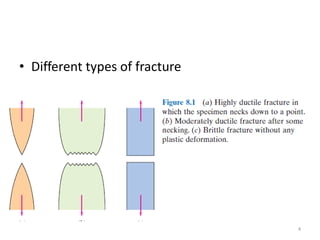
This document discusses different failure mechanisms in materials including fracture, fatigue, and creep. It defines fracture as breaking into two or more pieces due to an external load. There are two main steps in the fracture process: crack initiation and crack propagation. Fracture can be brittle, exhibiting little plastic deformation before failure, or ductile. Creep is the permanent deformation of materials over time when under a constant load at high temperatures. Creep curves show the relationship between creep strain and time. Factors like temperature, grain size, and alloy composition affect a material's susceptibility to creep.