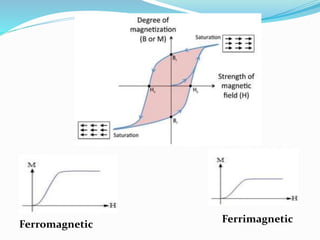
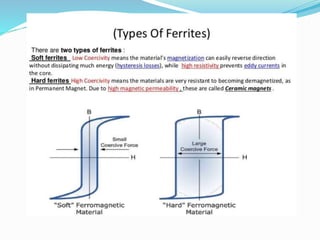
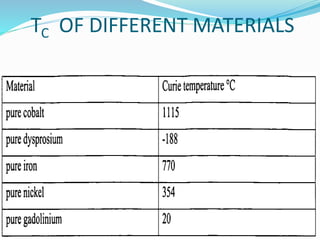
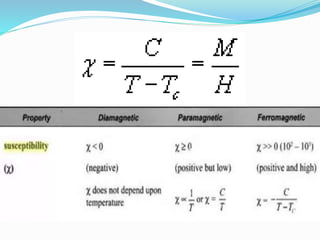
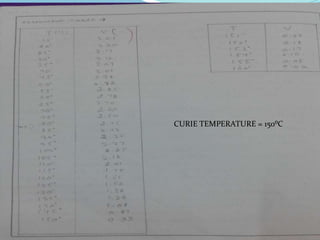
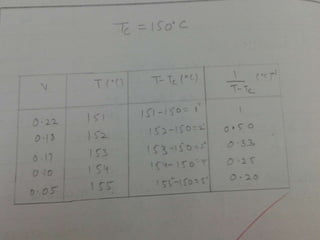
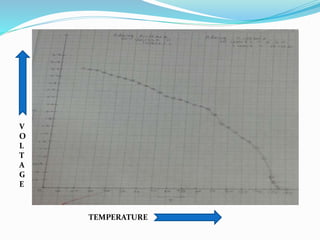
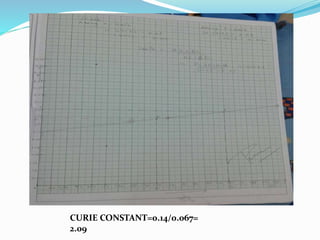
This document discusses the properties of ferrimagnetic materials. It defines ferrites as ceramic-like materials with magnetic properties that are used in electronic devices. Soft ferrites are used in transformer cores while hard ferrites are used in refrigerator magnets. The document discusses the B-H curve formation and Curie temperature of ferrimagnetic materials. It provides the Curie temperatures of different materials and describes the working of an apparatus used to measure Curie temperature. Finally, it outlines some applications of ferrites such as in microwave frequency devices, computer memory, and magnetic recording heads.