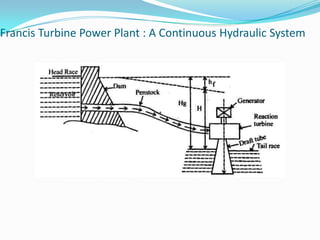
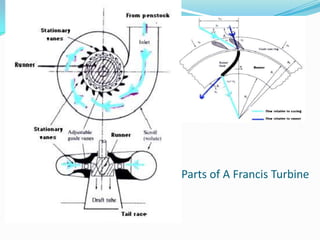
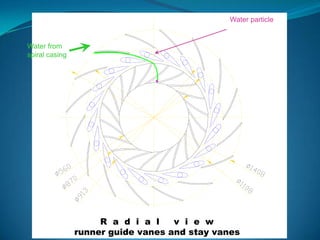
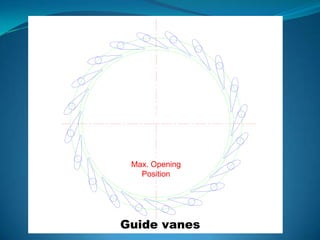
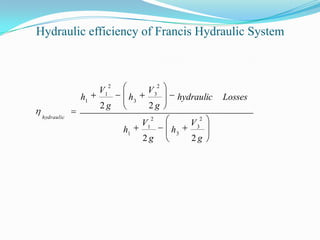
The Francis turbine was invented in Lowell, Massachusetts by Sir James B. Francis as an improvement on the Boyden turbine. Francis was able to redesign the turbine to achieve an efficiency of 88%, significantly higher than the Boyden turbine's 65% efficiency. The Francis turbine operates using both the kinetic energy and pressure energy of water to drive the turbine. It is the most commonly used water turbine today for electrical power production, powering generators with outputs ranging from 10 to 750 megawatts. The Francis turbine consists of a spiral casing, guide vanes, runner blades, and draft tube and can achieve efficiencies as high as 94%.