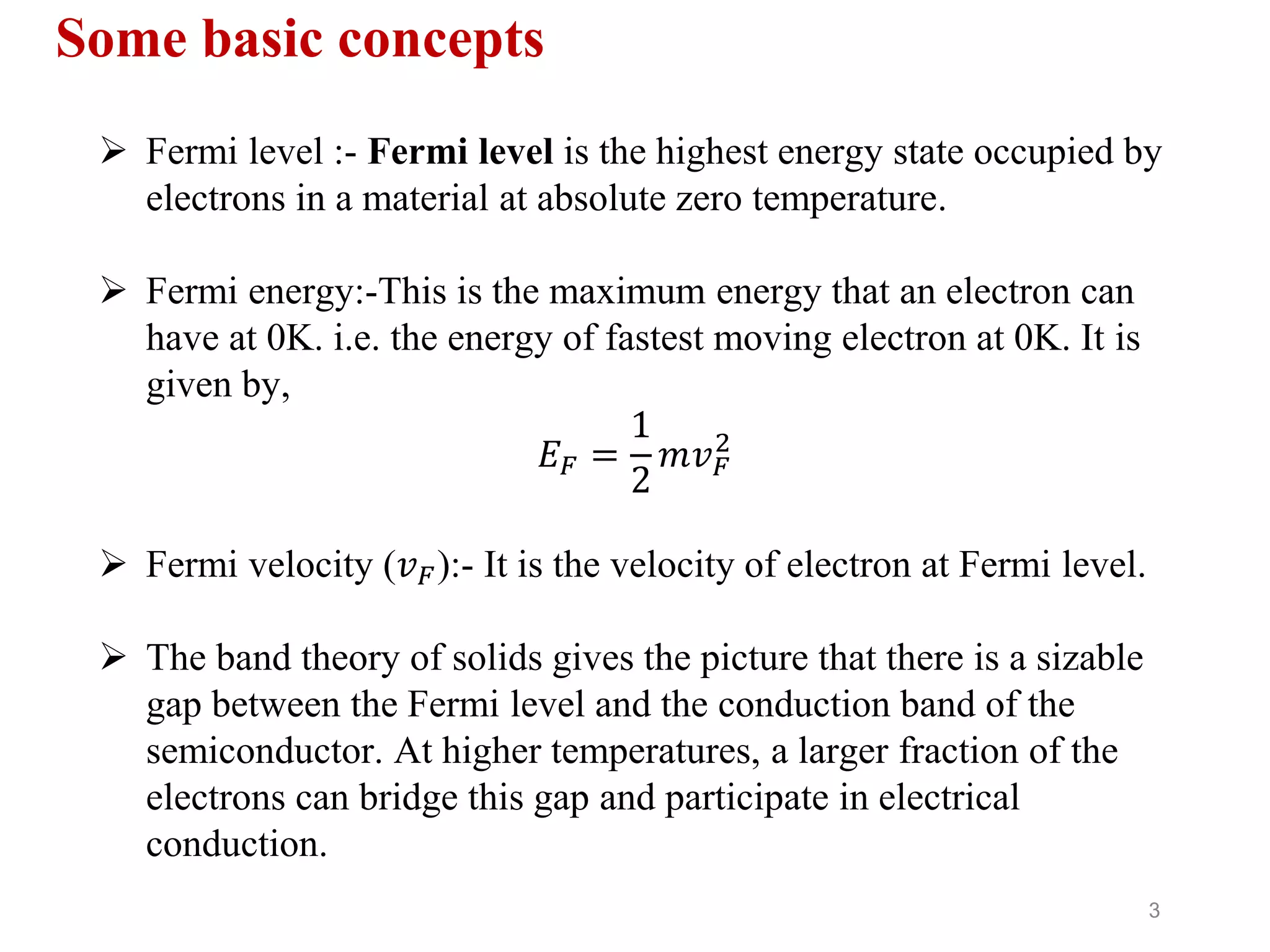
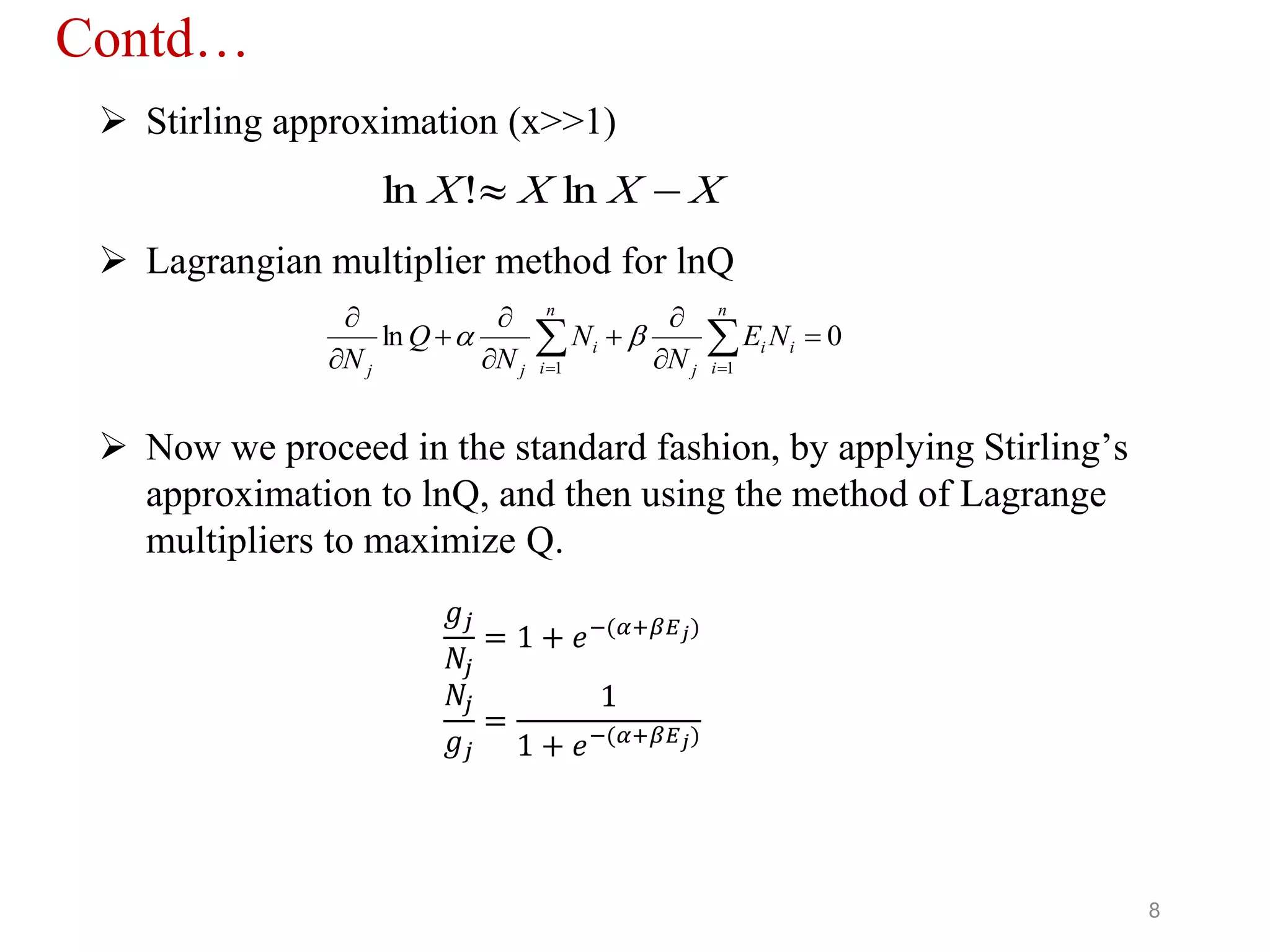
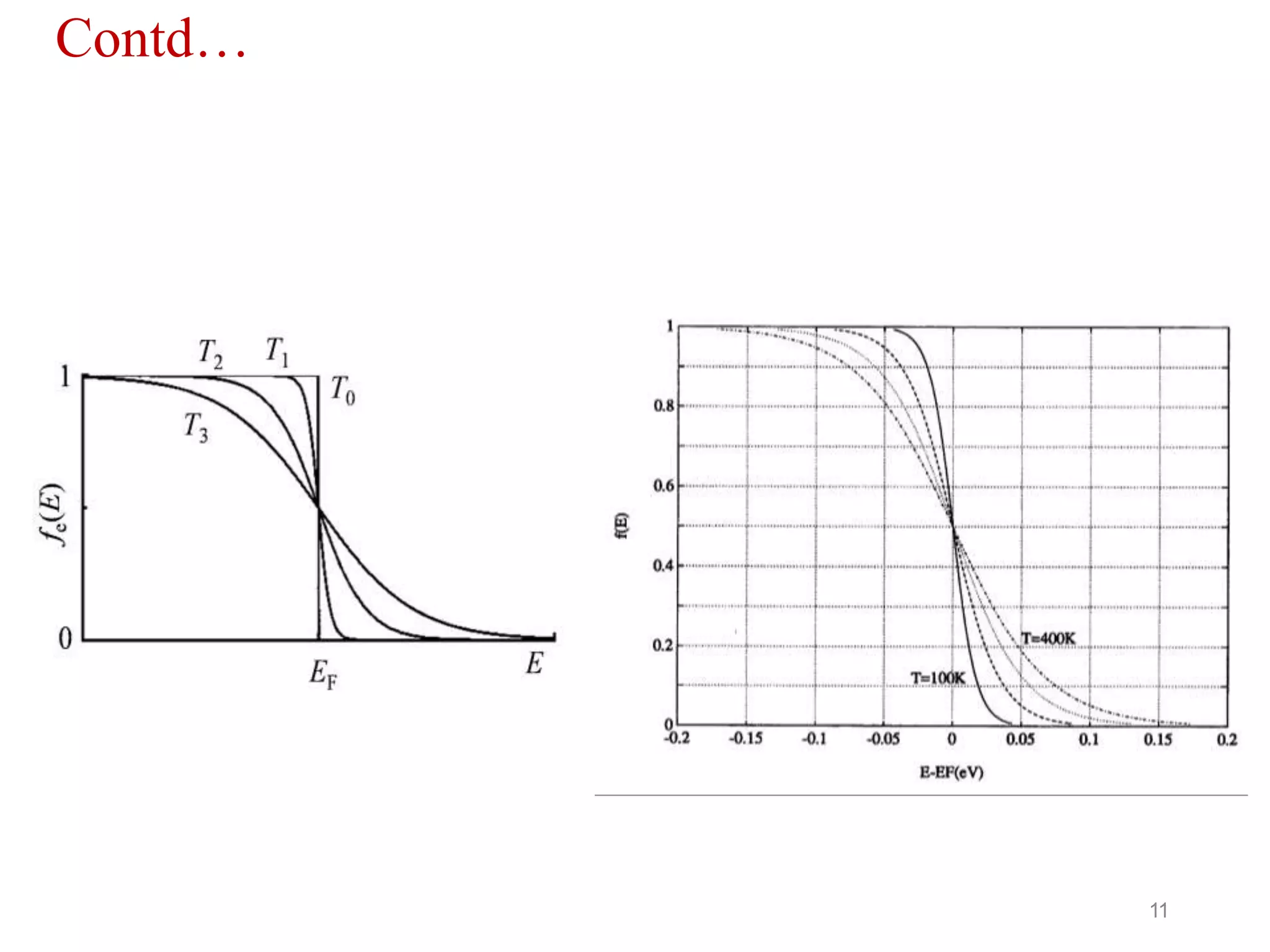
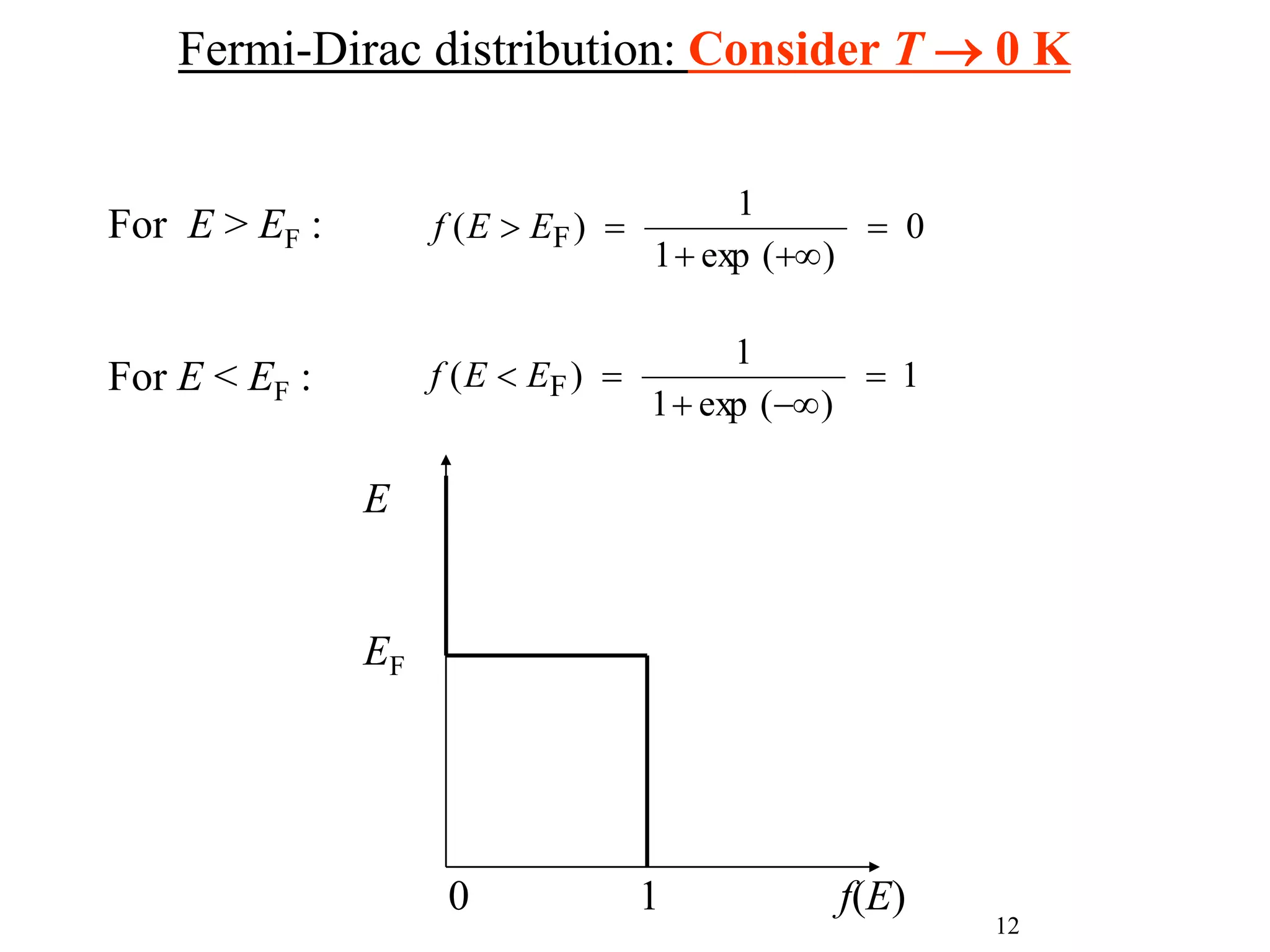
This document introduces the Fermi-Dirac distribution function. It begins by discussing basic concepts like the Fermi level and Fermi energy. It then covers Fermi and Bose statistics, and the postulates of Fermi particles. The derivation of the Fermi-Dirac distribution function is shown, which gives the probability of a quantum state being occupied at a given energy and temperature. Graphs are presented showing how the distribution varies with different temperatures. The classical limit of the distribution is discussed. References are provided at the end.