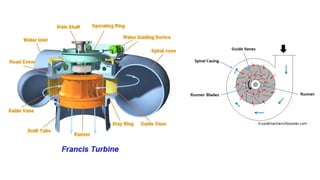
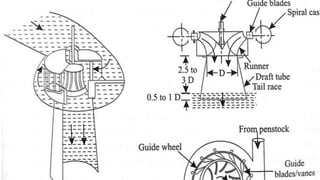
Francis turbine is a mixed-flow reaction turbine commonly used to generate electricity. It was designed by American scientist James Francis to improve upon an earlier design by Boyden. Francis turbines can operate under heads of 10-650 meters and work by converting the potential and kinetic energy of flowing water into rotational energy of a shaft. Water enters the spiral casing and is directed by guide vanes to the high-pressure runner, which spins to generate power before exiting through a draft tube. With efficiencies up to 90%, Francis turbines are widely employed for hydroelectric power worldwide.