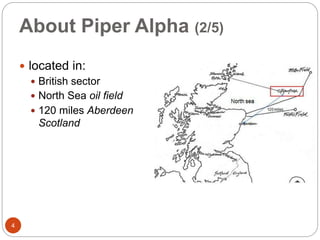
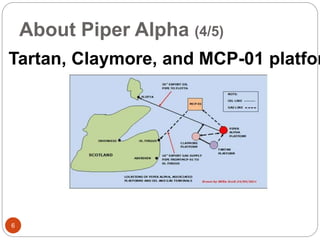
The Piper Alpha disaster, occurring on July 6, 1988, resulted from a series of maintenance and procedural failures, leading to an explosion that claimed the lives of 167 individuals and caused $3.4 billion in property damage. Key failures included inadequate safety measures, poor design of the control room, and management oversight during maintenance operations. The event underscores the importance of rigorous safety protocols and training to prevent such catastrophic incidents in the oil and gas industry.