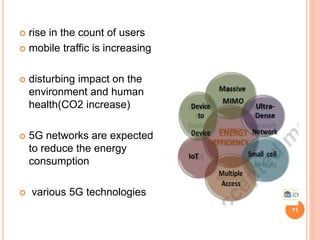
This document discusses green communication and security challenges in 5G wireless networks. It outlines techniques for power allocation and measuring greenness, including equal power allocation and game theory. It also covers 5G network technologies like device-to-device communication, massive MIMO, small cells, and the internet of things. The document notes security concerns with these technologies and potential solutions. It concludes that 5G networks aim to increase energy efficiency 1000x through combining efficient technologies while maintaining network security.