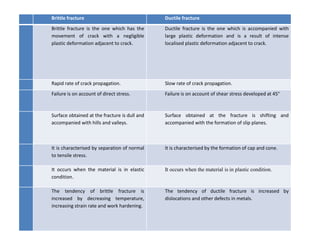
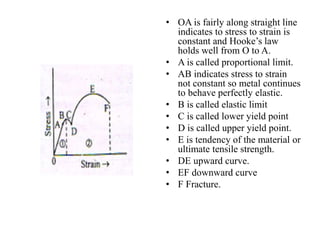
This document discusses different types of material fractures: brittle, ductile, fatigue, and creep. Brittle fractures occur with little plastic deformation, while ductile fractures involve significant plastic deformation. Fatigue fractures result from repeated cyclic stresses below the material's tensile strength. Creep fractures happen due to excessive deformation over time under steady loads. The mechanisms of each type are also described, such as Griffith's theory of stress concentrations leading to brittle fractures or dislocation movement causing creep fractures.