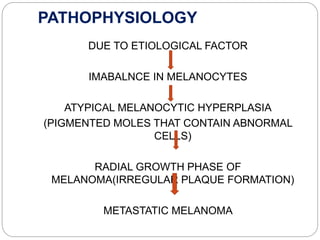
This document discusses malignant melanoma, a serious type of skin cancer. It begins by describing melanoma as cancer originating from melanocytes, which are skin cells that produce pigment. The document then covers risk factors for melanoma like family history and sun exposure. It discusses the different types of melanoma and explains their pathology is related to imbalances in melanocytes. The clinical manifestations, diagnostic process, treatment options involving surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, nursing management, and potential complications are then outlined.