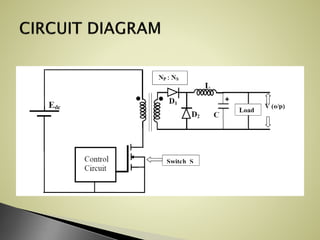
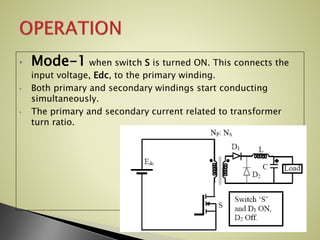
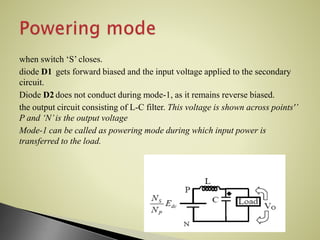
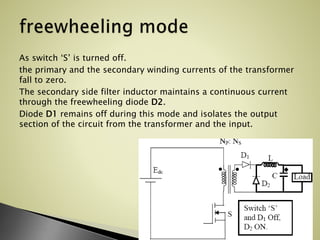
The forward converter uses a transformer to step up or down an input dc voltage and provide isolation for the load. It operates in two modes: when the switch is on, the input voltage is applied to the primary winding and power is transferred to the secondary winding and load; when the switch is off, the secondary inductor maintains current through a freewheeling diode. Key aspects of design include transformer turn ratio selection, inductor and capacitor sizing, and duty cycle adjustment for output voltage control. Benefits include better transformer utilization, filtered output, input-output isolation, and higher efficiency compared to flyback converters for power levels of 100-200 watts.