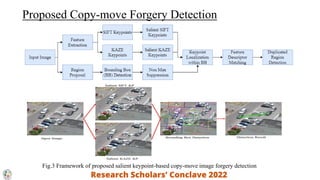
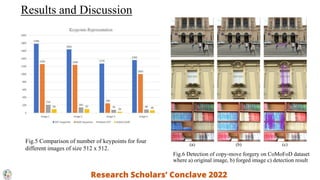
This document summarizes a presentation on detecting digital image forgery using salient keypoints. It introduces common types of image forgery and clues that reveal forgery. A framework is proposed that selects salient keypoints using distinctiveness, detectability, and repeatability to reduce keypoints and detect copy-move forgery. The approach uses SIFT and KAZE features and achieves promising results on standard datasets, outperforming other methods with lower false positive rates and higher precision and F1 scores. Future work could detect other forgery types and develop more robust detection algorithms.






![References
[1] Zheng L, Zhang Y, Thing VL. A survey on image tampering and its detection in real-world photos. J Visual
Commun Image Represent. 2019;58:380–399. doi:10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.12.022.
[2] Hashmi MF, Anand V, Keskar AG. Copy-move image forgery detection using an efficient and robust method
combining un-decimated wavelet transform and scale invariant feature transform. Aasri Procedia. 2014; 9:84–
91.
[3] Niyishaka P, Bhagvati C. Digital image forensics technique for copy-move forgery detection using DOG and
ORB. International conference on computer vision and graphics; 2018. p.472–483.
[4] Niyishaka P, Bhagvati C. Copy-move forgery detection using image blobs and brisk feature. Multimedia
Tools Appl. 2020;79(35):26045–26059. doi:10.1007/s11042-020-09225-6.
[5] X. Niu, H. Han, S. Shan, and X. Chen, “Synrhythm: Learning a deep heart rate estimator from general to
specific,” in 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 3580–3585, IEEE, (2018).
[6] Mukherjee P, Lall B. Saliency and KAZE features assisted object segmentation. Image Vis Comput.
2017;61:82–97. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0262885617300537.
[7] Lowe DG. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision; 1999. Vol. 2, p. 1150–1157.
[8] Alcantarilla PF, Bartoli A, Davison AJ. KAZE features. In: Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, Sato Y,
Schmid C, editors. Computer vision eccv 2012. Berlin (Heidelberg): Springer; 2012. p. 214–227.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/researchconclavenitish-220715141929-be03069b/85/Image-Forgery-Detection-10-320.jpg)
