acquisition by collecting fruit sample images in JPEG format. Image preprocessing steps like enhancement and noise removal are applied. Color and texture features are then extracted using color space conversion and Canny edge detection. Image segmentation is performed using a clustering algorithm. Morphological dilation is applied to segmented images to count fruit objects. The results show this technique can automatically count and distinguish fruits, providing a low-cost alternative to manual quality inspection.